The t-test is a check in statistics that’s used for testing hypotheses relating to the imply of a small pattern taken inhabitants when the usual deviation of the inhabitants will not be recognized.
- The t-test is used to find out if there’s a vital distinction between the technique of two teams.
- The t-test is used for speculation testing to find out whether or not a course of has an impact on each samples or if the teams are completely different from one another.
- Mainly, the t-test permits the comparability of the imply of two units of knowledge and the dedication if the 2 units are derived from the identical inhabitants.
- After the null and various hypotheses are established, t-test formulation are used to calculate values which can be then in contrast with customary values.
- Based mostly on the comparability, the null speculation is both rejected or accepted.
- The T-test is just like different checks just like the z-test and f-test besides that t-test is often carried out in circumstances the place the pattern dimension is small (n≤30).
T-test Formulation
T-tests could be carried out manually utilizing a system or by some software program.
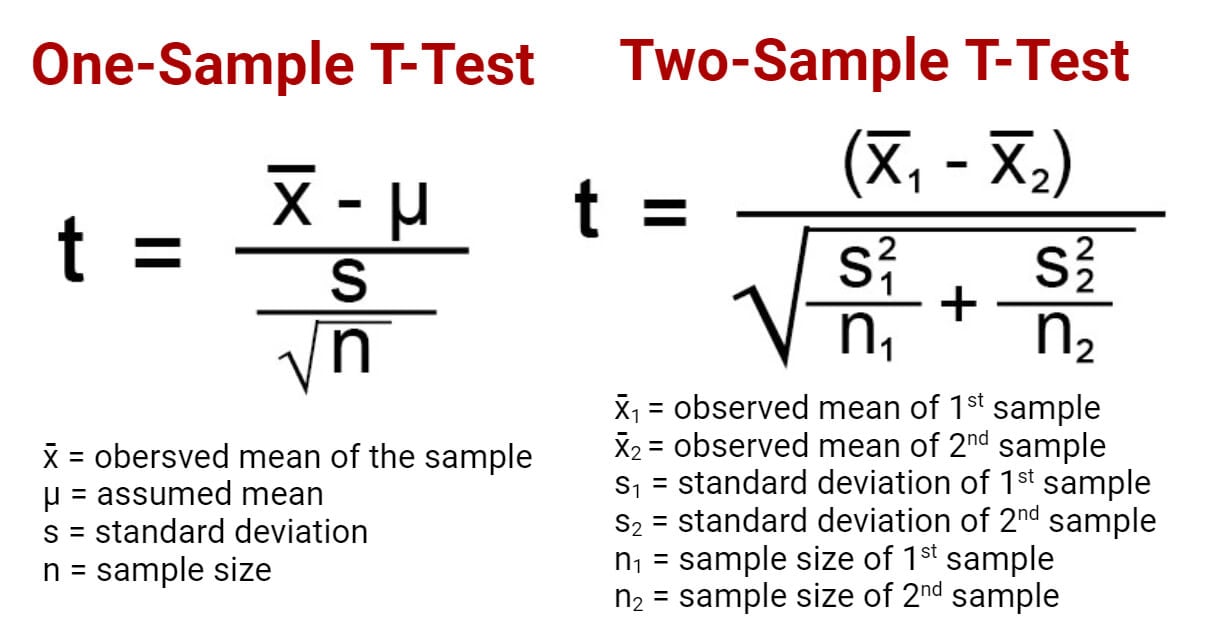
One pattern t-test (one-tailed t-test)
- One pattern t-test is a statistical check the place the vital space of a distribution is one-sided in order that the choice speculation is accepted if the inhabitants parameter is both higher than or lower than a sure worth, however not each.
- Within the case the place the t-score of the pattern being examined falls into the vital space of a one-sided check, the choice speculation is to be accepted as a substitute of the null speculation.
- A one-tailed check is used to find out if the inhabitants is both decrease than or greater than some hypothesized worth.
- A one-tailed check is acceptable if the estimated worth may depart from the pattern worth in both of the instructions, left or proper, however not each.

- For this check, the null speculation states that there isn’t a distinction between the true imply and the assumed worth whereas the choice speculation states that both the assumed worth is larger than or lower than the true imply however not each.
- As an illustration, if our H0: µ0 = µ and Ha: µ < µ0, such a check could be a one-sided check or extra exactly, a left-tailed check.
- Underneath such circumstances, there may be one rejection space solely on the left tail of the distribution.
- If we take into account µ = 100 and if our pattern imply deviates considerably from 100 in direction of the decrease course, H0 or null speculation is rejected. In any other case, H0 is accepted at a given stage of significance.
- Equally, if in one other case, H0: µ = µ0 and Ha: µ > µ0, that is additionally a one-tailed check (proper tail) and the rejection area is current on the appropriate tail of the curve.
- On this case, when µ = 100 and the pattern imply deviates considerably from 100 within the upward course, H0 is rejected in any other case, it’s to be accepted.
Two pattern t-test (two-tailed t-test)
- Two pattern t-test is a check a way during which the vital space of a distribution is two-sided and the check is carried out to find out whether or not the inhabitants parameter of the pattern is larger than or lower than a particular vary of values.
- A two-tailed check rejects the null speculation in circumstances the place the pattern imply is considerably greater or decrease than the assumed worth of the imply of the inhabitants.
- This kind of check is acceptable when the null speculation is a few assumed worth, and the choice speculation is about as the worth not equal to the desired worth of the null speculation.
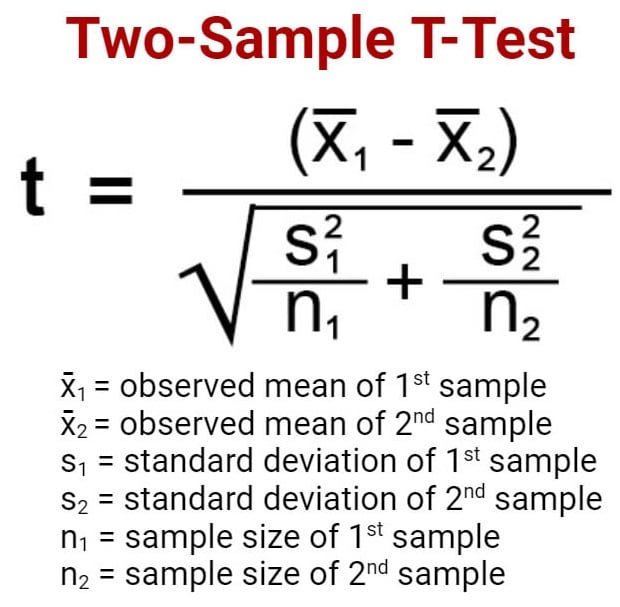
- The 2-tailed check is acceptable when we now have H0: µ = µ0 and Ha: µ ≠ µ0 which can imply µ > µ0 or µ < µ0.
- Due to this fact, in a two-tailed check, there are two rejection areas, one in both course, left and proper, in direction of every tail of the curve.
- Suppose, we take µ = 100 and if our pattern imply deviates considerably from 100 in both course, the null speculation could be rejected. But when the pattern imply doesn’t deviate significantly from µ, the null speculation is accepted.
Impartial t-test
- An Impartial t-test is a check used for judging the technique of two unbiased teams to find out the statistical proof to show that the inhabitants means are considerably completely different.
- Topics in every pattern are additionally assumed to return from completely different populations, that’s, topics in “Pattern A” are assumed to return from “Inhabitants A” and topics in “Pattern B” are assumed to return from “Inhabitants B.”
- The populations are assumed to vary solely within the stage of the unbiased variable.
- Thus, any distinction discovered between the pattern means also needs to exist between inhabitants means, and any distinction between the inhabitants means have to be because of the distinction within the ranges of the unbiased variable.
- Based mostly on this data, a curve could be plotted to find out the impact of an unbiased variable on the dependent variable and vice versa.
T-test Functions
- The T-test compares the imply of two samples, dependent or unbiased.
- It can be used to find out if the pattern imply is completely different from the assumed imply.
- T-test has an software in figuring out the boldness interval for a pattern imply.
References and Sources
- R. Kothari (1990) Analysis Methodology. Vishwa Prakasan. India.
- 3% – https://www.investopedia.com/phrases/o/one-tailed-test.asp
- 2% – https://towardsdatascience.com/hypothesis-testing-in-machine-learning-using-python-a0dc89e169ce
- 2% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Two-tailed_test
- 1% – https://www.scribbr.com/statistics/t-test/
- 1% – https://www.scalelive.com/null-hypothesis.html
- 1% – https://www.investopedia.com/phrases/t/two-tailed-test.asp
- 1% – https://www.investopedia.com/ask/solutions/073115/what-assumptions-are-made-when-conducting-ttest.asp
- 1% – https://www.chegg.com/homework-help/questions-and-answers/sample-100-steel-wires-average-breaking-strength-x-50-kn-standard-deviation-sigma-4-kn–fi-q20558661
- 1% – https://help.minitab.com/en-us/minitab/18/help-and-how-to/statistics/basic-statistics/supporting-topics/fundamentals/null-and-alternative-hypotheses/
- 1% – https://libguides.library.kent.edu/SPSS/IndependentTTest
- 1% – https://keydifferences.com/difference-between-t-test-and-z-test.html
- 1% – https://keydifferences.com/difference-between-t-test-and-f-test.html
- 1% – http://www.sci.utah.edu/~arpaiva/courses/UT_ece3530/hypothesis_testing.pdf
- <1% – https://www.thoughtco.com/overview-of-the-demand-curve-1146962
- <1% – https://www.slideshare.internet/aniket0013/formulating-hypotheses
- <1% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Null_hypothesis



