Cohort traits
The principle goal of this research was to carry out an unbiased proteomic research of CSF to outline biomarkers and pathways which might be related or divergent between African People and Caucasians with AD. Determine 1A gives an summary of our research method, which included the technology of balanced units of CSF samples from African American and Caucasian people, matched for age and intercourse with roughly equal numbers of management and AD circumstances (Desk 1). This included 53 Caucasian controls, 52 African American controls, 47 AD Caucasians, and 51 AD African People. The bulk have been feminine and on common the controls (64.5 years) have been barely youthful than AD (68 years). Notably, there have been no statistical variations between the ages of the African People and the Caucasians inside analysis (management: p = 0.8848, AD: p = 0.9998). As anticipated, AD circumstances had decrease Montreal Cognitive Evaluation (MoCA) scores than controls, however there have been no statistically vital variations between MoCA scores throughout race inside controls and AD (management: p = 0.7559, AD:p = 0.2055). The AD circumstances additionally had decrease Amyloid-beta1-42 (Aβ42) ranges and elevated whole Tau (tTau) and phosphorylated Tau181 (pTau181) ranges. Notably, Aβ42 ranges have been considerably decrease in African American controls in comparison with Caucasian controls (p = 0.0021) however not completely different between African American AD and Caucasian AD. This will likely point out doubtlessly early adjustments in mind amyloid deposition or processing of APP in African American controls versus Caucasian controls. Notably, the distribution of APOE4 carriers didn’t differ considerably by race within the management inhabitants and so doesn’t account for the sample noticed (Supplemental Desk 1). Conversely, tTau and pTau181 ranges have been considerably decrease in African People with AD (tTau:p < 0.0001, pTau181:p < 0.0001) however not completely different between African American and Caucasian controls. Knowledge on comorbid situations, together with whether or not or not the individual had hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, or cerebrovascular illness, is introduced for all circumstances in Supplemental Desk 1. Notably, not one of the comorbid situations was statistically overrepresented in both racial group.
Mass spectrometry and immunoassay measurements of Tau strongly correlate
Following enzymatic digestion, TMT labeling, and off-line fractionation, all samples have been subjected to liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC–MS/MS) (Fig. 1A). In whole, TMT-MS proteomic evaluation recognized 34,330 peptides mapping to 2,941 protein teams throughout the 203 samples (16 whole batches). To account for lacking protein measurements throughout batches, we included solely these proteins quantified in a minimum of 50% of samples following outlier removing as beforehand described [22,23,24,25,26], ensuing within the last quantification of 1,840 proteins. Protein abundance was adjusted for batch and age and intercourse have been regressed. Protein ranges of Tau (MAPT) by TMT-MS correlated strongly to independently measured tTau ranges by way of immunoassay (r = 0.83, p = 4.7e-47). As anticipated, Tau ranges have been considerably elevated in each African People and Caucasians with AD throughout each platforms in comparison with controls (Fig. 1B and C). In keeping with the immunoassay measurements, TMT-MS Tau ranges additionally confirmed considerably decrease ranges in African People with AD in comparison with Caucasians with AD (Fig. 1C). Thus, on this research, each platform measures of CSF Tau help a discount in Tau ranges in African People with AD, according to earlier findings [16, 17].
Differential expression evaluation of African American and Caucasian CSF proteome reveals distinctive and shared adjustments in AD
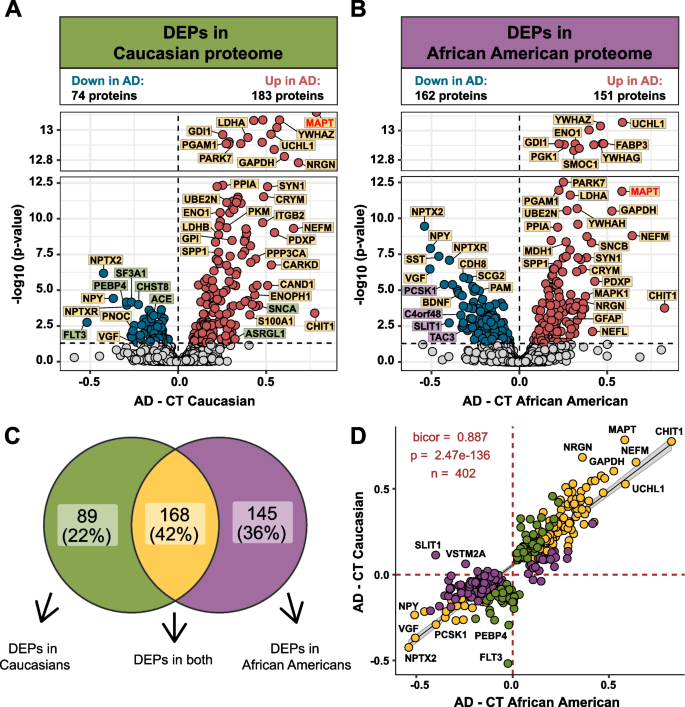
Differential expression evaluation was carried out to determine adjustments within the CSF proteome by race in AD (Supplemental Desk 5). In keeping with earlier proteomic analyses of AD CSF [25, 26, 41,42,43], there was a big improve in Tau (MAPT), 14–3-3 proteins, (YWHAZ, YWHAG, and YWHAE), SMOC1, neurofilaments (NEFM and NEFL) and proteins concerned in glucose metabolism in each African People and Caucasians with AD in contrast with race matched controls (Fig. 2A and B). Nevertheless, Caucasians with AD exhibited a bias in direction of proteins that have been elevated in AD, the place the variety of differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) was practically double (n = 183 proteins) the variety of decreased DEPs in AD (n = 74 proteins) (Fig. 2A). In distinction, in African People the variety of elevated and decreased DEPs was extra balanced (151 elevated proteins vs. 162 decreased proteins). A Venn diagram illustrates the overlap of DEPs from African People and Caucasians with AD (Fig. 2C), with nearly all of proteins (n = 168 proteins) differentially expressed in each races. Moreover, a correlation evaluation of each shared and distinctive DEPs confirmed general excessive settlement in route of change (bicor = 0.887, p = 2.47e-136, Fig. 2D). Nevertheless, there have been some exceptions together with SLIT1 and VSTM2A, which have been considerably elevated in Caucasians, however decreased in African People with AD. Each proteins are predominantly enriched in neuronal-cell sorts [44, 45]. Thus, regardless of the variations within the variety of vital DEPs in African People in comparison with Caucasians with AD, the route of change with illness stays largely related throughout each races.
Differential expression of Caucasian and African American CSF proteomes in AD. Volcano plot displaying the log2 fold change (FC) (x-axis) in opposition to one-way ANOVA with Tukey correction derived -log10 p-value (y-axis) for all proteins (n = 1840) evaluating AD versus controls for Caucasians A and African People B. Cutoffs have been decided by vital differential expression (p < 0.05) between management (CT) and AD circumstances. Proteins with considerably decreased ranges in AD are proven in blue whereas proteins with considerably elevated ranges in illness have been indicated in crimson. Choose proteins have been denoted and labeled by whether or not they have been differentially expressed in each proteomes (yellow), in solely the Caucasian proteome (inexperienced), or in solely the African American proteome (purple). C Venn diagram illustrating the variety of differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) that have been uniquely modified in a single proteome (inexperienced or purple) or modified in each proteomes (yellow) D The correlation between the fold change of all DEPs (n = 402) throughout the African American proteome (x-axis) and the Caucasian proteome (y-axis) have been strongly correlated (bicor = 0.887, p = 2.47e-136), no matter whether or not the DEP was vital in a single (inexperienced or purple) or each proteomes (yellow)
Community evaluation of the CSF proteome reveals modules associated to pathways and mind cell-types
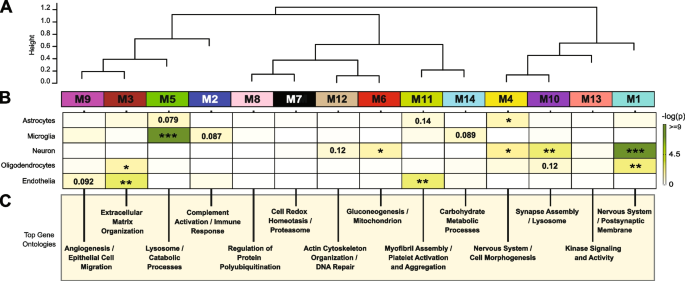
Co-expression community evaluation of the AD mind proteome organizes proteins into modules associated to molecular pathways, organelles, and cell sorts impacted by AD pathology [22,23,24,25]. Furthermore, integration of the human AD mind and CSF proteome revealed that roughly 70% of the CSF proteome overlapped with the mind proteome [26]. Whereas proteomic networks in AD mind have been examined, community adjustments within the AD CSF proteome, together with these related to race and AD biomarkers are much less nicely understood. Thus, we utilized Weighted Gene Co-expression Community Evaluation (WGCNA) to outline tendencies in protein co-expression throughout 1840 CSF proteins in all people. These parameters recognized 14 modules (M), ranked by measurement, starting from the biggest M1, with 370 proteins to the smallest, M14, with 16 proteins (Fig. 3A). Many of those modules have been considerably enriched for brain-specific cell sorts (Fig. 3B) in addition to established mind gene ontologies (GO), mobile capabilities and/or organelles (Fig. 3C, Supplemental Desk 7). The three largest modules have been related to classes of “Postsynaptic Membrane” (M1), “Complement Activation” (M2), and “Extracellular Matrix” (M3) whereas M5 represented “Lysosome / Catabolism” and M6 “Gluconeogenesis”. Different modules included these with GO phrases linked to “Cell Morphogenesis” (M4), “Cell Redox / Proteasome” (M7), “Protein Polyubiquitination” (M8), “Angiogenesis / Cell Migration” (M9), “Synapse Meeting” (M10), Myofibril Meeting (M11), “Actin Cytoskeleton” (M12), “Kinase Signaling / Exercise” (M13), and “Carbohydrate Metabolism” (M14).
Community evaluation classifies the CSF proteome into modules related to particular mind cell-types and gene ontologies. A Weighted Gene Co-expression Community Evaluation cluster dendrogram teams proteins (n = 1840) into 14 distinct protein modules (M1-M14). B Cell-type enrichment was assessed by cross referencing module proteins by matching gene symbols utilizing a one-tailed Fisher’s precise check in opposition to a listing of proteins decided to be enriched in neurons, oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, microglia and endothelia. The diploma of cell-type enrichment will increase from yellow to darkish inexperienced with asterisks denoting the next statistical significance (*p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ .001). C Prime gene ontology (GO) phrases have been chosen from vital GO annotations
Protein-based community evaluation in AD mind tissue has proven that the mobile composition represents a serious supply of organic variance and that lots of the community modules are enriched in proteins which might be expressed by particular mind cell sorts [24, 25]. To find out if an analogous relationship exists with protein-based networks in CSF, we evaluated the overlap of proteins in every module with mind cell-type particular makers (Fig. 3B, Supplemental Desk 8), generated beforehand from cultured or acute remoted neurons, oligodendrocytes, astrocytes, endothelial, and microglia from mind [44, 45]. The most important module, M1, was enriched with neuron/synaptic proteins (i.e., NPTX1, NPTXR, SCG2, VGF, NRN1, and L1CAM) and to a lesser diploma oligodendrocyte proteins (i.e., IGSF8, VCAN, APLP1). Neuronal loss or the lively secretion of neuronal proteins into the extracellular area might account for the presence of neuronal proteins within the CSF. The M4 module was additionally enriched for neuronal protein markers together with RTN4R1, LINGO2, OLFM1, and PLXNA2, related to “Nervous Programs and Cell Morphogenesis”. Modules most enriched with microglia markers have been M2 (i.e., C2, C3, C1RL, C1QA, C1QB, C1QC, LCP1, and many others.) and M5 (i.e., HEXB, CTSZ, HEXA, CTSA, CTSB) according to a job in complement activation and lysosome perform, respectively. Lastly, endothelial markers have been primarily overrepresented in modules M3 (i.e., NID2, ECM2, NID1, LTBP4, LAMA5, LAMC1), M9 (IGFBP7, F5, SDCBP, BGN) and M11 (FLNA, ANXA5, S100A11, MYL6) according to roles in extracellular matrix, angiogenesis and myofibril meeting, respectively. Thus, as seen within the community evaluation of bulk proteome from human mind [24, 25], sure modules of co-expressed proteins in CSF have been enriched with markers of particular mind cell-types. To additional help this statement, we assessed the protein overlap between modules in CSF and modules from a latest large-scale consensus TMT-MS proteomic community of bulk human AD mind tissue [24]. (Supplemental Fig. 2). Aside from M9, M10 and M14, which had minimal overlap with the mind, all different modules (79% whole) within the CSF community considerably overlapped with a minimum of one of many 44 mind modules (B-M1 to B-M44). For instance, there was overlap with CSF proteins in M1 “Postsynaptic Membrane” with a number of neuronal modules within the consensus mind community (B-M1, B-M4, B-M5, B-M10, and B-M15). As well as, M2 “Complement Activation” in CSF overlaps with modules in human mind related to complement and immune response (B-M26 and B-M40), whereas M3 “Extracellular Matrix” strongly overlapped with B-M27 in mind enriched with endothelial cell markers (Supplemental Fig. 2). Collectively, this helps that the co-expression in protein ranges is, partly, shared between CSF and mind tissue, which might mirror adjustments in activation or phenotypes of particular mind cell sorts.
CSF protein modules correlate to race and clinicopathological phenotypes of AD
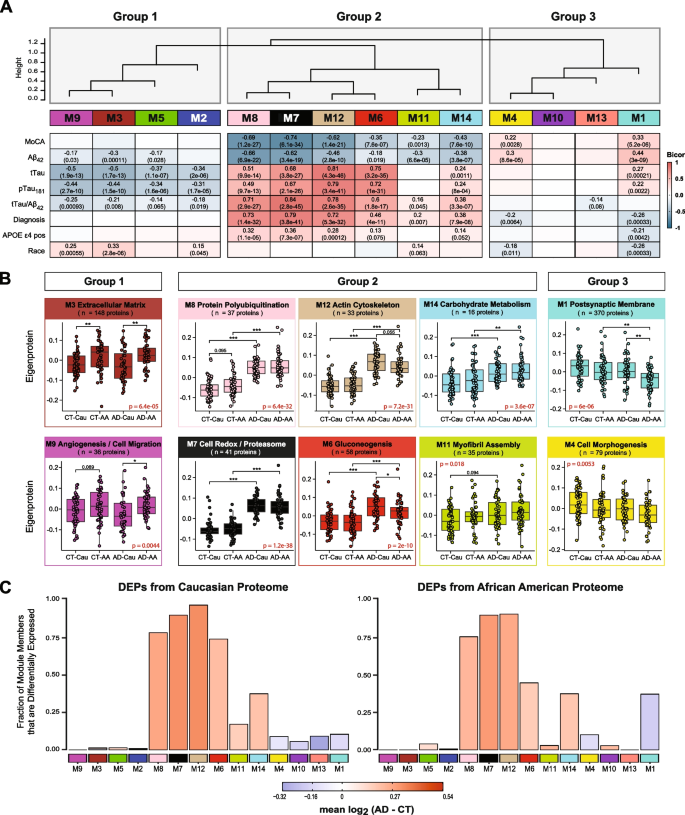
We assessed module correlation to race, cognitive scores (MoCA), and the hallmark AD biomarkers Aβ42, tTau, and pTau181. The protein community resulted in three primary teams/clusters primarily based on module relatedness (Fig. 4A). The primary cluster (Group 1) was comprised of 4 modules (M2 “Complement Activation”, M5 “Lysosome / Catabolism”, M3 “Extracellular Matrix”, and M9 “Angiogenesis / Cell Migration”. Of those modules, M3 and M9 exhibited baseline racial variations in abundance ranges (Fig. 4B). Notably, the eigenprotein, which corresponds to the primary principal part of a given module and serves as a abstract expression profile for all proteins inside a module, have been elevated for these two modules in African People in comparison with Caucasians. Of observe, these modules have been enriched with endothelial cell markers (Fig. 3B) which means that genetic ancestry and/or environmental variations affect expression or secretion of those cell-type markers. Equally, M2 and M5, each of which demonstrated enrichment for microglial markers, trended in direction of greater ranges in each African American controls and AD (Supplemental Fig. 3A), suggesting an accompanying immune response to the vascular alterations seen in modules M3 and M9.
CSF protein modules correlate to race and clinicopathological phenotypes of AD. A Modules have been clustered primarily based on relatedness outlined by correlation of protein co‐expression eigenproteins (indicated by place in peak). There have been three primary clusters within the community: Teams 1, 2 and three. Biweight midcorrelation (bicor) evaluation of module eigenprotein ranges with diagnostic measures of AD, together with MoCA rating, immunoassay Amyloid-beta1-42 (Aβ42), whole Tau (tTau), phosphorylated Tau181 (pTau181), ratio measures of tTau/Aβ42, analysis, whether or not the pattern has APOE ε4 allele or not, and race. The energy of constructive (crimson) and adverse (blue) correlations are proven by a heatmap with annotated bicor correlations and related p-values. B Eigenprotein values distributed by race and analysis of consultant modules for every cluster. C Differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) from AD samples in comparison with controls, by module with Caucasian proteome on the left and African People on the fitting. The peak of the bars represents the fraction of module member proteins that have been additionally DEPs in comparison with controls. The bars are shade coded by heatmap for common log2 distinction in abundance, the place crimson represents a rise in abundance in AD, and blue represents a lower in abundance in AD
The second cluster of modules (Group 2) was comprised of six modules (M8, M7, M12, M6, M11, and M14) that have been all elevated in AD (Fig. 4A). These AD modules additionally demonstrated vital adverse correlations to MoCA scores and, conversely, vital constructive correlations to tTau/Aβ42 ratio. Aside from M11, these modules additionally exhibited constructive correlations to APOE ε4 danger (Fig. 4A). Curiously, a hub protein of the M12 “Actin Cytoskeleton” module was Tau (MAPT). In keeping with CSF ranges noticed for Tau by immunoassay and TMT-MS (Fig. 1 B and C), the M12 eigenprotein had decrease ranges in African People, in comparison with Caucasians with AD, albeit not vital (p = 0.055) (Fig. 4B). Notably, M6 “Gluconeogenesis” was considerably decrease in African People in comparison with Caucasians with AD, highlighting one other module of CSF proteins that differed by race in AD (Fig. 4 A and B). This additionally indicated that the elevated glycolytic signature of AD beforehand reported in CSF [25, 26] is greater in Caucasians with AD. Constantly, a larger proportion of elevated DEPs in Caucasians with AD mapped to M6 in comparison with African People with AD (Fig. 4C). In distinction, M7 “Cell Redox / Proteasome” and M8 “Protein Polyubiquitination”, had the strongest correlations to tTau/Aβ42 ratio and cognition (Fig. 4B), and each demonstrated robust, equal elevations in African People and Caucasians with AD (Fig. 4B). That is according to an equal fraction of elevated DEPs mapping to those modules in African American and Caucasians with AD (Fig. 4C). Subsequently, proteins in these modules together with 14–3-3 relations (YWHAZ, YWAHB, YWHAG, YWHAE) doubtless signify the most effective class of CSF AD biomarkers that aren’t influenced by race. M14 “Carbohydrate Metabolism” and M11 “Myofibril Meeting” have been each elevated in each African People and Caucasians with AD (Fig. 4A and B), but to a lesser diploma than M7 and M8.
The ultimate group of modules (Group 3) contained two modules, M1 “Postsynaptic Membrane” and M4 “Cell Morphogenesis”, that confirmed robust correlations to each race and AD analysis (Fig. 4A). Each modules have been i) decreased in AD in comparison with controls and ii) and have been decrease in African People in comparison with Caucasians. As well as, each M1 and M4 have been enriched with neuronal markers and positively related to cognitive MoCA scores (Fig. 4A). Markedly, pairwise statistical evaluation of eigenprotein ranges for M1 throughout analysis and race revealed considerably decrease ranges in African People with AD (Fig. 4B). To this finish, a lot of the decreased DEPs in African People with AD mapped to M1 and to a lesser diploma M4, whereas decreased DEPs in Caucasians with AD have been equally distributed to M1, M4, M13 and M10 (Fig. 4C). Notably, M10 and M13 inside Group 3 didn’t present any variations with AD or race and didn’t considerably correlate with traits explored on this research (Fig. 4 and Supplemental Fig. 3). General, community evaluation successfully organizes the CSF proteome into protein modules which might be strongly linked to hallmark AD biomarkers (Aβ42, tTau and pTau181) and cognition, which in some circumstances have been additionally influenced by race.
Validation of shared and divergent CSF protein alterations throughout AD and race
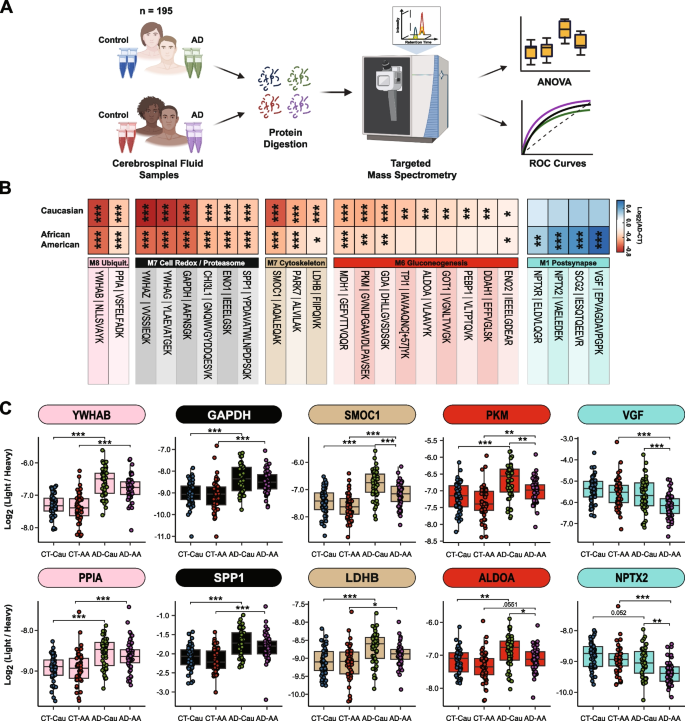
To additional validate these community findings, we used a focused mass spectrometry methodology, chosen response monitoring (SRM), with heavy labeled inner requirements to measure CSF proteins throughout 195 of the 203 circumstances included within the discovery TMT-MS assays (Fig. 5A). The proteins and corresponding focused peptides have been beforehand chosen primarily based on their sturdy detection and vital differential expression in earlier CSF discovery proteomic datasets [26, 46]. We used pooled CSF samples of management, and AD circumstances as quality control replicates (n = 29 samples whole) to evaluate technical reproducibility. Of the peptides focused, 85 peptides (mapping to 58 proteins) had a coefficient of variation of < 20% in each the management and AD swimming pools with no lacking values (Supplemental Tables 9 and 10). Following changes of co-variates (i.e., age and intercourse), peptide ranges have been extremely correlated with protein ranges measured by TMT-MS from the identical samples (Supplemental Tables 11 and 12). If a protein was measured by multiple peptide essentially the most correlated peptide to the TMT-MS protein degree was chosen for additional evaluation. The ultimate peptide record might be present in Supplemental Desk 13. ANOVA analyses decided pairwise significance between the 4 teams (i.e., Management-Caucasians vs Management-African People vs AD-Caucasians vs AD-African People, Supplemental Desk 14). Determine 5B highlights peptides (n = 24) that reached significance and that mapped to proteins in CSF modules related to race and/or AD. In keeping with the TMT-MS protein measurements, proteins measured by SRM inside M7 (GAPDH and YWHAG) and M8 (YWAHB and PPIA) had robust elevations (p < 0.001) in abundance in AD in each races, whereas proteins in M12 (SMOC1, PARK7, and LDHB) had a larger magnitude of change in Caucasians than African People with AD (for a listing of all M12 members, see Supplemental Desk 6). Equally, a majority of the proteins measured by SRM in M6 (PKM, GDA, TPI1, GOT1, ALDOA and ENO2) have been extra elevated in Caucasians than African People with AD (Fig. 5B and C). Proteins within the synaptic M1 module (VGF, SCG2, NPTX2, and NPTXR) have been considerably decreased in African People with AD in comparison with Caucasians (Fig. 5B and C), once more according to TMT-MS protein degree abundance. Notably, African People with or with out APOE ε4 allele within the AD group had lowered ranges of those CSF peptide biomarkers in comparison with Caucasians indicating that race and never APOE standing was driving the distinction in abundance (Supplemental Fig. 4A). Moreover, these variations throughout race remained constant even after eradicating sufferers with a number of comorbid situation (i.e., hypertension, diabetes, dyslipidemia, or cerebrovascular illness; Supplemental Fig. 4B and Supplemental Desk 1).
Validation of shared and divergent CSF protein ranges throughout AD and race. A Schematic of experimental workflow for SRM evaluation of cerebrospinal fluid proteome B Heatmap of peptides that have been considerably differentially expressed between management and AD Caucasians or African People. Stars are indicative of the extent of serious distinction (*p ≤ 0.05; **p ≤ 0.01; ***p ≤ 0.001) seen for every peptide between AD and management inside every race. In the meantime the colours are indicative of the log2 fold change (FC) of every peptide from management and AD for every race the place blue is indicative of the diploma of lower and shade of crimson is indicative of the diploma of improve. C Log2 abundance of peptides that mapped to modules of curiosity distributed by race and analysis. Pairwise significance was calculated utilizing one-way ANOVA with Tukey adjustment
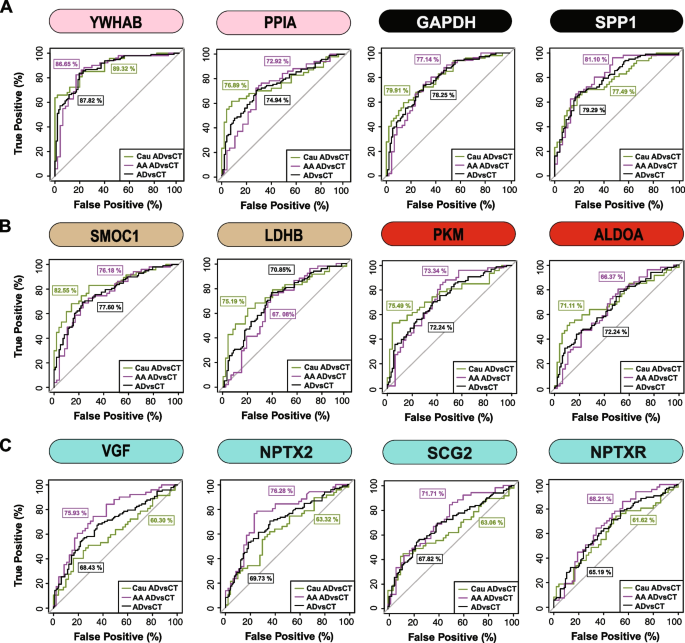
Lastly, a receiver working attribute (ROC) curve evaluation was carried out to evaluate the efficiency of every peptide biomarker in differentiating controls and AD by race (Fig. 6 and Supplemental Desk 15). We generated an space below the curve (AUC) for AD in African American and Caucasian people for every protein biomarker (thought of individually in every race). As anticipated, proteins mapping to M8 and M7 together with 14–3-3 proteins (YWHAB, YWHAG and YWHAZ) have been equally capable of discriminate AD from management no matter racial background. Notably, regardless of having decrease ranges in African People with AD in comparison with Caucasians with AD, solely a modest enchancment within the AUC for SMOC1 was noticed for classifying AD in Caucasians AUC = 0.8255 (p = 1.71e-08, CI = 0.7421–0.9090) in comparison with African People AUC = 0.7618 (p = 4.12e-06, CI = 0.6660–0.8576). Related findings have been noticed for an additional M12 protein, LDHB, in addition to M6 proteins PKM and ALDOA. Nevertheless, the M1 protein VGF was solely nominally vital at classifying AD in Caucasian AUC = 0.6030 (p = 0.0406, CI = 0.4887–0.7173), but extremely vital in African People AUC = 0.7593 (p = 5.03e-06, CI = 0.6634–0.8552). Related outcomes have been noticed for different synaptic M1 proteins, NPTX2 and SCG2, whereas NPTXR confirmed solely a modest enchancment within the AUC between African People in comparison with Caucasians with AD (Fig. 6 and Supplemental Desk 15). Collectively this helps a speculation that African People with AD have decrease ranges of a subset of neuronal biomarkers in comparison with Caucasians with AD.
ROC evaluation to judge CSF protein classification of AD by race. A YWHAB, PPIA, GAPDH, and SPP1 had related efficiency in classifying Caucasians and African People with AD B SMOC1, LDHB, PKM and ALDOA confirmed modest enchancment within the AUC for Caucasians with AD in comparison with African People with AD C VGF, SCG2, and NPTX2 have been higher classifiers for AD in African People in comparison with Caucasians, whereas NPTXR confirmed modest enchancment in classification of AD in African People. All protein AUCs with p-values and confidence internals (CI) are supplied in Supplemental Desk 15