Core Ideas
Acid energy is determined by a wide range of chemical elements, together with electronegativity, atomic radius, and resonance. Maintain studying to study all concerning the chemistry behind acid energy.
Subjects Coated in Different Articles
Robust vs Weak Acids
When selecting between acids for an experiment or different goal, chemists have a tendency to take a look at acid energy as crucial issue. When it comes to energy, acids are likely to fall into two broad teams: sturdy acids and weak acids.
Robust acids are outlined by their fast dissociation, rapidly releasing a proton and forming a extremely secure conjugate base. Weak acids, against this, launch their protons extra slowly and type a comparatively unstable conjugate base. Whereas the sturdy and weak acid categorization is commonly helpful to rapidly perceive the final energy of an acid, you might wish to as a substitute evaluate strengths between acids. For this, you’ll wish to take a look at an acid’s pKa.
The technical definition of pKa is the negative-log of an acid’s proton dissociation fixed (Okaya), which represents the proportion of the acid that releases a proton at chemical equilibrium. Which means that pKa decreases as acid energy will increase. In less complicated phrases, stronger acids have decrease pKa values, generally decrease than 0, whereas weaker acids have greater pKa values.
Nonetheless, whereas figuring out which acids are stronger than others is effective within the chemistry lab, understanding the elements behind acid energy enable for extra superior mastery of acid-base chemistry. So let’s delve into the underlying chemistry of acid energy!
Binary Acid Energy: Atomic Radius
First, let’s take into account binary acids, which solely contain one atom sure to proton, earlier than we transfer on to extra difficult polyatomic ion acids. The most typical binary acids embody the haloacids, which contain a halogen sure to a proton, similar to HF, HCl, HBr, and HI. A very powerful issue affecting binary acid energy is anionic atomic radius. As we already know, atomic radius follows a periodic pattern: atomic radius will increase as you progress down the periodic desk.

To evaluate the energy of a binary acid, we particularly take into account the atomic radius of the conjugate base. Usually, stronger binary acids contain bigger atomic radii. It’s because conjugate bases with greater atomic radii can higher stabilize the detrimental cost ensuing from proton dissociation than bases with smaller radii. With respect to the haloacids, which means that HI is the strongest, since I– has the most important atomic radius of the halides. The pattern follows that HBr is the subsequent strongest, adopted by HCl, with HF being the weakest haloacid.

Polyatomic Ion Acid Energy
WIth acids involving polyatomic conjugate bases, the atomic radius pattern nonetheless holds when contemplating the proton-bound atom. Particularly, thiols have decrease pKas than alcohols since sulfur has a higher atomic radius than oxygen.

Nonetheless, most acids with polyatomic anions contain components like carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen sure to the acidic proton. Since these components are similarly-sized, different elements outweigh atomic radius in figuring out acid energy, particularly bond polarity and resonance.
Bond Polarity in Acid Energy
Usually, stronger acids contain extra polar bonds. When evaluating completely different atoms sure to an acidic proton, bond polarity corresponds to the periodic pattern of electronegativty. Particularly, electronegativity will increase as you progress proper throughout the periodic desk. The extra electronegative the proton-bound atom, the extra polar the bond, and subsequently the stronger the acid. It’s because extra electronegative atoms, just like bigger atoms, can higher stabilize detrimental cost than much less electronegative components. Thus, since nitrogen is extra electronegative than carbon, ammonia is a stronger acid than methane. As a result of oxygen is but extra electronegative, water is a fair stronger acid and hydrofluoric acid is even stronger than water.

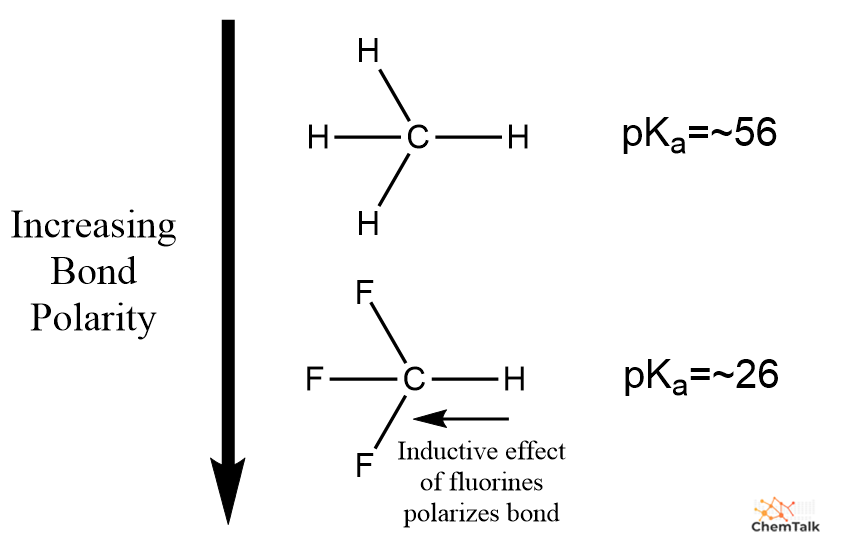
Bond polarity additionally determines energy when evaluating acids with the identical atom sure to an acidic proton, however with completely different inductive results. Particularly, after we evaluate methane with fluoroform, we discover that the extremely electronegative fluorines in fluoroform pull electron density on the C-H bond. This ends in a extra extremely polarized bond, and thus a stronger acid relative to methane.
Resonance in Acid Energy
Persevering with with the theme of higher stabilized conjugate bases akin to stronger acids, resonance stabilization also can enhance acid energy. Particularly, stronger acids have resonance stabilized polyatomic bases relative to non-resonance stabilized bases. We are able to observe this after we evaluate the acidity of propane and propene. The sp3 C-H bond in propene is extra acidic than the terminal C-H bonds of propane as a result of the ensuing allylic anion broadly distributes its detrimental cost. The propanyllic anion, against this, has a extra concentrated detrimental cost on one atom, leading to much less stabilization.

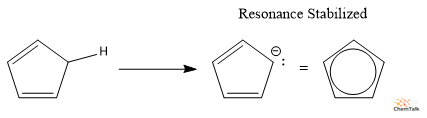
We are able to see but stronger acids when the conjugate base will not be solely resonance stabilized, however fragrant. Cyclopentadiene is a famously sturdy natural acid as a result of its outcome and cyclopentadienyl anion kinds an excellent secure fragrant ring.
Oxyacids
One particular sort of polyatomic ion acid which follows completely different acid energy guidelines is the oxyacids. Oxyacids are outlined as an acid with a conjugate base of a central atom sure to completely to a number of oxygens. Acidic protons could be sure to at least one or many of those oxygens. Widespread oxyacids embody nitric acid, sulfuric acid, hypochlorous acid, and carbonic acid.

Oxyacid energy is decided by two elementary elements: the electronegativity of the central atom and the variety of oxygens.
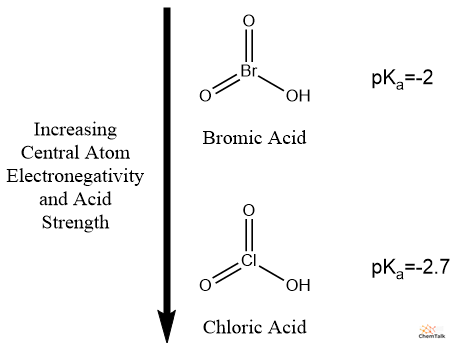
Particularly, stronger oxyacids have extra electronegative central atoms. It’s because electronegative central atoms have an inductive impact that makes the O-H bond extra polar. This pattern explains why nitric acid is stronger than phosphorous acid and why chloric acid is stronger than bromic acid.
Additional, stronger oxyacids have extra oxygens. This outcomes from having extra extremely electronegative oxygens concerned within the molecular construction additionally has an inductive impact that makes the O-H bond extra polar. This pattern explains why sulfuric and nitric acid are stronger than sulforous and nitrous acid, respectively.




