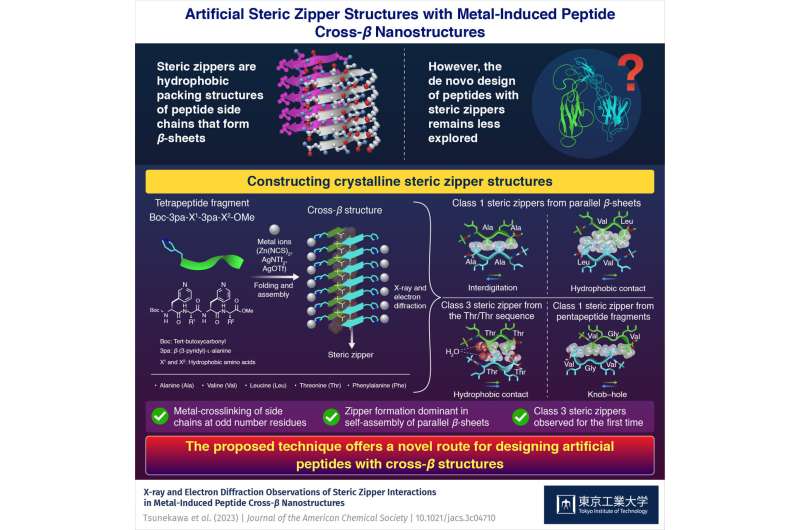
Steric zippers are a particular sort of hydrophobic packing construction that kind between two adjoining layers of peptide β-sheets in amyloid and comparable fibrils. These buildings play an important position within the stability and propagation of amyloid fibrils, and might support in designing new peptide-based supplies. Nevertheless, creating synthetic steric zippers is difficult owing to the sturdy aggregation tendency of β-sheet peptides. This usually results in the formation of gels and fibrils, making it tough to acquire buildings of their crystalline kind.
Now, in a brand new research printed within the Journal of the American Chemical Society, researchers from Japan, led by Affiliate Professor Tomohisa Sawada from Tokyo Institute of Expertise (Tokyo Tech), have introduced a novel method for the development of crystalline synthetic steric zippers.
“Though earlier research have revealed that peptide fragments derived from native protein sequences exhibit steric zipper buildings, their de novo designs have not often been studied,” explains Dr. Sawada.
The researchers started by making ready customized Boc-3pa-X1-3pa-X2-OMe tetrapeptide buildings, the place Boc refers to tert-butoxycarbonyl, 3pa represents β-(3-pyridyl)-ʟ-alanine, OMe is the methoxy group, and X1 and X2 denote the hydrophobic amino acids, particularly alanine, valine, leucine, threonine, and phenylalanine.
The tetrapeptide buildings had been designed such that the pyridyl teams and the hydrophobic amino acid teams fashioned aspect chains on both aspect of the peptide spine. This particular association of the residues within the peptide sequence performed an important position within the formation of steric zippers within the crystalline state.
The tetrapeptide fragments had been launched in microtubes along with a steel salt (Zn(NCS)2, AgNTf2, or AgOTf) and incubated at room temperature. These salts enabled the formation of reversible coordination bonds between the pyridyl group of peptides and the steel ions. Basically, this interplay prevented the uncontrollable aggregation of β-sheet peptides, resulting in the formation of needle-shaped crystals containing steric zippers.
By utilizing totally different mixtures of hydrophobic amino acids in peptides, the researchers constructed varied steric zipper buildings. Hydrophobic amino acids containing methyl aspect chains, akin to alanine, valine, and leucine teams, resulted in school 1 steric zippers, with peptide backbones organized parallel to one another.
Furthermore, the kind of interplay between the β-sheets relied on the steric bulkiness of the alkyl aspect chains current within the hydrophobic amino acids. For example, tetrapeptide buildings containing alanine, which has a smaller methyl aspect chain, exhibited interlocked buildings via interdigitation. In distinction, when the alkyl aspect chains of hydrophobic amino acids had been bigger, as in valine and leucine, the β-sheets had been linked through hydrophobic contact.
Notably, the researchers noticed a category 3 steric zipper for the primary time. These distinctive buildings emerged attributable to hydrophobic amino acids with aspect teams apart from alkyl teams, akin to threonine and phenylalanine. In these zippers, two β-sheets confronted the identical course, including to the range of steric zipper configurations.
Lastly, the researchers prolonged the system to a knob–hole-type zipper utilizing pentapeptide fragments. “The design of peptide supplies based mostly on steric zippers has to date been restricted to organic methods. The current outcomes open up a brand new route for the design of synthetic peptide supplies based mostly on these buildings,” remarks Dr. Sawada.
In conclusion, the insights into the structural traits of steric zippers can pave the best way for novel therapeutic methods for stopping or reversing ailments attributable to amyloid fibrils.
Extra info:
Eisuke Tsunekawa et al, X-ray and Electron Diffraction Observations of Steric Zipper Interactions in Metallic-Induced Peptide Cross-β Nanostructures, Journal of the American Chemical Society (2023). DOI: 10.1021/jacs.3c04710
Offered by
Tokyo Institute of Expertise
Quotation:
Steric zipper interactions in synthetic crystalline peptide β-sheets (2023, August 2)
retrieved 3 August 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-08-steric-zipper-interactions-artificial-crystalline.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.



