There are three layers of the coronary heart. They’re:
- Epicardium (Outermost Layer of Coronary heart)
- Myocardium (Center Layer of Coronary heart)
- Endocardium (Innermost Layer of Coronary heart)
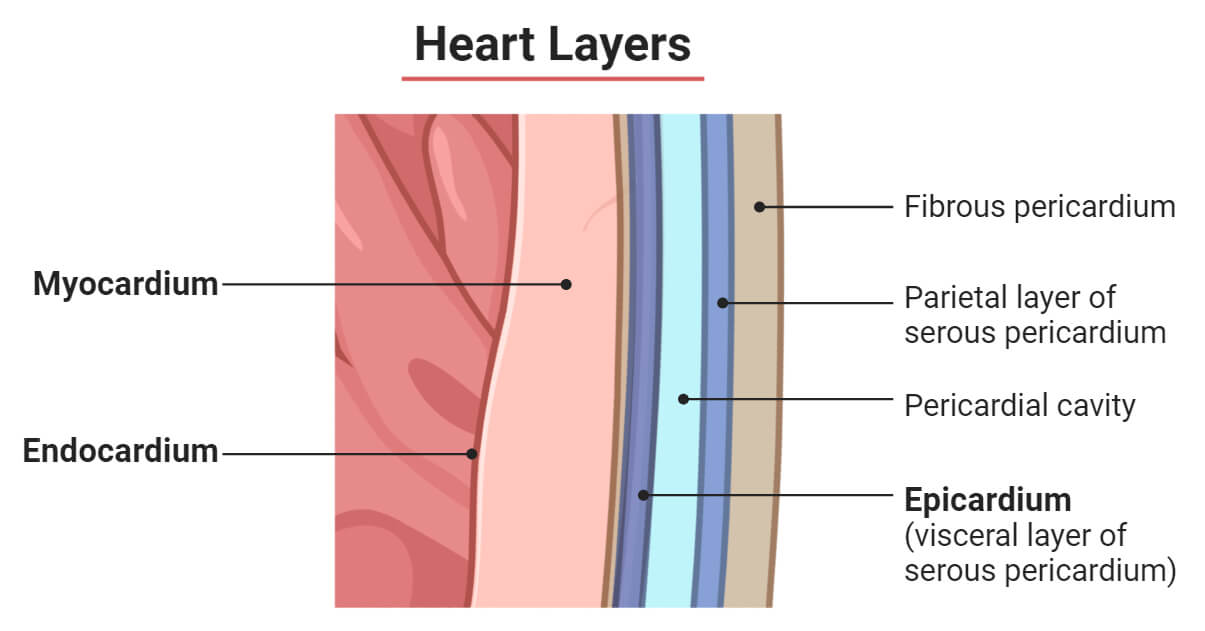
1. Epicardium (Outermost Layer of Coronary heart)
- The epicardium is the outermost layer of the center wall made up of mesothelium, fat, and connective tissues. It varieties the inside serous layer of the pericardium; therefore, additionally it is often known as the visceral serous pericardium.
- Epicardium encloses the center in addition to the basis of main blood vessels rising from the center just like the aorta and the 2 vena cava. It’s also equipped by a number of coronary blood vessels, nerve fibers, and lymphatic vessels.
- Location: Anatomically, it’s situated simply beneath the parietal serous pericardium layer of the pericardium and is in direct contact with the myocardium.
Epicardium Construction
- Histologically, it incorporates an outer layer of epithelium cells known as the mesothelium beneath which is the subserosal layer manufactured from connective tissues and a layer of fatty tissues. It may be divided into two sub-layers primarily based on their composition, viz. serous membrane and subepicardial layer.
- The serous membrane/layer is the outer layer manufactured from mesothelial tissue. Whereas, the subepicardial layer is beneath the serous layer and is manufactured from unfastened connective tissues and adipose tissue.
- The subepicardial layer homes blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and sympathetic in addition to parasympathetic nerves.
Capabilities of Epicardium
- Its main operate is to supply mechanical safety to the center.
- The serous layer secrets and techniques skinny fluid known as the pericardial fluid that lubricates the center and reduces friction through the pumping of the center.
- Being equipped with blood and lymph vessels, it additionally helps to distribute vitamins and oxygen to the center wall and gather and transport the wastes.
Epicardium-associated Ailments
- Epicardium itself alone will not be typically affected by illnesses; nonetheless, illnesses of pericardium or endocardium might lengthen as much as epicardium and have an effect on it.
2. Myocardium (Center Layer of Coronary heart)
- Myocardium is the center thickest muscular layer made up of cardiomyocytes. It’s accountable for the contraction and rest actions of the center. The SA (sinoatrial) and the AV (atrioventricular) nodes of the center conduction system are principally situated on this layer.
- Location: It’s the center layer situated between the epicardium and the endocardium.
Myocardium Construction
- Histologically, the myocardium is primarily composed of cardiac muscle cells (cardiomyocytes) (organized in a bunch known as myofibers) and some fibroblast cells. The cardiomyocytes are linked with one another by the intercalated discs.
- Anatomically, it’s the thickest layer of the center wall. It’s thicker within the ventricular wall than within the auricular wall – significantly within the left ventricle, which is the thickest layer. The left ventricular myocardium is additional subdivided into three sub-layers, specifically subepicardial, mid-myocardial, and subendocardial layers.
- It’s properly equipped with coronary arteries and coronary veins and cardiac lymphatic vessels. It’s also innervated with a cardiac conduction system composed of specialised cardiomyocytes.
Capabilities of Myocardium
- Its main operate is to contract and generate the drive for the contraction of the center wall.
- The myocardium homes the Pacemaker cells and specialised cardiomyocytes that generate and conduct the cardiac electrical impulses.
Myocardium-associated Ailments
The myocardium is affected by a variety of illnesses collectively known as myocardial illnesses. A few of the widespread myocardial illnesses are listed beneath.
| Illness | Introduction |
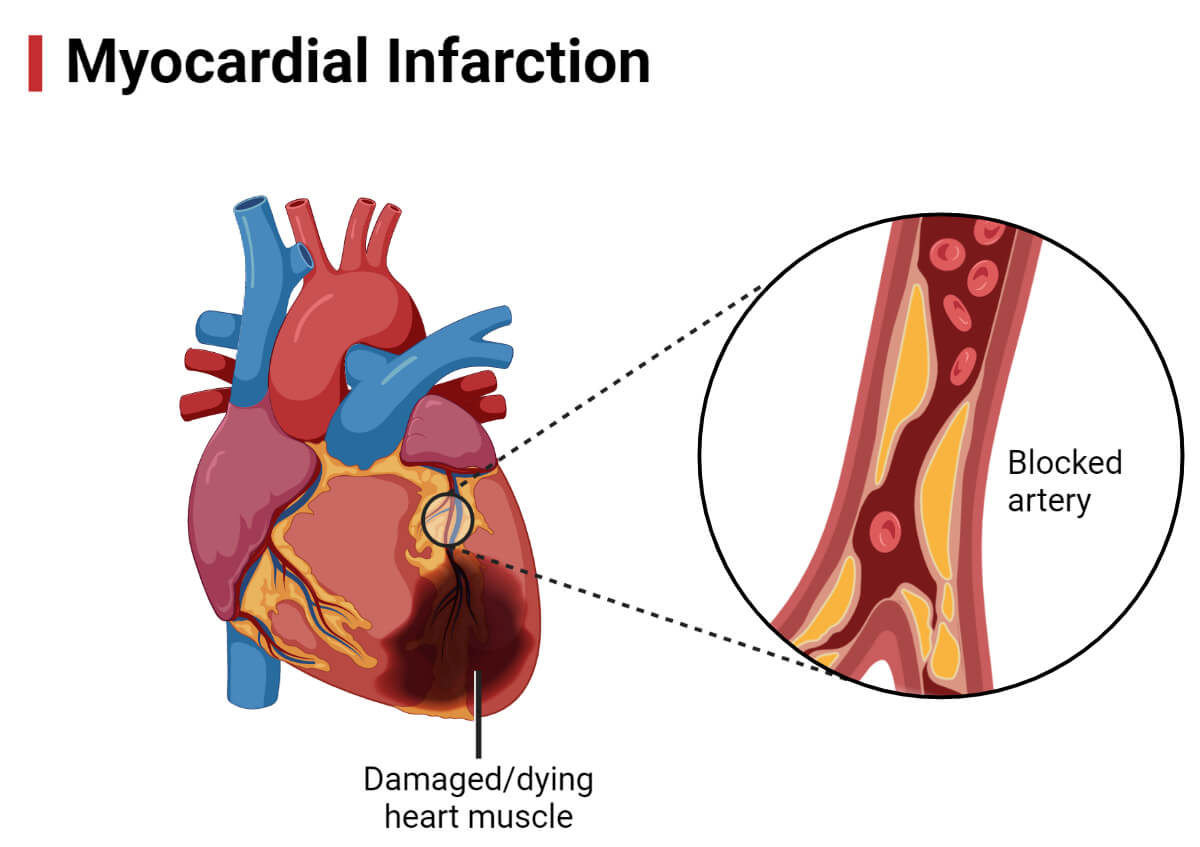
| Myocardial infarction | Blockage of the blood circulate within the myocardium results in a coronary heart assault. |
| Myocarditis | Irritation of the myocardium. |
| Myocardial fibrosis | A situation of the formation of extreme fibrous tissues within the myocardium. |
| Myocardial ischemia | Discount within the oxygen provide to the myocardium attributable to restriction in blood circulate. |
3. Endocardium (Innermost Layer of Coronary heart)
- The endocardium is the innermost layer of the center wall lining the inner chambers of the center and the center valves. It offers a easy floor for environment friendly blood circulate inside the center chambers. It additionally homes capillaries to provide blood to the center muscle tissues, nerve fibers, and coronary heart conduction cells.
- Location: It’s discovered alongside the partitions of the atria and the ventricles and because the outer overlaying of the 4 coronary heart valves.
Endocardium Construction
The endocardium is primarily composed of easy endothelial and connective tissues and a smaller fraction of easy muscle cells. Anatomically, the endocardium may be divided into three sub-layers, viz. the endothelial layer, the subendothelial layer, and the subendocardial layer.
- Endothelial Layer
It’s the innermost layer composed of specialised flat and easy endothelial cells. This layer makes the floor easy and permits simple blood circulate with none friction, clotting, or sticking.
- Sub-endothelial Layer (fibro-elastic tissue layer)
It’s the center layer composed of connective tissue containing collagen, elastic fibers, and some easy muscle cells. Resulting from its composition, additionally it is known as the ‘fibro-elastic tissue layer’. This layer offers structural assist to the endocardium.
- Sub-endocardial Layer
It’s the innermost layer primarily composed of connective tissues. This layer is enriched with capillaries, nerves, and cardiac conductive cells (Purkinje fiber).
Capabilities of Endocardium
- It traces the chambers and valves of the center and offers a non-adhesive floor for environment friendly blood circulate with out adherence of platelets and blood clotting.
- It acts as a blood-heart barrier.
- It additionally permits easy opening and shutting of the center valves.
- It homes the Purkinje fibers and therefore helps the center’s conductive system.
Endocardium related medical situations
The endocardium is affected by a number of medical situations known as endocardial illnesses. A few of the widespread endocardial illnesses are listed beneath.
| Illness | Introduction |
| Infective Endocarditis | Irritation of the endocardium attributable to an infection. |
| Endocardial Fibroelastosis | A situation the place the elastic and fibrous layer of the endocardium is thickened. |
| Nonbacterial Thrombotic Endocarditis (NBTE) | A situation characterised by the formation of a blood clot on the endocardium resulting in its irritation. |
| Libman-Sacks Endocarditis | A situation characterised by the formation of small sterile vegetations, totally on the valves. |
| Carcinoid Coronary heart Illness (CHD) | A situation characterised by fibrosis and thickening of principally the endocardium of the best aspect of the center in sufferers with carcinoid tumors. |
References
- Epicardium: What Is It, Capabilities, and Extra | Osmosis
- The three Layers of the Coronary heart Wall (thoughtco.com)
- Epicardium | anatomy | Britannica
- Pericardium. (2023, Could 21). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Pericardium
- Epicardium | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org
- Epicardium – an summary | ScienceDirect Matters
- Epicardium: Definition, Operate, Pericardial Membranes and Pericardial Issues – Scope Heal
- Human cardiovascular system – Cardiac Muscle Cells, Actin & Myosin Filaments, Intercalated Discs | Britannica
- Epicardium – Definition & Operate – Human Anatomy | Kenhub – YouTube
- Coronary heart histology: Cells and layers | Kenhub
- Epicardium – Earth’s Lab (earthslab.com)
- Ross & Wilson Anatomy & Physiology in Well being and Sickness. thirteenth ed. Churchill Livingstone Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7020-7276-5
- The three Layers of the Coronary heart Wall (thoughtco.com)
- Myocardium of the Coronary heart (thoughtco.com)
- Myocardium Definition and Examples – Biology On-line Dictionary
- Myocardium | Radiology Reference Article | Radiopaedia.org
- Myocardium | anatomy | Britannica
- Myocardium Operate, Location & Elements | What’s the Myocardium? – Video & Lesson Transcript | Research.com
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/myocardial-ischemia/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20375422
- Crossman DC. The pathophysiology of myocardial ischaemia. Coronary heart. 2004 Could;90(5):576-80. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2003.029017. PMID: 15084567; PMCID: PMC1768241.
- https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/well being/conditions-and-diseases/cardiomyopathy
- Bailey, Regina. “Myocardium of the Coronary heart.” ThoughtCo, Aug. 27, 2020, thoughtco.com/myocardium-anatomy-373234.
- Dye, B., & Lincoln, J. (2020). The Endocardium and Coronary heart Valves. Chilly Spring Harbor Views in Biology, 12(12). https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a036723
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/matters/pharmacology-toxicology-and-pharmaceutical-science/endocardial-disease
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/matters/medicine-and-dentistry/endocardial-fibroelastosis
- Sana MK, Mahajan Okay. Endocardial Fibroelastosis. [Updated 2023 Jan 24]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Out there from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK559128/
- Ibrahim AM, Siddique MS. Libman Sacks Endocarditis. [Updated 2022 Sep 5]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2023 Jan-. Out there from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532864/
- Ram, P., Penalver, J. L., U. Lo, Okay. B., Rangaswami, J., & Pressman, G. S. (2019). Carcinoid Coronary heart Illness: Assessment of Present Data. Texas Coronary heart Institute Journal, 46(1), 21-27. https://doi.org/10.14503/THIJ-17-6562
- Endocardium: Operate, Location, and Significance (verywellhealth.com)
- Endocardium. (2023, March 5). In Wikipedia. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Endocardium
- Layers of the center: Epicardium, myocardium, endocardium | Kenhub
- 17.1C: Layers of the Coronary heart Partitions – Drugs LibreTexts
- The three Layers of the Coronary heart Wall (thoughtco.com)
- Coronary heart histology: Cells and layers | Kenhub
- Endocardium Overview, Elements & Operate | What’s the Endocardium? – Video & Lesson Transcript | Research.com
- The Anatomy of the Coronary heart, Its Buildings, and Capabilities (thoughtco.com)
- The Coronary heart Wall – TeachMeAnatomy
- Endocardium – an summary | ScienceDirect Matters



