1. Introduction
Human well being is significantly threatened by the dramatic environmental and life-style modifications of the trendy period. An unprecedented rise in a various vary of neurological problems is without doubt one of the main international challenges. For the reason that final decade, it has been evident that the intestine microbiota has a possible function in mind operate by mediating signaling pathways by microbial metabolites (Grochowska et al., 2019; Iannone et al., 2019). On the connection of neuroscience and microbiology, groundbreaking research, largely performed over the previous ten years, have revealed lively relations between animals and the microbial populations that stay inside them that assist the event and operation of neurological techniques. These interactions, which contain immunological, neural, and chemical communication, are advanced, however they’re very important to the well being of people and our understanding of neurological problems (Morais et al., 2021). The intestine microbiota residing within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract performs an necessary function within the well being standing of the host by regulating cells in native and distant organs, together with the mind. Bidirectional transmission happens within the intestine–mind axis (GBA) within the type of a two-way communication mechanism between the intestine and the neurological system of the host. This info might be transferred by mind networks, hormones, and the immune system, which facilitate the intestinal microbiota. Bidirectional transmission within the GBA regulates mind dysfunction mechanistically, maintains a mutualistic affiliation with the host and regulates the innate and adaptive immune techniques (Collins et al., 2012; Carabotti et al., 2015). This axis includes totally different pathways, such because the autonomic and enteric nervous system, the endocrine system, the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA), the immune system, and the microbiota and its metabolites (Blaser, 2017; Burberry et al., 2020). A wholesome intestine microbiota advantages the host by producing microbial metabolites and neurotransmitters for communication with host cells, similar to intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) and immune cells. Alterations within the intestine microbiota and microbial metabolite manufacturing have been linked to a variety of immune-related neurological problems, together with developmental problems, neurodegeneration, and emotional dysregulation. The mind is the organ chargeable for all of a person’s habits and for controlling it. It’s composed of many numerous populations of neuronal and nonneuronal cells which might be related by extremely refined structural networks (Deidda and Biazzo, 2021). The digestive tract (GI) is the habitat for greater than 98% of the micro organism in our our bodies. The time period “intestine microbiota” refers back to the specific microorganisms which might be current and reside within the intestine (Ma et al., 2019).
The event of omics methods has contributed to the understanding of the intestine microbiota as one of many key regulators of the interactions between the intestine and the mind (Bhattarai et al., 2021; Zhu et al., 2022). Animal and human analysis has offered proof that the intestine microbiota would possibly affect mind habits and cognitive growth by producing hormones, immunological components, and metabolites, which additionally means that altering the intestine microbiome could enhance or doubtlessly deal with mind problems (Lee et al., 2011; Braniste et al., 2014; Jasarevic et al., 2015; Ogbonnaya et al., 2015; Yano et al., 2015; Wang and Wang, 2016). Indicators from the mind can have an effect on the sensorimotor and secretory capabilities of the abdomen by intricate neurohumoral networks, and likewise, visceral afferent indicators coming within the gastrointestinal tract can have an effect on mind operate (Cryan and Dinan, 2012). The gut-brain axis has lately emerged as a key participant within the regulation of regular mind functioning underneath physiologically regular circumstances in addition to within the growth of neuropathological ailments as a threat issue or situation (Ma et al., 2019).
Nevertheless, there’s a lack of widespread affirmation of the mechanisms underlying hyperlinks between the intestine microbiota and mind problems (Martin et al., 2018). New applied sciences are being created to transcend correlative analysis and discover and validate organic mechanisms of motion which have the actual potential to deal with human illness. On this evaluation, we focus on the interplay between the intestine and mind and their signaling pathways. Moreover, we focus on the operate of the microbiota and neurological problems similar to neuropsychiatric problems (schizophrenia and ADS), temper problems (anxiousness and despair), and neurodegenerative problems (PD, AD, and MS).
2. Intestine microbiota-brain axis
The intestine microbiome consists of micro organism, archaea, viruses, and eukaryotic microbes that colonize the digestive tract. The intestine microbiota, which contains roughly 100–150 instances extra genes than the human genome, is discovered within the human intestines and consists of roughly 1,000 species and seven,000 varieties of micro organism, gram-positive or gram-negative Firmicutes (together with the species Lactobacillus, Eubacterium, and Clostridium), and gram-negative Bacteroidetes kind the vast majority of the micro organism (containing Bacteroides and Prevotella) (Flowers and Ellingrod, 2015; Blaser, 2017; Askarova et al., 2020; Tarawneh and Penhos, 2022). The next 5 phyla make up the vast majority of the intestine microbial neighborhood: Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Verrucomicrobia (The Human Microbiome Mission Consortium, 2012). People’ food regimen, age, gender, surroundings, and genes had an impression on the composition of their intestine microbiota (Takagi et al., 2019). Dysbiosis of the human intestine microbiome has been related to numerous pathologies (Perry et al., 2016). Intestine dysbiosis, as proven by variations within the range and frequency of the microbial neighborhood (total taxa and species) that comprise the intestine flora, has been related in each animal and human research to irregular mind protein aggregation, irritation, immune dysregulation, and decreased neuronal and synaptic exercise research of AD (Cryan et al., 2020; Gubert et al., 2020).
The aptitude of the intestine microbiota to have an effect on brain-related actions means that it triggers the manufacturing of immune components that focus on each the CNS and the enteric nervous system (ENS), similar to cytokines and inflammatory mediators (Wooden and Galligan, 2004). The autonomic nervous system, a part of the peripheral nervous system, regulates physiological processes not topic to aware management. It controls very important visceral capabilities by coordinating complimentary responses between the sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous techniques. Understanding the bidirectional communication between the CNS and the digestive tract was vastly superior by the invention of the ENS, a department of the autonomic nervous system. The ENS, generally generally known as the “second mind within the physique,” is maintained in a wholesome state by the cooperation of enteric neurons and connections to the CNS (Rao and Gershon, 2018). The ENS is made up of thousands and thousands of neurons which might be discovered within the mucosa of the digestive tract. These neurons are chargeable for sustaining the equilibrium of intestinal actions. Essentially the most direct route of communication between the intestine and the mind is the vagus nerve (de la Fuente-Nunez et al., 2018). A deeper understanding of the gut-brain connection confirmed a fancy communication pathway that not solely maintains the well being of the gastrointestinal system however can be more likely to have quite a lot of penalties on how the mind capabilities as an entire, together with greater cognitive operate and motivation (Rhee et al., 2009). The gut-brain axis (GBA), which is a complicated bidirectional communication community between the gut and the CNS, is the place communication happens between the CNS and gut (Determine 1; Sudo et al., 2004; Rao and Gershon, 2018; Skonieczna Zydecka et al., 2018). The routes of communication contain the autonomic nervous system [for example, the enteric nervous system (ENS) and the vagus nerve], the neuroendocrine system, the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis, the immune system and metabolic pathways (Duvallet et al., 2017; Blacher et al., 2019; Burberry et al., 2020). A number of neurotransmitters (Yano et al., 2015; O’Keefe, 2016) and metabolites, together with short-chain fatty acids, secondary bile acids, very important nutritional vitamins, and amino acids (Ellwardt et al., 2016; Engelhardt et al., 2016; Mittal et al., 2017), modulate many immune system pathways (Baj et al., 2019; Dalile et al., 2019), which in flip have an effect on cognition, habits, studying, motion, and neurodegenerative ailments (Jenkins et al., 2016; Kennedy et al., 2017; Feng et al., 2020). The gut-brain axis has been termed the GMB axis because it seems to manage the immune system, digestive tract, habits, stress response, and CNS processes (Savignac et al., 2011; Collins et al., 2012; De Palma et al., 2014; Fond et al., 2015; Pirbaglou et al., 2016; Rincel and Darnaudery, 2020). Notably, developments in intestine microbiota sequencing have revealed a powerful relationship between the advanced ecosystem and the CNS (Knight et al., 2018). Lately, there was rising curiosity in learning interactions between the mind, gastrointestinal microbiome and their bidirectional relationship.
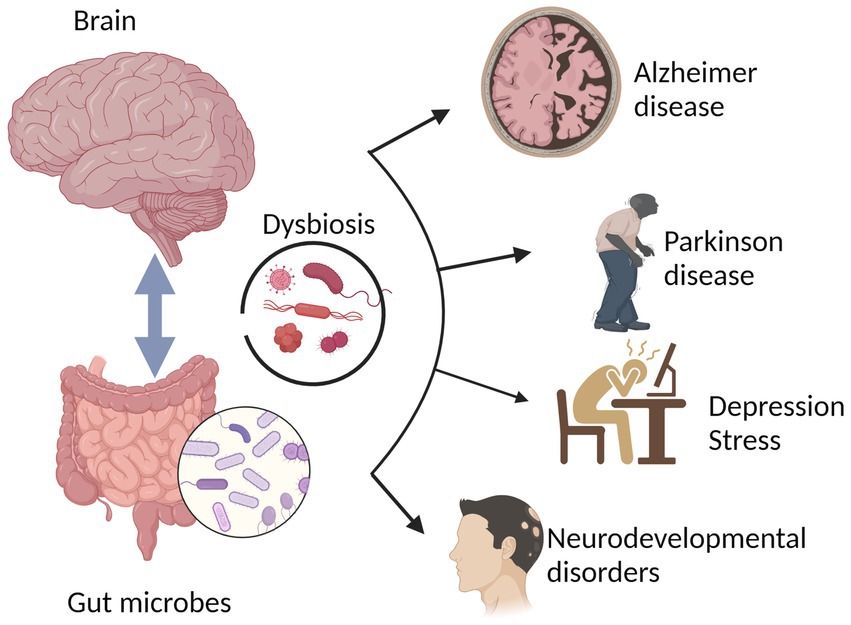
Determine 1. The physiological homeostasis attained throughout typical mind functioning is a results of the interactions between the mind and the gut-brain (intestine microbiota). A number of mind problems, together with Parkinson’s illness, neurodegenerative ailments, despair, stress, Alzheimer’s illness, and neurodevelopmental problems, have been linked to altered intestine microbiota or intestine dysbiosis.
3. How the intestine microbiota impacts the mind
The CNS and ENS talk with each other utilizing a lot of chemical signaling mechanisms, together with direct neuronal, immune, and endocrine pathways (Yoo and Mazmanian, 2017). The gut-brain axis is a community of connections involving a number of organic techniques that facilitates bidirectional communication between intestine micro organism and the mind and is significant for sustaining the gastrointestinal, neurological, and microbial techniques of animals (Martin et al., 2018; Cryan et al., 2019). Along with the neurological system, the intestine microbiota additionally impacts the mind by the endocrine, immunological, and metabolic techniques (the gut-brain neuroanatomical pathway) (Cryan and Dinan, 2012; Montiel-Castro et al., 2013). Within the intestine microbiota-brain axis, extra emphasis is positioned on the involvement of micro organism as a result of the intestine microbiota can be utilized as an impartial variable and modified deliberately (Al Omran and Aziz, 2014). Microbes can have an effect on how the nervous system develops, matures, ages, and maintains homeostasis, for instance, by altering how neurotrophic components and N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor subunits within the hippocampus are expressed (Bercik et al., 2011a; Heijtz et al., 2011). The primary ways in which the microbiota can affect the event and performance of the nervous system are organic networks, together with direct and oblique transmission through chemical transmitters, the immune system, neuronal pathways, and endocrine pathways, as proven in Determine 2.
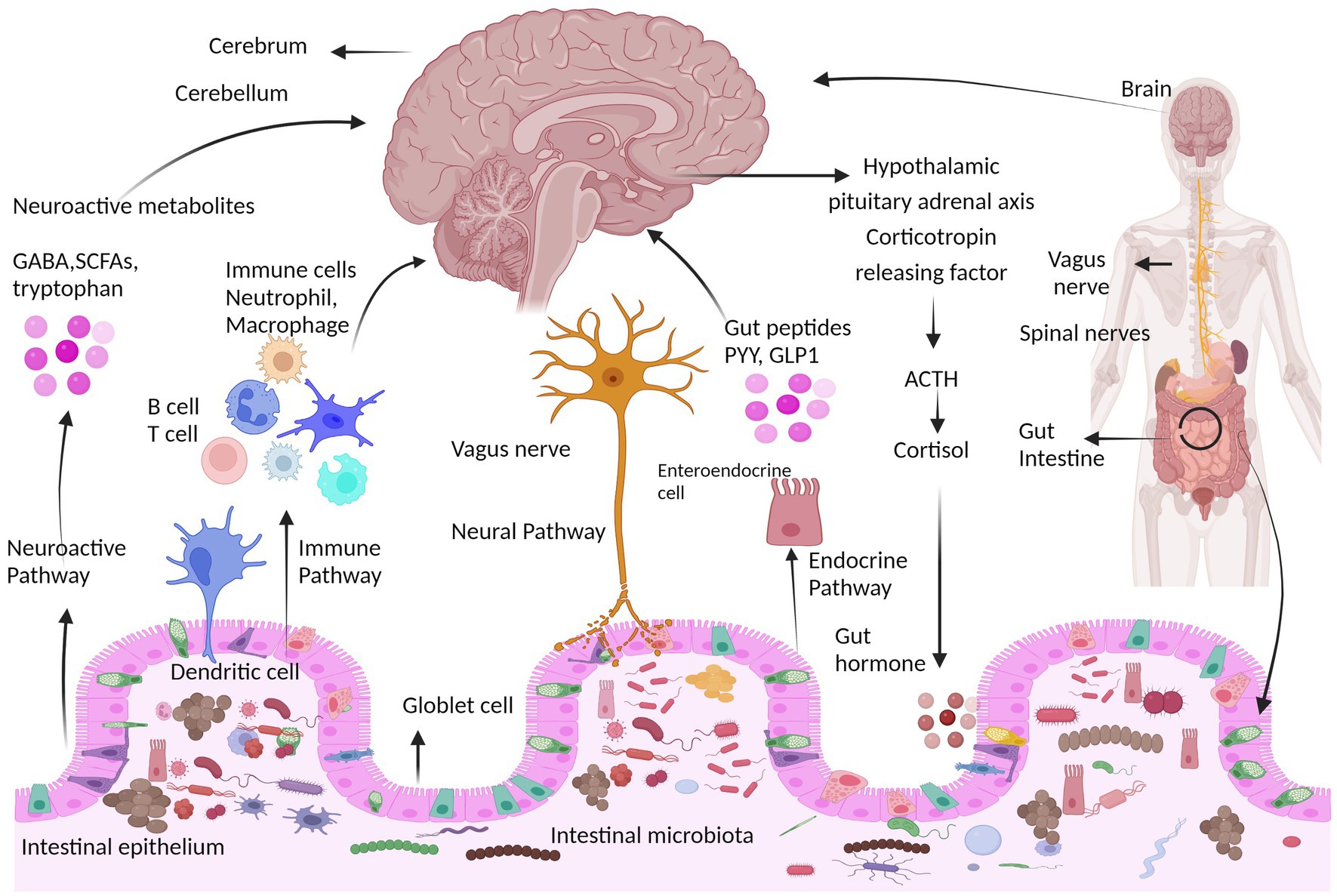
Determine 2. Communication pathways between the mind and intestine microbiota. The interplay between the central nervous system (CNS) and intestine microorganisms is mediated through a number of direct and oblique gut-brain axis mechanisms. They embrace the immune pathway (together with cytokines), short-chain fatty acids and microbial metabolites; the neuroactive pathway, together with neurotransmitters and neuroactive metabolites; the neural pathway [enteric nervous system, vagus nerve, and spinal nerves (Sgritta et al., 2019); and the endocrine pathway, hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis (HPA) (Lyte, 2014b)]. HPA axis response that includes neurons of the hypothalamus that launch hormones similar to corticotropin receptor hormone (CRH) into the portal circulation or the mind, inflicting the discharge of the hormone adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), which begins the manufacturing of cortisol and its launch. The neuroimmune signaling reactions are regulated by cortisol.
3.1. Microbiota and neurotransmitters
Intestine microbes might help regulate bodily capabilities and alter habits of their animal host by chemical interactions with the nervous system, together with each “direct” and “oblique” communication (Morais et al., 2021). Microorganisms have the power to synthesize among the neuroactive compounds themselves in addition to stimulate the manufacturing of different metabolites and neurotransmitters by the host that regulate gut-brain signaling (Poutahidis et al., 2013). The microbiota can be required for the conventional maturation, activation, and growth of microglia, that are innate immune cells within the mind (Zheng et al., 2020). Evidently immune programming by microglia is regulated by indicators from microbial metabolism as a result of administering bacterial-derived short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) to germ-free (GF) mice restores microglial form and performance (Erny et al., 2015). Microbial-derived molecules signaling to the mind. Neurotransmitters similar to dopamine, serotonin, norepinephrine, glycine, and gamma-aminobutyric acids are produced by the intestinal microbiota, and every has a selected impression on mind γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). Imbalances in these neurotransmitters can result in problems similar to AD, PD, autism spectrum dysfunction, anxiousness problems, and depressive problems (Chen et al., 2021).
For instance, Bifidobacterium infantis will increase blood plasma tryptophan ranges, which impacts central serotonin transmission; GABA might be produced by Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium; noradrenaline might be produced by Escherichia, Bacillus, and Saccharomyces species; serotonin might be produced by Streptococcus, Candida, Escherichia, and Enterococcus species; dopamine might be produced by micro organism; and acetylcholine might be produced by Lactobacillus (Lyte, 2014a). SCFAs, a kind of direct signaling, are lipids generated by intestinal microbes by the fermentation of dietary fiber which have the power to affect the immune system, epigenetics, and neuroplasticity within the CNS (Dalile et al., 2019). The mind, vitality steadiness, and metabolism are all impacted by SCFAs, which embrace butyrate, propionate, and acetate and are very important metabolic byproducts of intestine microbial exercise (Dinan et al., 2015). Moreover, SCFAs function endogenous ligands for orphan G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), and intracellular SCFAs regulate gene expression by stopping histone deacetylases. As well as, SCFAs work together with vagal afferents, which impacts irritation and hormone regulation. The interactions of SCFAs with specific mobile techniques and gut-brain signaling pathways assist the concept SCFAs can play a big function in GMB communication (Dalile et al., 2019). By oblique chemical communication, the microbiota additionally impacts the neurological system and habits, as evidenced by the microbial regulation of the neuroendocrine system (Sudo et al., 2004). Intestine microbiota can have an effect on their host’s urge for food and consuming patterns by altering the endocrine indicators produced by enteroendocrine cells (EECs) within the intestine epithelium, which includes the manufacturing of the hormone glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP1) (Aresti Sanz and El Aidy, 2019). The microbiota within the intestine can produce neurotransmitters on their very own and may stimulate the creation of those chemical substances of their animal hosts. For instance, a lot of microbes, together with Escherichia spp., Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium, and its species, are recognized to generate the neurotransmitter GABA (Strandwitz et al., 2019). Micro organism have been demonstrated to be important for the manufacturing of the neurotransmitter serotonin 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) in animal mouse mannequin techniques (Clarke et al., 2013). Microbial metabolites similar to indole, SCFAs, secondary bile acids, α-tocopherol, p-aminobenzoate, and tyramine have an effect on the era and secretion of 5-HT by enteroendocrine cells (EECs) (Yano et al., 2015; Morris et al., 2017). Intestine microbes synthesize SCFAs, 5-HT, dopamine, butyric acid, gamma amino acids, and gamma amino acids (Forsythe et al., 2014; Lyte, 2014b), and these substances are accessible between microbial cells (Forsythe et al., 2014). The intestine, notably intestinal cells, can synthesize giant quantities of 5-HT, which impacts the mind. Moreover, microbial enzymes can manufacture neurotoxins such D-lactic acid and ammonia (Manicassamy et al., 2010; Smith, 2015). These neuroactive metabolites, such because the neurotransmitters GABA, dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin, amino acids (for instance, tryptophan and tyramine) T lipopolysaccharide (LPS), short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), long-chain fatty acids (LCFAs), trimethylamine-N-oxide (TAMO), and polysaccharide A (PSA), both straight or not directly induce the migration of peripheral immune cells to the mind and are thought to trigger neuroinflammation and affect CNS capabilities (Harms et al., 2018; Morais et al., 2021). Microbial-associated molecular patterns (MAMPs), that are launched, additionally join the CNS to the microbiota (Sampson and Mazmanian, 2015). MAMPs are molecules produced by intestine microbes, similar to double-stranded RNA, lipopolysaccharides, and lipoproteins, which might be recognized by quite a lot of receptors, particularly Toll-like receptors (Akira and Hemmi, 2003; Schachtle and Rosshart, 2021). Nevertheless, 5-HT and its metabolic precursor tryptophan concentrations within the hippocampus had been decreased in germ-free mice, indicating a doable function for the intestine microbiota in regulating 5-HT signaling pathways within the CNS (Clarke et al., 2013). In actual fact, it’s tough to guage how a lot microbial metabolism straight impacts CNS exercise, partly as a result of we don’t totally perceive the typical charge of transport for quite a few microbial metabolites into the mind (Muller et al., 2020).
3.2. Endocrine pathway
SCFAs can alter the operate of the gut-brain axis by regulating the manufacturing of intestine hormones. The activation of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) by SCFAs within the colon is the mechanism underlying the manufacturing of those intestine hormones, which reinforces the discharge of peptide YY (PYY) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP1) from enteroendocrine L cells (Tolhurst et al., 2012; Psichas et al., 2015; Larraufie et al., 2018). These hormones in flip have the ability to have an effect on temper, reminiscence, and studying. By the usage of free fatty acid receptors (FFARs), SCFAs can sign to the mind by straight activating vagal afferents (Dalile et al., 2019). GLP1 has many receptors all through the physique and might have an effect on mind capabilities through each humoral and neuronal routes, together with the CNS and PNS, in addition to the guts, lungs, intestines and pancreas (Alvarez et al., 2005; Katsurada and Yada, 2016). GLP1 is concerned in enhanced reminiscence and studying in mice (Isacson et al., 2011), enhanced neuroplasticity and neuroprotection within the hippocampus (McClean et al., 2011; Porter et al., 2011), in animal fashions of AD, and in decreased βamyloid plaques and microglia activation (McClean et al., 2011). One other anorexic neuropeptide, PYY, reduces urge for food and prevents gastric motility. Along with the distal gastrointestinal tract’s L cells secreting it (colon and ileum), the hypothalamus and pituitary gland have the very best ranges of PYY expression within the human mind, which is expressed all through the mind (Morimoto et al., 2008). The commonest type of circulating PYY is PYY3–36, a truncated type of the protein that preferentially interacts with the Y2 neuropeptide Y receptor (Murphy and Bloom, 2006). In response to analysis performed on animals, PYY impacts each urge for food and mind exercise by both mechanisms that cross the blood–mind barrier (BBB) (Nonaka et al., 2003) or by activating vagal afferent pathways that connect with the intestine wall’s lamina propria and myenteric plexus and transmitting to the brainstem (Koda et al., 2005; Waise et al., 2018). Different metabolic hormones that have an effect on mind operate and are influenced by SCFAs embrace ghrelin, leptin, and insulin; nevertheless, analysis on these hormones has been much less centered than that on PYY and GLP1. Leptin is a hormone that induces weight reduction that’s largely produced by adipose cells (Hube et al., 1996), and it’s well-known for regulating the physique’s vitality steadiness by activating its hypothalamic receptors to specific orexigenic and anorexigenic neuropeptides similar to neuropeptide Y and α melanoma-stimulating hormone, which reduces urge for food (Elias et al., 1999).
3.3. Immune pathway
The immune system is influenced and straight affected by each the CNS and the intestine microbiome. The intestine microbiota has a big impression on the event and performance of the peripheral immune system (Zheng et al., 2020). The microbiota is critical for the event and activation of innate immune cells within the mind (Abdel-Haq et al., 2019). The pathophysiology of psychiatric problems could contain immune responses and irritation (Miller and Raison, 2016). CNS-cytokine interactions have an effect on mind capabilities and affect neurocircuits that regulate motivation, motor exercise, and temper (Capuron and Miller, 2011). Moreover, by the systemic immune system and circulating cytokines, the intestine microbiota and the mind talk (Hsiao et al., 2013). Immune cells straight penetrate the BBB and attain the CNS, or they’ll produce cytokines and chemokines within the mind (Morais et al., 2021). Cytokines are substances made within the gut that may journey by the bloodstream and, underneath sure circumstances, affect the hypothalamus and different areas of the mind (El Aidy et al., 2014). The BBB is a bodily barrier that separates the mind microenvironment from the remainder of the physique. It’s fabricated from tight junction proteins that join the mural and microvascular endothelial cells (Morais et al., 2021). The BBB regulates the motion of molecules between the bloodstream and the cerebrospinal fluid of the CNS. Permeability of the BBB is influenced by the intestine microbiota, as some studies present that GF mice have elevated BBB permeability relative to regulate mice, partially because of decreased expression of tight-junction proteins similar to occludin and claudin 5 (Braniste et al., 2014). The BBB permits it to successfully management the stream of chemical substances, ions, and cells between the physique’s surroundings and the mind (Engelhardt and Liebner, 2014). The BBB is necessary as a result of it protects the mind towards pathogens and unfavorable immune responses that would hurt the neurons and the connections between them (Daneman and Prat, 2015). Many psychiatric problems, similar to main despair, schizophrenia, autism spectrum dysfunction, and obsessive–compulsive dysfunction, have been linked to microglial dysregulation (Frick et al., 2013). SCFAs have a direct impression on immune cells and immunological modulators to take care of homeostasis. The affect of SCFAs on intestinal mucosal immunity is nicely described by Corrêa-Oliveira et al. (2016). Nevertheless, SCFAs can also have an effect on the peripheral immune system, modulating mind exercise. By rising the intestinal barrier and inhibiting the switch of micro organism and bacterial metabolites or by direct contact between SCFAs and immune cells, which might lower neuroinflammation within the mind, systemic irritation could also be decreased (Dalile et al., 2019). SCFAs regulate the maturation and activation of T lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells (DCs), and neutrophils (Corrêa-Oliveira et al., 2016). Neutrophils, essentially the most prevalent granulocyte sort, are a necessary a part of the innate immune system and are produced within the bone marrow. They’re the primary to look on the website of irritation, they usually exploit the manufacturing of cytokines to attract in different cells, such macrophages (Rodrigues et al., 2016). SCFAs have an instantaneous impact on neutrophils by regulating the manufacturing of proinflammatory cytokines similar to tumor necrosis issue (TNF), probably by histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibition. By regulating the synthesis of chemokines similar to CXC motif chemokine ligand 1 (CXCL1) and CXC motif ligand 8 (CXCL8), in addition they operate as neutrophil chemoattractants. SCFAs have an effect on neutrophil chemotaxis by inflicting free fatty acid receptor 2 (FFAR2) in these cells to turn out to be lively (Rodrigues et al., 2016). SCFAs can have an effect on adaptive immune responses by straight or not directly affecting T-cell growth and proliferation (Kim et al., 2014).
3.4. Neuronal pathways for intestine–mind interactions
The intestine and mind are bodily linked by neurological connections. Essentially the most vital of those neural networks is the vagus nerve, which emerges from the brainstem and innervates the gastrointestinal tract and ENS (Yoo and Mazmanian, 2017). Essentially the most direct and well-studied hyperlink between the intestine and the CNS, the vagus nerve, is one other pathway by which intestine microbes talk with the mind (Fülling et al., 2019). Nearly the entire digestive system is innervated by the vagus nerve, which has 80% afferent and 20% efferent fibers. The vagal afferent nerve terminals innervate a number of layers of the digestive wall, whereas the mucosal afferents finish inside the lamina propria of the intestinal mucosa (Waise et al., 2018). Vagal receptors sense inflammatory chemical substances, dietary parts, bacterial metabolites, and regulatory intestine peptides to switch indicators to the central nervous system (De Lartigue et al., 2011). Nevertheless, there’s some proof that the micro organism within the intestine can straight activate neurons. Toll-like receptors 3 and seven, which detect viral RNA, in addition to Toll-like receptors 2 and 4, which detect peptidoglycan and lipopolysaccharide, are current within the enteric nervous techniques of each mice and people (Brun et al., 2013; Martin et al., 2018). Bacteroides fragilis, Lactobacillus rhamnosus (JB-1), and remoted polysaccharide A of B. fragilis have all been demonstrated to stimulate gut afferent neurons ex vivo (Mao et al., 2013). Power remedy with Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 decreased the signs of tension induced by persistent intestine irritation (Bercik et al., 2011b). The consequences seen in these trials had been eradicated when the vagus nerve’s integrity was compromised by vagotomy (Bravo et al., 2011; Bercik et al., 2011b). Moreover, microbial metabolites have the capability to straight activate neurons. The receptors FXR and TGR5 are expressed in mind neurons, though wholesome people have low or undetectable bile acid concentrations in these organs (Huang et al., 2016). Numerous research have recognized the superior cervical ganglion as the situation of G protein-coupled receptor 41 (GPR41) and free fatty acid receptor 3 (FFAR3) receptors (Kimura et al., 2011), prevertebral ganglia (Received et al., 2013), submucosal and myenteric ganglia neurons (Nohr et al., 2013), sympathetic ganglia of the thoracic and lumbar sympathetic trunks, and vagal ganglion (Nohr et al., 2015), suggesting neuronal activation by microbially derived SCFAs. Neuronal innervation of the colonic epithelium is decreased in GF mice and restored by microbial colonization (De Vadder et al., 2018). Intestine micro organism additionally help within the growth of enteric glial cells in mice, that are important for sustaining neuronal networks and controlling intestine homeostasis (Kabouridis et al., 2015; Aktar et al., 2020). The exercise of enteric neurons might be influenced by the intestine microbiota by chemical communication, in accordance with a current examine exhibiting that activating aryl hydrocarbon receptors in grownup mice can have an effect on intestine motility by affecting the ENS (Obata et al., 2020).
4. Intestine microbiota and neurological problems
Neurological and neuropsychiatric problems are related to modifications within the composition of the intestine microbiota (Cryan et al., 2019; Tian et al., 2023). Neurological problems are illnesses of the central and peripheral nervous system that will hurt the mind, spinal wire, cranial and peripheral nerves, autonomous nervous system, nerve roots, and neuromuscular plaque. Quite a few circumstances can result in mind bleeding, together with ailments of the blood vessels, problems brought on by points with nervous system growth, accidents to the spinal wire or mind, and mind tumors (Dugger and Dickson, 2017). All kinds of neurological ailments are related to dysbiosis of the human intestine microbiome (Frank et al., 2007; Bibbo et al., 2017; Gavin et al., 2018; Kasselman et al., 2018; Duan et al., 2019). In distinction, sufferers with neurological ailments and wholesome controls have dramatically totally different microbiota compositions (Sampson et al., 2016; Blacher et al., 2019; Valles-Colomer et al., 2019). Importantly, communication alongside the intestine microbiota–mind axis happens all through life, as seen in ailments of neurodevelopment (for instance, ASD), neurodegeneration (for instance, PD and AD) and habits (for instance, despair and anxiousness) (Determine 1). In response to some current research in animals and people, most of which had been affiliation research, modifications in microbial range are linked to damaging well being outcomes and will trigger alterations within the CNS (Desk 1); these alterations are related to ASD, despair, and anxiousness (Felice and O’Mahony, 2017). Different research have reported extra hyperlinks between the microbiota composition and despair, anxiousness, and ASD (Bercik et al., 2010; Sekirov et al., 2010; Claesson et al., 2012). Thus, the composition of the microbiota, which evolves over time, could have implications in mind operate. On this Perspective, we evaluation current developments within the discipline of neuromicrobiology, notably the hyperlinks between the intestine microbiota and neurological illness. In exploring the function that intestine microbes play in neurological problems, we particularly centered on ASD, AD, PD, despair, and anxiousness problems.
4.1. Alzheimer’s illness
Alzheimer’s illness (AD) impacts roughly 50 million folks globally and is essentially the most frequent reason for progressive persistent and irreversible neurological illness and the commonest sort of dementia in aged people. Because the situation progresses, signs that impair considering and reminiscence can significantly compromise even essentially the most primary day by day actions (Scheltens et al., 2016; Rutsch et al., 2020). Lack of neurons and progressively worsening synaptic dysfunction are signs of AD (Tiraboschi et al., 2004; Alzheimer’s, 2016). AD is brought on by the formation of aggregates of polymerized types of β-amyloid precursor protein (Aβ) in soluble multimeric and/or insoluble amyloid deposits within the mind that set off a cascade of pathological occasions resulting in neurofibrillary tangles, aggregates of hyperphosphorylated tau proteins, formation of neurofibrillary lesions, and in the end dementia (Scheltens et al., 2016). The inflammasome and its merchandise have been related to the pathogenesis of AD since a better expression of IL-1β and IL-18 has been noticed within the microglia, astrocytes, and neurons that encompass Ab plaques or within the plasma of AD sufferers (Malaguarnera et al., 2006; Ojala et al., 2009). Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from AD sufferers additionally confirmed better expression of NLRP3, ASC, caspase-1, caspase-5, IL-1β, and IL-18 (Saresella et al., 2016). Sufferers with tauopathies, that are neurodegenerative ailments characterised by the buildup of aberrant tau protein within the mind, sometimes exhibit elevated ranges of cleaved caspase-1 and ASC in addition to mature IL-1β within the cortex (Ising et al., 2019). Vital proof hyperlinks neuroinflammation brought on by the NLRP3 inflammasome to the event and development of AD. AD pathogenesis has been related to a lot of microbiological causes (Atarashi et al., 2011; Geuking et al., 2011). In comparison with controls, AD sufferers’ stool samples confirmed greater ranges of Bacteroidetes and decrease ranges of Firmicutes and Actinobacteria. Ruminococcaceae, Turicibacteraceae, and Clostridiaceae had been all Firmicutes households the place AD sufferers had decrease abundances (Vogt et al., 2017). In response to a number of research, there could also be mechanistic hyperlinks between the pathophysiology of AD and different microbes, such spirochaetes, fungi, and Chlamydia pneumoniae (Lim et al., 2014; Stojkovi et al., 2020). In current research, the intestine microbiota has additionally been related to the etiology of AD. A metabolite microbiota-derived protein discovered within the cerebral fluid of AD sufferers and related to 2 disease-related biomarkers (phosphorylated tau and phosphorylated tau/A-42) raises the chance that the intestine microbiome performs a job within the etiology of AD (Vogt et al., 2018). When evaluating fecal microbiomes and fecal SCFAs between AD-affected mice and wild-type mice at numerous ages, dramatic will increase in Proteobacteria and Verrucomicrobia and marked decreases in Butyricicoccus and Ruminococcus had been noticed in AD mice, indicating altered microbiota composition and variety. The decreased stage of SCFAs additional signifies alterations in lots of metabolic pathways (Zhang et al., 2017). It was demonstrated that, in comparison with non-transgenic wild-type mice, the intestine microbiota range of the generally utilized APP/PS1 double transgenic mice—which produce a chimeric mouse/human amyloid precursor protein (APP) and a mutant human presenilin 1 (PS1)—was markedly modified. Moreover, in comparison with wholesome management mice with intestine microbiota, germ-free APP/PS1 transgenic animals present a putting discount within the diploma of cerebral β-amyloid pathology (Harach et al., 2017). Bäuerl et al. (2018) reported comparable findings concerning the shift in microbiota composition within the transgenic APP/PS1 mouse mannequin, which reveals elevated numbers of the intently associated inflammatory Erysipelotrichaceae household. Moreover, germ-free APP/PS1 mice confirmed decreased amyloid pathology in comparison with standard mice (Radde et al., 2006).
4.2. Parkinson’s illness
Parkinson’s illness (PD), which impacts greater than 1% of the aged inhabitants and 0.3% of the overall inhabitants worldwide, is the second most prevalent neurodegenerative situation after AD (Tysnes and Storstein, 2017). PD is a progressive neurodegenerative dysfunction characterised by the shortcoming to regulate voluntary actions because of extreme alterations within the operate of the substantia nigra and striatum. The degradation of dopaminergic neurons, the buildup of phosphorylated variations of the neuronal protein α-synuclein (αSyn), mitochondrial malfunction, an extra of reactive oxygen species, and an increase in microglia activation are a few of these alterations (Blandini et al., 2000). Irritation and α-synuclein misfolding are each key pathological mechanisms underlying α-synucleinopathies similar to PD (Lema Tom et al., 2013). The pathogenesis of PD largely relies on the buildup of α-synuclein. The gene for α-synuclein has 5 exons and is situated on chromosome 4q21.3-q22. -synuclein is a protein with 140 amino acids (Mehra et al., 2019). PD signs embrace tremors, bother strolling, a hunched posture, and muscle rigidity. Gastrointestinal points, most steadily constipation, could have an effect on as much as 80% of sufferers with Parkinson’s illness (Chen et al., 2015) and might precede PD diagnoses by a few years (Cersosimo et al., 2013). Rising proof means that intestine dysbiosis contributes to the onset, growth, and development of PD (Zhu et al., 2022). Evaluating sufferers with prodromal and/or clinically identified PD to topics underneath management, we discovered that these sufferers had dysbiosis of the intestine microbiota. The overall group and composition of the intestine microbiota related to PD have been examined utilizing culture-independent high-throughput sequencing methods, and options of the altered microbiota profiles in PD sufferers have been discovered (Zhu et al., 2022). Quite a few earlier research discovered that PD sufferers had greater α-diversity however decrease bacterial range than wholesome folks (Qian et al., 2018; Barichella et al., 2019). Moreover, one examine revealed that there have been variations in β-diversity (between samples) between PD sufferers and controls (Boertien et al., 2019). There was a connection between the medical traits of PD and the decline in bacterial range, which is primarily assessed utilizing α-diversity indexes similar to Shannon and Simpson. In response to a current examine by Heinzel et al. (2021), sure signs of PD could also be notably associated to the prodromal microbiome, together with constipation, doable speedy eye motion sleep habits dysfunction (RBD), bodily inactivity, smoking, urate ranges, and subthreshold parkinsonism. Opposite to intercourse, inactivity, suspected RBD, constipation, and smoking, which had been all related to β-diversity, had been constipation, occupational solvent publicity, and the three beforehand talked about variables. Age and medicines that cut back urate had been linked to each α and β-diversity (Heinzel et al., 2021). Nevertheless, analysis by Plassais et al. (2021) revealed that the intestine microbiome’s α-diversity isn’t a biomarker of PD. The intestinal permeability and irritation brought on by the intestine dysbiosis related to PD, similar to elevated Akkermansia and decreased SCFA-producing micro organism, can facilitate the publicity of the intestinal neural plexus to toxins similar to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) and pesticides, which may trigger irregular α-synuclein fibril aggregation and the event of Lewy our bodies (Hirayama and Ohno, 2021). Regardless of folks with different ailments, folks with PD have a distinct microbiome composition from people who find themselves wholesome or produce other neurological problems (Hasegawa et al., 2015; Keshavarzian et al., 2015; Scheperjans et al., 2015). The intestinal flora in PD sufferers is missing in micro organism that produce SCFAs (largely butyrate), similar to taxa from the Lachnospiraceae household (Hill-Burns et al., 2017; Petrov et al., 2017; Barichella et al., 2019) and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii (Keshavarzian et al., 2015; Unger et al., 2016), which have recognized anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, sure bacterial species, similar to Proteus mirabilis, which causes mice to develop motor impairments, could also be the reason for PD-like illness (Choi et al., 2018). Potential long-term longitudinal microbiome investigations are required to trace the event of the illness and characterize modifications within the microbiome’s taxonomic composition that contributed to or could doubtlessly have outlined the illness state. Uncertainty persists concerning the exact means during which the intestine microbiome could have an effect on PD-related signs.
4.3. A number of sclerosis
A number of sclerosis (MS) is a neurological and inflammatory situation that impacts over two million people worldwide. The primary signs of this situation embrace demyelination, axonal loss, lymphocyte infiltration into the CNS, and neuroinflammation. A number of the medical indicators of MS embrace ataxia, poor coordination, hyperreflexia, stiffness, visible and sensory impairment, fatigue, and cognitive deficits. The vast majority of sufferers undergo a sort of illness generally known as relapsing–remitting, which is characterised by a gradual however vital deterioration in neurological operate and a progressive reappearance of signs (McFarland and Martin, 2007). Most sufferers have mind lesions or lesions within the mind and spinal wire; nevertheless, some folks solely have lesions within the spinal wire (McFarland and Martin, 2007; Rutsch et al., 2020). Microbes (and the substances they secrete or toxins they produce) are a big contributor to the pathophysiology of MS amongst environmental variables (Ronchi et al., 2016; Rutsch et al., 2020). MS sufferers have a distinct microbiome composition than wholesome people (Oleskin and Shenderov, 2016). It’s attention-grabbing to notice that even MS sufferers with lively illness have a distinct microbiome from those that are in remission, whose microbiota is extra akin to that of wholesome controls (Bhargava and Mowry, 2014; Chen et al., 2016; Jangi et al., 2016; Pröbstel and Baranzini, 2018). Better Firmicutes abundance and the absence of Fusobacteria in pediatric MS sufferers had been related to a shorter time to relapse (Tremlett et al., 2017). In comparison with wholesome folks, fecal samples from folks with MS present alterations within the richness of Mycoplana, Dorea, Pseudomonas, Blautia, and Akkermansia species (Mangalam et al., 2017). Attenuated a number of sclerosis-like illness seems in preclinical fashions in GF mice (Lee et al., 2011), and mice receiving the intestinal microbiota of MS sufferers skilled extra extreme experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and had decrease proportions of anti-inflammatory regulatory T cells than mice receiving the microbiome of wholesome people (Berer et al., 2017; Cekanaviciute et al., 2017). The exceptional discovering was that transplanting the intestinal microbes of the MS twins into GF animals, that are genetically predisposed to creating experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), was enough to advertise the sickness in vivo with a considerably greater incidence than transplanting the microbes of the wholesome twins (Berer et al., 2017). Curiously, immune cells from mice that acquired MS-derived samples produced much less IL-10 than cells from animals that had their microbiota from wholesome twins colonize (Berer et al., 2017). In mice inoculated with wholesome fecal samples, the neutralization of IL-10, one of many primary regulatory cytokines, elevated the incidence of illness (Berer et al., 2017). This necessary discovering demonstrated how the human microbiome could produce specific immune system modifications that could be the trigger or consequence of the onset of MS. Uncertainty persists concerning whether or not this function performs a vital half to start with and growth of the illness. In mild of this, there’s appreciable curiosity within the variations within the microbiota of MS sufferers in comparison with wholesome controls.
4.4. Autism spectrum dysfunction
Autism spectrum dysfunction (ASDs) are a set of neurological growth modifications marked by difficulties with social interplay and communication in addition to stereotyped and repetitive conduct (Maiuolo et al., 2021). Constipation, diarrhea, belly ache, flatulence, and intestinal gasoline are widespread amongst folks with ASD issues (23–70%) and are steadily comorbid with gastrointestinal ailments (Mulle et al., 2013). The intestine microbiota mediates the degrees of chemical transmitters similar to GABA, glutamate, oxytocin and serotonin 5-HT advanced in ASD. As a result of low-grade irritation that ASD sufferers expertise, microbial influences on the immune system can also be crucial in figuring out neuroimmune responses in ASD. New applied sciences are being utilized on this quickly increasing discipline of analysis because it turns into apparent how a lot microbial metabolites, together with taurine, bile acid metabolites, SCFAs, and 5-aminovaleric acid, have an effect on ASD signs (Morais et al., 2021). There are few and usually inconsistent ASD research that spotlight the function of the microbiome in pathogenesis. Nevertheless, there are a couple of that spotlight the variations in micro organism similar to Firmicutes, Clostridiales, Prevotella, Bifidobacterium, and Clostridium perfringens, species which might be seen between ASD sufferers and controls (Ho et al., 2020). This ends in a change within the composition of the intestine microbiota, a discount in dietary high quality, and a deficiency in vitamins (Berding and Donovan, 2016). The scientific literature information usually present a discount of Bacteroides with a ratio (% ASD youngster/% management youngsters) equal to 0.71; a discount of Bifidobacterium with a ratio (% ASD youngster/% management youngsters) equal to 0.52; a discount of Escherichia coli with a ratio (%) equal to 0.3; a rise in Faecalibacterium with a ratio (%) equal to 1.32; and a rise in Lactobacillus Clostridium continues to be current in a largely unchanged quantity (Tomova et al., 2015). It’s evident that these neurological problems are accompanied by decreased quantities of helpful micro organism and bigger ranges of lethal micro organism, despite the fact that it can’t be mentioned that sure micro organism are appropriate and related with the beginning of ASD (Iglesias-Vázquez et al., 2020). The intestine microbiota and its metabolites could also be crucially vital within the pathophysiology of ASD (Xu et al., 2019).
4.5. Nervousness and despair
Nervousness and despair are psychological and neurological problems that have an effect on 25% of the worldwide inhabitants. These two pathological circumstances seem like intimately associated: in reality, 85% of individuals with despair and 90% of individuals with anxiousness problems each expertise appreciable anxiousness (Bui and Fava, 2017; Maiuolo et al., 2021). Early and late levels of those pathologies have considerably totally different medical indicators (Groeneweg-Koolhoven et al., 2017). Teenage suicide deaths have elevated in current many years because of the rise in depressed signs (Jorm et al., 2017; Matsumoto et al., 2017; Weinberger et al., 2018; Twenge et al., 2019). The connection between anxiousness and despair and modifications within the stability and composition of the intestine microbiota has been totally investigated (Tognini, 2016; Zhao et al., 2018; Bastiaanssen et al., 2019). Quite a few research have lately centered on the connection between the intestinal microbiota and individuals who undergo from anxiousness and temper problems. Specifically, proof from human analysis has demonstrated that when considering microbial range and taxonomic compositions, there’s steadily some variation within the fecal microbiota between sufferers and wholesome controls. Moreover, it was revealed that sure micro organism had been linked to medical traits and metabolic or inflammatory profiles (Huang et al., 2019). There have been some research on human microbial range, however the majority of them have been unable to indicate a connection between low microbial range and depressive problems (Chen et al., 2014; Naseribafrouei et al., 2014; Zheng et al., 2016). Even if just one examine discovered that people with main depressive dysfunction (MDD) had a better alpha range of the intestine microbiota than wholesome topics, alpha range is the variety of species that may be detected in a microbial ecosystem (Jiang et al., 2015). Evaluating sufferers with MDD to drug-responders with wholesome controls, sufferers with MDD confirmed greater fecal a-diversity (greater ranges of Enterobacteriaceae and Alistipes however decrease ranges of Faecalibacterium). Due to this, the authors reported a hyperlink between Faecalibacterium and the depth of despair signs that was damaging (Jiang et al., 2015). Attention-grabbing modifications within the fecal microbiota have additionally been present in sufferers with anxiousness problems. They noticed that sufferers with generalized anxiousness dysfunction (GAD) had decrease ranges of microbial range and richness, which was correlated with decrease ranges of short-chain fatty acid producers similar to Eubacterium rectale and Fecalibacterium and better ranges of Ruminococcus, Escherichia, Shigella, and Fusobacterium (Jiang et al., 2018). In response to one other examine, probiotics (Bifidobacterium bifidum, Lactobacillus acidophilus, and Lactobacillus casei) administered to MDD sufferers dramatically decreased despair signs when in comparison with a placebo (Akkasheh et al., 2016). The potential of micro organism to provide 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, a metabolite of dopamine, correlates favorably with psychological well being in accordance with fecal metagenomic information, which raises the chance that microbes play a job within the manufacturing of various neuroactive molecules throughout despair than underneath regular circumstances (Valles-Colomer et al., 2019). Lactobacillus rhamnosus releases GABA and prompts GABA receptors within the mind (that’s, GABA Aα2 and GABA B1b receptors) and has been revealed to attenuate despair and anxiety-like behaviors in mice (Bravo et al., 2011).
4.6. Stroke
Stroke is the second main reason for loss of life worldwide. The morbidity and mortality of stroke develop in lots of international locations, contributing to monetary burden and lack of life high quality and thus diminishing the nationwide happiness index. Roughly 15 million folks world wide are victims of a stroke yearly (Feigin et al., 2017). They might happen because of modifications in numerous ailments, similar to cerebrovascular illness, atherosclerosis, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and arterial hypertension (Goldman et al., 2022). Nevertheless, up to now, few research have centered on exploring the correlation between hemorrhagic stroke and the intestine microbiota. GM microflora could also be concerned within the growth of stroke and/or mind accidents (Singh et al., 2016). Research have reported that ischemic stroke accounts for ~80% of all strokes (Sadler et al., 2020), and the intestine microbiota performs a necessary function within the pathogenesis and prognosis of ischemic stroke. A number of research have proven that ischemic stroke considerably modifications the intestine microbiota composition (Ling et al., 2020; Xiang et al., 2020; Xu et al., 2021). Sufferers affected by transient ischemic assault or stroke have been discovered to have opportunistic pathogens similar to Desulfovibrio, Enterobacter, Megasphaera, and Osicillibacter, in addition to fewer helpful or commensal pathogens similar to Bacteroides, Fecalibacterium, and Prevotella (Yin et al., 2015). The abundance of Peptococcaceae and Prevotellaceae is linked to stroke severity (Tiwari et al., 2023). Lately, a preclinical examine additionally prompt that alterations within the intestine microbiota had been related to hemorrhagic transformation (HT). The relative abundance of Proteobacteria and Actinobacteria was considerably elevated in HT rats after experimental stroke, indicating that the intestine microbiota is concerned within the development of ischemic stroke (Huang et al., 2022). The exact function and mechanism of GM within the onset and development of stroke and mind damage stay unknown. Though animal fashions have yielded fascinating outcomes, extra medical analysis is required to totally elucidate the potential of such microbial therapeutic modalities.
5. Conclusion and future instructions
The intestine microbiome is necessary for the host’s well being and illness states, and a lot of the analysis on this topic up to now has solely revealed associations between sure medical problems and bacterial profiles. The intestine microbiota has a considerable impression on each the physiology and pathophysiology of the mind because of the interplay between the gut and neurological system in each instructions. This communication takes place through quite a lot of pathways and includes the vagal nerve, neuroendocrine techniques, neurotransmitters of the CNS, and inflammatory substances. The mentioned proof is accrued from preclinical and medical research on intestine microbiota, its dysbiosis and affiliation with the event and development of neurological dysfunction neurodevelopmental abnormalities to despair and Parkinson’s ailments, even when figuring out their precise mode of motion requires extra analysis, and probiotic complement therapies are helpful with promising therapeutic prospects for neurological ailments. Probiotic complement therapies are efficient instruments with appreciable therapeutic potential for neurological problems, despite the fact that figuring out their exact mode of motion requires extra analysis. Future research on this discipline could present perception into the connection between the microbiota and the CNS and developments within the remedy of neurological problems. The fields of microbiology and neuroscience, in addition to different disciplines, should proceed to work collectively to develop thorough and pertinent strategies to determine mechanisms of motion for outcomes which might be at present observational, together with accountable efforts in translating these discoveries to enhance human well being. World’s main populations are affected by neurological problems, that are anticipated to rise by 13% by 2030. Therefore, there’s an urgency to develop extra dependable biomarkers and possible therapeutic choices in view of the ailments’ pathogenicity. A number of research have proven that the GM is vital for mind growth and performance. In a lot of preclinical and medical analysis research, the GIT microbiome within the GBA has been reviewed for its affiliation with a number of neurological problems, similar to AD, MS, PD, ASD, epilepsy, stroke, and mind damage. Nevertheless, deeper analysis is required to grasp the mechanism of motion and performance of GM in illness pathogenesis and its additional applicability for therapeutic or prognostic functions. Nevertheless, the impression on the GM and the composition of their helpful species within the GBA nonetheless must be elucidated in future research. As a result of many sufferers are given a number of medicines, extra analysis is required to make clear any potential GM–drug interactions. The GM is a brand new line that separates human well being from quite a lot of problems, and future neurotherapeutic analysis will present vital info on this matter. Regardless of current developments in our understanding of the GBA, additional analysis is required to find out whether or not this information might be useful in a medical surroundings. Future research should make clear the underlying hyperlinks between the GM and numerous neurological ailments and decide whether or not treating the microbiota is a secure and efficient course of remedy. It might be doable to develop methods that focus on the intestine microbiota to supply revolutionary, secure, and environment friendly remedy choices for neurodegenerative problems if conventional mind problems are seen comprehensively and now as total circumstances with a big function for the gastrointestinal tract.
Creator contributions
HU and SA: authentic draft preparation and conceptualization. YT, C-qL, YC, LQ, MK, and IH: methodology. HU: evaluation and modifying of the manuscript. KL: supervision. All authors have learn and agreed to the printed model of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank American Journal Consultants (AJEs) for proofreading the article.
Battle of curiosity
The authors declare that the analysis was performed within the absence of any business or monetary relationships that may very well be construed as a possible battle of curiosity.
Writer’s observe
All claims expressed on this article are solely these of the authors and don’t essentially signify these of their affiliated organizations, or these of the writer, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that could be evaluated on this article, or declare that could be made by its producer, isn’t assured or endorsed by the writer.
Abbreviations
GM, intestine microbiota; GBA, gut-brain axis; CNS, central nervous system; AD, Alzheimer’s illness; PD, Parkinson’s illness; GI, digestive tract; MS, a number of sclerosis; ASD, autism spectrum dysfunction; ENS, enteric nervous system; GBA, gut-brain axis; HPA, hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; GABA, gamma-aminobutyric acid; EECs, enteroendocrine cells; GLP1, glucagon-like peptide 1; 5-HT, 5-hydroxytryptamine; LPS, T lipopolysaccharide; LCFAs, long-chain fatty acids; TAMO, trimethylamine-N-oxide; PSA, polysaccharide A; MAMPs, microbial-associated molecular patterns; GPCRs, G protein-coupled receptors; PYY, peptide YY; GLP1, glucagon-like peptide 1; FFARs, free fatty acid receptors; BBB, blood–mind barrier; TNF, tumor necrosis issue; DCs, dendritic cells; HDAC, histone deacetylase; CXCL1, CXC motif chemokine ligand 1; CXCL8, CXC motif ligand 8; FFAR2, free fatty acid receptor 2; GPR41, G protein-coupled receptor 41; FFAR3, free fatty acid receptor 3; PBMCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells; APP, amyloid precursor protein; PS1, presenilin 1; αSyn, α-synuclein; GAD, generalized anxiousness dysfunction; EAE, experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis.
References
Abdel-Haq, R., Schlachetzki, J. C. M., Glass, C. Okay., and Mazmanian, S. Okay. (2019). Microbiome microglia connections through the gutâ mind axis. J. Exp. Med. 216, 41–59. doi: 10.1084/jem.20180794
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Adams, J. B., Johansen, L. J., Powell, L. D., Quig, D., and Rubin, R. A. (2011). Gastrointestinal flora and gastrointestinal standing in youngsters with autism comparisons to typical youngsters and correlation with autism severity. BMC Gastroenterol. 11, 1–13. doi: 10.1186/1471-230X-11-22
Aizawa, E., Tsuji, H., Asahara, T., Takahashi, T., Teraishi, T., Yoshida, S., et al. (2016). Attainable affiliation of Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus within the intestine microbiota of sufferers with main depressive dysfunction. J. Have an effect on. Disord. 202, 254–257. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2016.05.038
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Akbari, E., Asemi, Z., Daneshvar Kakhaki, R., Bahmani, F., Kouchaki, E., Tamtaji, O. R., et al. (2016). Impact of probiotic supplementation on cognitive operate and metabolic standing in Alzheimer’s illness: a randomized, double-blind and managed trial. Entrance. Getting older Neurosci. 8:256. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2016.00256
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Akkasheh, G., Kashani-Poor, Z., Tajabadi-Ebrahimi, M., Jafari, P., Akbari, H., Taghizadeh, M., et al. (2016). Medical and metabolic response to probiotic administration in sufferers with main depressive dysfunction: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Vitamin 32, 315–320. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2015.09.003
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Aktar, R., Parkar, N., Stentz, R., Baumard, L., Parker, A., Goldson, A., et al. (2020). Human resident intestine microbe Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron regulates colonic neuronal innervation and neurogenic operate. Intestine Microbes 11, 1745–1757. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1766936
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Al Omran, Y., and Aziz, Q. (2014). The brain-gut axis in well being and illness. Microbial Endocrinol, 817, 135–153. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0897-4_6
Alvarez, E., Martinez, M. D., Roncero, I., Chowen, J. A., Garcia-Cuartero, B., Gispert, J. D., et al. (2005). The expression of GLP1 receptor mRNA and protein permits the impact of GLP-1 on glucose metabolism within the human hypothalamus and brainstem. J. Neurochem. 92, 798–806. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02914.x
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Aresti Sanz, J., and El Aidy, S. (2019). Microbiota and intestine neuropeptides: a twin motion of antimicrobial exercise and neuroimmune response. Psychopharmacology 236, 1597–1609. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-05224-0
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Askarova, S., Umbayev, B., Masoud, A. R., Kaiyrlykyzy, A., Safarova, Y., Tsoy, A., et al. (2020). The hyperlinks between the intestine microbiome, growing older, fashionable life-style and Alzheimer’s illness. Entrance. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 10:104. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00104
Atarashi, Okay., Tanoue, T., Shima, T., Imaoka, A., Kuwahara, T., Momose, Y., et al. (2011). Induction of colonic regulatory T cells by indigenous Clostridium species. Science 331, 337–341. doi: 10.1126/science.1198469
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Baj, A., Moro, E., Bistoletti, M., Orlandi, V., Crema, F., and Giaroni, C. (2019). Glutamatergic signaling alongside the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 20:1482. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061482
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Barichella, M., Severgnini, M., Cilia, R., Cassani, E., Bolliri, C., Caronni, S., et al. (2019). Unraveling intestine microbiota in Parkinson’s illness and atypical parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. 34, 396–405. doi: 10.1002/mds.27581
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Bastiaanssen, T. F. S., Cowan, C. S. M., Claesson, M. J., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2019). Making sense of the microbiome in psychiatry. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 22, 37–52. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyy067
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Bäuerl, C., Collado, M. C., Diaz Cuevas, A., Viña, J., and Martínez, G. P. (2018). Shifts in intestine microbiota composition in an APP/PSS 1 transgenic mouse mannequin of Alzheimer’s illness throughout lifespan. Lett Appl Microbiol. 66, 464–471. doi: 10.1111/lam.12882
Bercik, P., Denou, E., Collins, J., Jackson, W., Lu, J., Jury, J., et al. (2011a). The intestinal microbiota have an effect on central ranges of brain-derived neurotropic issue and habits in mice. Gastroenterology 141:e593, 599–609.e3. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2011.04.052
Bercik, P., Park, A. J., Sinclair, D., Khoshdel, A., Lu, J., Huang, X., et al. (2011b). The anxiolytic impact of Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 includes vagal pathways for gut-brain communication. J Gastrointestinal Motility 23, 1132–1139. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2011.01796.x
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Bercik, P., Verdu, E. F., Foster, J. A., Macri, J., Potter, M., Huang, X., et al. (2010). Power gastrointestinal irritation induces anxiety-like habits and alters central nervous system biochemistry in mice. Gastroenterology 139:e2101. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.063
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Berding, Okay., and Donovan, S. M. (2016). Microbiome and diet in autism spectrum dysfunction: present information and analysis wants. Nutr. Rev. 74, 723–736. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuw048
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Berer, Okay., Gerdes, L. A., Cekanaviciute, E., Jia, X., Xiao, L., Xia, Z., et al. (2017). Intestine microbiota from a number of sclerosis sufferers allows spontaneous autoimmune encephalomyelitis in mice. PNAS 114, 10719–10724. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711233114
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Bhargava, P., and Mowry, E. M. (2014). Intestine microbiome and a number of sclerosis. Curr. Neurol. Neurosci. Rep. 14, 1–8. doi: 10.1007/s11910-014-0492-2
Bhattarai, Y., Si, J., Pu, M., Ross, O. A., McLean, P. J., Until, L., et al. (2021). Position of intestine microbiota in regulating gastrointestinal dysfunction and motor signs in a mouse mannequin of Parkinson’s illness. Intestine Microbes 13:1866974. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1866974
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Bibbo, S., Dore, M. P., Pes, G. M., Delitala, G., and Delitala, A. P. (2017). Is there a job for intestine microbiota in sort 1 diabetes pathogenesis? Ann. Med. 49, 11–22. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2016.1222449
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Blacher, E., Bashiardes, S., Shapiro, H., Rothschild, D., Mor, U., Dori-Bachash, M., et al. (2019). Potential roles of intestine microbiome and metabolites in modulating ALS in mice. Nature 572, 474–480. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1443-5
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Blandini, F., Nappi, G., Tassorelli, C., and Martignoni, E. (2000). Purposeful modifications of the basal ganglia circuitry in Parkinson’s illness. Prog. Neurobiol. 62, 63–88. doi: 10.1016/S0301-0082(99)00067-2
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Boertien, J. M., Pereira, P. A. B., Aho, V. T. E., and Scheperjans, F. (2019). Rising comparability and utility of intestine microbiome research in Parkinson ‘s illness: a scientific evaluation. J. Parkinsons Dis. 9, S297–S312. doi: 10.3233/JPD-191711
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Braniste, V., al-Asmakh, M., Kowal, C., Anuar, F., Abbaspour, A., Tóth, M., et al. (2014). The intestine microbiota influences blood–mind barrier permeability in mice. Sci. Transl. Med. 6:263ra158. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3009759
Bravo, J. A., Forsythe, P., Chew, M. V., Escaravage, E., Savignac, H. M., Dinan, T. G., et al. (2011). Ingestion of Lactobacillus pressure regulates emotional habits and central GABA receptor expression in a mouse through the vagus nerve. PNAS 108, 16050–16055. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102999108
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Brun, P., Giron, M. C., Qesari, M., Porzionato, A., Caputi, V., Zoppellaro, C., et al. (2013). Toll-like receptor 2 regulates intestinal irritation by controlling integrity of the enteric nervous system. Gastroenterology 145, 1323–1333. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.08.047
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Bu, X. L., Yao, X. Q., Jiao, S. S., Zeng, F., Liu, Y. H., Xiang, Y., et al. (2015). A examine on the affiliation between infectious burden and Alzheimer’s illness. Eur. Neurol. 22, 1519–1525. doi: 10.1111/ene.12477
Burberry, A., Wells, M. F., Limone, F., Couto, A., Smith, Okay. S., Keaney, J., et al. (2020). C9orf72 suppresses systemic and neural irritation induced by intestine micro organism. Nature 582, 89–94. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2288-7
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Capuron, L., and Miller, A. H. (2011). Immune system to mind signaling: neuropsychopharmacological implications. Pharm. Therap. 130, 226–238. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2011.01.014
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Carabotti, M., Scirocco, A., Maselli, M. A., and Severi, C. (2015). The gut-brain axis: interactions between enteric microbiota, central and enteric nervous techniques. Annals Gastroenterol 28:203.
Cekanaviciute, E., Yoo, B. B., Runia, T. F., Debelius, J. W., Singh, S., Nelson, C. A., et al. (2017). Intestine micro organism from a number of sclerosis sufferers modulate human T cells and exacerbate signs in mouse fashions. PNAS 114, 10713–10718. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1711235114
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Cersosimo, M. G., Raina, G. B., Pecci, C., Pellene, A., Calandra, C. R., Gutiérrez, C., et al. (2013). Gastrointestinal manifestations in Parkinson’s illness: prevalence and prevalence earlier than motor signs. J. Neurol 260, 1332–1338. doi: 10.1007/s00415-012-6801-2
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Chen, J., Chia, N., Kalari, Okay. R., Yao, J. Z., Novotna, M., Paz Soldan, M. M., et al. (2016). A number of sclerosis sufferers have a definite intestine microbiota in comparison with wholesome controls. Sci. Rep. 6, 1–10. doi: 10.1038/srep28484
Chen, Y., Xu, J., and Chen, Y. (2021). Regulation of neurotransmitters by the intestine microbiota and results on cognition in neurological problems. Vitamins 13:2099. doi: 10.3390/nu13062099
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Chen, H., Zhao, E. J., Zhang, W., Lu, Y., Liu, R., Huang, X., et al. (2015). Meta-analyses on prevalence of chosen Parkinson’s nonmotor signs earlier than and after prognosis. Transl. Neurodegen. 4, 1–8. doi: 10.1186/2047-9158-4-1
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Chen, J., Zheng, P., Liu, Y., Zhong, X., Wang, H., Guo, Y., et al. (2014). Intercourse variations in intestine microbiota in sufferers with main depressive dysfunction. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Deal with. 14:647.
Choi, J. G., Kim, N., Ju, I. G., Eo, H., Lim, S. M., Jang, S. E., et al. (2018). Oral administration of Proteus mirabilis damages dopaminergic neurons and motor capabilities in mice. Sci. Rep. 8, 1–13. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19646-x
Claesson, M. J., Jeffery, I. B., Conde, S., Energy, S. E., O’Connor, E. M., Cusack, S., et al. (2012). Intestine microbiota composition correlates with food regimen and well being within the aged. Nature 488, 178–184. doi: 10.1038/nature11319
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Clarke, G., Grenham, S., Scully, P., Fitzgerald, P., Moloney, R. D., Shanahan, F., et al. (2013). The microbiome-gut-brain axis throughout adolescence regulates the hippocampal serotonergic system in a sex-dependent method. Molec Psychiat 18, 666–673. doi: 10.1038/mp.2012.77
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Corrêa-Oliveira, R., Fachi, J. L., Vieira, A., Sato, F. T., and Vinolo, M. A. (2016). Regulation of immune cell operate by short-chain fatty acids. CTI 5:e73. doi: 10.1038/cti.2016.17
Cryan, J. F., O’Riordan, Okay. J., Cowan, C. S. M., Sandhu, Okay. V., Bastiaanssen, T. F. S., Boehme, M., et al. (2019). The microbiota-gut-brain axis. Physiol. Rev. 99, 1877–2013. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00018.2018
Cryan, J. F., O’Riordan, Okay. J., Sandhu, Okay., Peterson, V., and Dinan, T. G. (2020). The intestine microbiome in neurological problems. Lancet Neurol. 19, 179–194. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30356-4
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Dalile, B., Van Oudenhove, L., Vervliet, B., and Verbeke, Okay. (2019). The function of short-chain fatty acids in microbiota intestine mind communication. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 16, 461–478. doi: 10.1038/s41575-019-0157-3
De la Fuente-Nunez, C., Meneguetti, B. T., Franco, O. L., and Lu, T. Okay. (2018). Neuromicrobiology: how microbes affect the mind. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 9, 141–150. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00373
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
De Lartigue, G., de La Serre, C. B., and Raybould, H. E. (2011). Vagal afferent neurons in excessive fats diet-induced weight problems; intestinal microflora, intestine irritation and cholecystokinin. Physiol. Behav. 105, 100–105. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.02.040
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
De Palma, G., Collins, S. M., Bercik, P., and Verdu, E. F. (2014). The microbiota-gut-brain axis in gastrointestinal problems: confused bugs, confused mind or each? J Physiol (London) 592, 2989–2997. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.273995
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
de Vadder, F., Grasset, E., Mannerås Holm, L., Karsenty, G., Macpherson, A. J., Olofsson, L. E., et al. (2018). Intestine microbiota regulates maturation of the grownup enteric nervous system through enteric serotonin networks. PNAS 115, 6458–6463. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1720017115
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Deidda, G., and Biazzo, M. (2021). Intestine and Mind: Investigating physiological and pathological interactions between microbiota and mind to realize new therapeutic avenues for mind ailments. Entrance. Neurosci 15:753915. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.753915
Desbonnet, L., Garrett, L., Clarke, G., Kiely, B., Cryan, J. F., and Dinan, T. G. (2010). Results of the probiotic Bifidobacterium infantis within the maternal separation mannequin of despair. Neurosci. J. 170, 1179–1188. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.08.005
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Dinan, T. G., Stilling, R. M., Stanton, C., and Cryan, J. F. (2015). Collective unconscious: how intestine microbes form human habits. J. Psychiatr. Res. 63, 1–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2015.02.021
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Duan, Y., Prasad, R., Feng, D., Beli, E., Li Calzi, S., Longhini, A. L. F., et al. (2019). Bone marrow-derived cells restore purposeful integrity of the intestine epithelial and vascular limitations in a mannequin of diabetes and ACE2 deficiency. Circ. Res. 125, 969–988. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.119.315743
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Duvallet, C., Gibbons, S. M., Gurry, T., Irizarry, R. A., and Alm, E. J. (2017). Meta-analysis of intestine microbiome research identifies disease-specific and shared responses. Nat. Commun. 8, 1–10. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01973-8
El Aidy, S., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2014). Immune modulation of the brain-gut-microbe axis. Entrance Media :146.
Elias, C. F., Aschkenasi, C., Lee, C., Kelly, J., Ahima, R. S., Bjorbæk, C., et al. (1999). Leptin differentially regulates NPY and POMC neurons projecting to the lateral hypothalamic space. Neuron 23, 775–786. doi: 10.1016/S0896-6273(01)80035-0
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Engelhardt, B., Carare, R. O., Bechmann, I., Laman, J. D., and Weller, R. O. (2016). Vascular, glial, and lymphatic immune gateways of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 132, 317–338. doi: 10.1007/s00401-016-1606-5
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Engelhardt, B., and Liebner, S. (2014). Novel insights into the event and upkeep of the blood- mind barrier. Cell Tissue Res. 355, 687–699. doi: 10.1007/s00441-014-1811-2
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Erny, D., Hrabě de Angelis, A. L., Jaitin, D., Wieghofer, P., Staszewski, O., David, E., et al. (2015). Host microbiota consistently management maturation and performance of microglia within the CNS. Nat. Neurosci. 18, 965–977. doi: 10.1038/nn.4030
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Feng, Y., Zhou, Z., Zheng, C., Feng, F., Xie, F., and Wu, Z. (2020). Interleukin 17-producing´ T-cell induced demyelination of the mind in angiostrongylus cantonensis an infection.
Flowers, S. A., and Ellingrod, V. L. (2015). The microbiome in psychological well being: potential contribution of intestine microbiota in illness and pharmacotherapy administration. Pharmacotherapy 35, 910–916.
Fond, G., Boukouaci, W., Chevalier, G., Regnault, A., Eberl, G., Hamdani, N., et al. (2015). The “psychomicrobiotic”: Focusing on microbiota in main psychiatric problems: a scientific evaluation. Pathol. Biol. 63, 35–42. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2014.10.003
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Forsythe, P., Bienenstock, J., and Kunze, W. A. (2014). Vagal pathways for microbiome-brain-gut axis communication. Microbial Endocrinol. 817, 115–133. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0897-4_5
Frank, D. N., St. Amand, A. L., Feldman, R. A., Boedeker, E. C., Harpaz, N., and Tempo, N. R. (2007). Molecular-phylogenetic characterization of microbial neighborhood imbalances in human inflammatory bowel ailments. PNAS 104, 13780–13785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0706625104
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Frick, L. R., Williams, Okay., and Pittenger, C. (2013). Microglial dysregulation in psychiatric illness. Clin. Develop. Immunol. 2013:608654. doi: 10.1155/2013/608654
Gavin, P. G., Mullaney, J. A., Bathroom, D., Cao, Okay. L., Gottlieb, P. A., Hill, M. M., et al. (2018). Intestinal metaproteomics reveals host-microbiota interactions in topics in danger for sort 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 41, 2178–2186. doi: 10.2337/dc18-0777
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Geuking, M. B., Cahenzli, J., Lawson, M. A. E., Ng, D. C. Okay., Slack, E., Hapfelmeier, S. M., et al. (2011). Intestinal bacterial colonization induces mutualistic regulatory T-cell responses. Immunity 34, 794–806. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2011.03.021
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Goldman, L., Siddiqui, E. M., Khan, A., Jahan, S., Rehman, M. U., Mehan, S., et al. (2022). Understanding acquired mind damage: a evaluation. Biomedicine 10:2167. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10092167
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Groeneweg-Koolhoven, I., Ploeg, M., Comijs, H. C., WJH Penninx, B., van der Mast, R. C., Schoevers, R. A., et al. (2017). Apathy in early and late-life despair. J. Have an effect on. Disord. 223, 76–81. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2017.07.022
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Gubert, C., Kong, G., Renoir, T., and Hannan, A. J. (2020). Train, food regimen and stress as modulators of intestine microbiota: Implications for neurodegenerative ailments. Neurobiol. Dis. 134:104621. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.104621
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Harach, T., Marungruang, N., Duthilleul, N., Cheatham, V., Mc Coy, Okay. D., Frisoni, G., et al. (2017). Discount of Abeta amyloid pathology in APPPS1 transgenic mice within the absence of intestine microbiota. Sci. Rep. 7, 1–15. doi: 10.1038/srep41802
Harms, A. S., Thome, A. D., Yan, Z., Schonhoff, A. M., Williams, G. P., Li, X., et al. (2018). Peripheral monocyte entry is required for alpha-synuclein induced irritation and neurodegeneration in a mannequin of Parkinson illness. Exp. Neurol. 300, 179–187. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.11.010
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Hasegawa, S., Goto, S., Tsuji, H., Okuno, T., Asahara, T., Nomoto, Okay., et al. (2015). Intestinal dysbiosis and lowered serum lipopolysaccharide-binding protein in Parkinson’s illness. PLoS One 10:e0142164. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142164
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Heijtz, R. D., Wang, S., Anuar, F., Qian, Y., Björkholm, B., Samuelsson, A., et al. (2011). Regular intestine microbiota modulates mind growth and habits. PNAS 108, 3047–3052. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1010529108
Heinzel, S., Aho, V. T. E., Suenkel, U., von Thaler, A. Okay., Schulte, C., and Deuschle, C. (2021). Intestine microbiome signatures of threat and prodromal markers of Parkinson illness. Ann. Neurol. 90, E1–E12. doi: 10.1002/ana.26128
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Hill-Burns, E. M., Debelius, J. W., Morton, J. T., Wissemann, W. T., Lewis, M. R., Wallen, Z. D., et al. (2017). Parkinson’s illness and Parkinson’s illness medicines have distinct signatures of the intestine microbiome. Mov. Disord. 32, 739–749. doi: 10.1002/mds.26942
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Ho, L. Okay. H., Tong, V. J. W., Syn, N., Nagarajan, N., Tham, E. H., Tay, S. Okay., et al. (2020). Intestine microbiota modifications in youngsters with autism spectrum dysfunction: a scientific evaluation. Intestine Pathogens 12, 1–18. doi: 10.1186/s13099-020-0346-1
Hsiao, E. Y., McBride, S. W., Hsien, S., Sharon, G., Hyde, E. R., McCue, T., et al. (2013). Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities related to neurodevelopmental problems. Cells 155, 1451–1463. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.024
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Huang, Q., Di, L., Yu, F., Feng, X., Liu, Z., Wei, M., et al. (2022). Alterations within the intestine microbiome with hemorrhagic transformation in experimental stroke. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 28, 77–91. doi: 10.1111/cns.13736
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Huang, T. T., Lai, J. B., Du, Y. L., Xu, Y., Ruan, L. M., and Hu, S. H. (2019). Present understanding of intestine microbiota in temper problems: an replace of human research. Entrance. Genet. 10:98. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2019.00098
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Huang, C., Wang, J., Hu, W., Wang, C., Lu, X., Tong, L., et al. (2016). Identification of purposeful farnesoid X receptors in mind neurons. FEBS Lett. 590, 3233–3242. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.12373
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Hube, F., Lietz, U., Igel, M., Jensen, P. B., Tornqvist, H., Joost, H. G., et al. (1996). Distinction in leptin mRNA ranges between omental and subcutaneous belly adipose tissue from overweight people. Horm. Metab. Res. 28, 690–693. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-979879
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Iannone, L. F., Preda, A., Blottière, H. M., Clarke, G., Albani, D., Belcastro, V., et al. (2019). Microbiota-gut mind axis involvement in neuropsychiatric problems. Professional. Rev. Neurother. 19, 1037–1050. doi: 10.1080/14737175.2019.1638763
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Iglesias-Vázquez, L., Van Ginkel Riba, G., Arija, V., and Canals, J. (2020). Composition of intestine microbiota in youngsters with autism spectrum dysfunction: a scientific evaluation and meta-analysis. Vitamins 12:792. doi: 10.3390/nu12030792
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Isacson, R., Nielsen, E., Dannaeus, Okay., Bertilsson, G., Patrone, C., Zachrisson, O., et al. (2011). The glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist exendin-4 improves reference reminiscence efficiency and reduces immobility within the compelled swim check. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 650, 249–255. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.10.008
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Ising, C., Venegas, C., Zhang, S., Scheiblich, H., Schmidt, S. V., Vieira-Saecker, A., et al. (2019). NLRP3 inflammasome activation drives tau pathology. Nature 575, 669–673. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1769-z
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Jangi, S., Gandhi, R., Cox, L. M., Li, N., von Glehn, F., Yan, R., et al. (2016). Alterations of the human intestine microbiome in a number of sclerosis. Nat. Commun. 7, 1–11. doi: 10.1038/ncomms12015
Jasarevic, E., Howerton, C. L., Howard, C. D., and Bale, T. L. (2015). Alterations within the vaginal microbiome by maternal stress are related to metabolic reprogramming of the offspring intestine and mind. Endocrinology 156, 3265–3276. doi: 10.1210/en.2015-1177
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Jenkins, T. A., Nguyen, J. C. D., Polglaze, Okay. E., and Bertrand, P. P. (2016). Affect of tryptophan and serotonin on temper and cognition with a doable function of the gut-brain axis. Vitamins 8:56. doi: 10.3390/nu8010056
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Jiang, H., Ling, Z., Zhang, Y., Mao, H., Ma, Z., Yin, Y., et al. (2015). Altered fecal microbiota composition in sufferers with main depressive dysfunction. Mind Behav. Immun. 48, 186–194. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2015.03.016
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Jiang, H., Zhang, X., Yu, Z., Zhang, Z., Deng, M., Zhao, J., et al. (2018). Altered intestine microbiota profile in sufferers with generalized anxiousness dysfunction. J. Psychiatr. Res. 104, 130–136. doi: 10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.07.007
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Jorm, A. F., Patten, S. B., Brugha, T. S., and Mojtabai, R. (2017). Has elevated provision of remedy decreased the prevalence of widespread psychological problems? Overview of the proof from 4 international locations. World Psychiatry 16, 90–99. doi: 10.1002/wps.20388
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Kabouridis, P. S., Lasrado, R., McCallum, S., Chng, S. H., Snippert, H. J., Clevers, H., et al. (2015). Microbiota controls the homeostasis of glial cells within the intestine lamina propria. Neuron 85, 289–295. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.12.037
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Kang, D. W., Park, J. G., Ilhan, Z. E., Wallstrom, G., LaBaer, J., Adams, J. B., et al. (2013). Diminished incidence of Prevotella and different fermenters in intestinal microflora of autistic youngsters. PLoS One 8:e68322. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0068322
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Kasselman, L. J., Vernice, N. A., DeLeon, J., and Reiss, A. B. (2018). The intestine microbiome and elevated cardiovascular threat in weight problems and autoimmunity. Atherosclerosis 271, 203–213. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2018.02.036
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Katsurada, Okay., and Yada, T. (2016). Neural results of gut-and mind derived glucagonâ like peptideâ-1 and its receptor agonist. J. Diabetes Investig. 7, 64–69. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12464
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Kennedy, P. J., Cryan, J. F., Dinan, T. G., and Clarke, G. (2017). Kynurenine pathway metabolism and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Neuropharmacology 112, 399–412. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2016.07.002
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Keshavarzian, A., Inexperienced, S. J., Engen, P. A., Voigt, R. M., Naqib, A., and Forsyth, C. B. (2015). Colonic bacterial composition in Parkinson’s illness. Transfer. Disord. 30, 1351–1360. doi: 10.1002/mds.26307
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Kimura, I., Inoue, D., Maeda, T., Hara, T., Ichimura, A., Miyauchi, S., et al. (2011). Brief-chain fatty acids and ketones straight regulate sympathetic nervous system through G protein-coupled receptor 41 (GPR41). PNAS 108, 8030–8035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1016088108
Knight, R., Vrbanac, A., Taylor, B. C., Aksenov, A., Callewaert, C., Debelius, J., et al. (2018). Greatest practices for analysing microbiomes. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 16, 410–422. doi: 10.1038/s41579-018-0029-9
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Koda, S., Date, Y., Murakami, N., Shimbara, T., Hanada, T., and Toshinai, Okay. (2005). The function of the vagal nerve in peripheral PYY3â€36-induced feeding discount in rats. Endocrinology 146, 2369–2375. doi: 10.1210/en.2004-1266
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Larraufie, P., Martin-Gallausiaux, C., Lapaque, N., Dore, J., Gribble, F. M. R., Reimann, F., et al. (2018). SCFAs strongly stimulate PYY manufacturing in human enteroendocrine cells. Sci. Rep. 8:74. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-18259-0
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Lee, Y. Okay., Menezes, J. S., Umesaki, Y., and Mazmanian, S. Okay. (2011). Proinflammatory T-cell responses to intestine microbiota promote experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. PNAS 108, 4615–4622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1000082107
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Lema Tom, C. M., Tyson, T., Rey, N. L., Grathwohl, S., Britschgi, M., and Brundin, P. (2013). Irritation and α-synuclein’s prion-like habits in Parkinson’s illness—is there a hyperlink. Mol. Neurobiol. 47, 561–574. doi: 10.1007/s12035-012-8267-8
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Lim, C., Hammond, C. J., Hingley, S. T., and Balin, B. J. (2014). Chlamydia pneumoniae an infection of monocytes in vitro stimulates innate and adaptive immune responses related to these in Alzheimer’s illness. J. Neuroinflammation 11, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12974-014-0217-0
Ling, Y., Gong, T., Zhang, J., Gu, Q., Gao, X., Weng, X., et al. (2020). Intestine microbiome signatures are biomarkers for cognitive impairment in sufferers with ischemic stroke. Entrance. Getting older Neurosci. 12:511562. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2020.511562
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Lyte, M. (2014a). Microbial endocrinology and the microbiota-gut-brain axis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 817, 3–24. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-0897-4_1
Ma, Q., Xing, C., Lengthy, W., Wang, H. Y., Liu, Q., and Wang, R. F. (2019). Influence of microbiota on central nervous system and neurological ailments: the gut-brain axis. J. Neuroinflammation 16, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/s12974-019-1434-3
Maiuolo, J., Gliozzi, M., Musolino, V., Carresi, C., Scarano, F., Nucera, S., et al. (2021). The contribution of intestine microbiota- mind axis within the growth of mind problems. Entrance. Neurosci. 15:616883. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.616883
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Malaguarnera, L., Motta, M., Di Rosa, M., Anzaldi, M., and Malaguarnera, M. (2006). Interleukin†18 and remodeling progress issue beta 1 plasma ranges in Alzheimer’s illness and vascular dementia. Neuropathology 26, 307–312. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1789.2006.00701.x
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Mangalam, A., Shahi, S. Okay., Luckey, D., Karau, M., Marietta, E., Luo, N., et al. (2017). Human gut-derived commensal micro organism suppress CNS inflammatory and demyelinating illness. Cell Rep. 20, 1269–1277. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.07.031
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Manicassamy, S., Reizis, B., Ravindran, R., Nakaya, H., and Salazar-Gonzalez, R. M. (2010). Activation of beta-catenin in dendritic cells regulates immunity versus tolerance within the gut. Science 329, 849–853. doi: 10.1126/science.1188510
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Mao, Y. Okay., Kasper, D. L., Wang, B., Forsythe, P., Bienenstock, J., and Kunze, W. A. (2013). Bacteroides fragilis polysaccharide A is critical and enough for acute activation of intestinal sensory neurons. Nat. Commun. 4, 1–10. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2478
Matsumoto, M., Ooga, T., Kibe, R., Aiba, Y., Koga, Y., and Benno, Y. (2017). Colonic absorption of low-molecular-weight metabolites influenced by the intestinal microbiome: a pilot examine. PLoS One 12:e0169207. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0169207
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
McClean, P. L., Parthsarathy, V., Faivre, E., and Halscher, C. (2011). The diabetes drug liraglutide prevents degenerative processes in a mouse mannequin of Alzheimer’s illness. J. Neurosci. 31, 6587–6594. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0529-11.2011
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Mehra, S., Sahay, S., and Maji, S. Okay. (2019). α-Synuclein misfolding and aggregation: Implications in Parkinson’s illness pathogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Most cancers 1867, 890–908. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2019.03.001
Messaoudi, M. L., Lalonde, R., Violle, N., Javelot, H., Desor, D., and Nejdi, A. (2011). Evaluation of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human topics. Br. J. Nutr. 105, 755–764. doi: 10.1017/S0007114510004319
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Miller, A. H., and Raison, C. L. (2016). The function of irritation in despair: from evolutionary crucial to fashionable remedy goal. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 16, 22–34. doi: 10.1038/nri.2015.5
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Mittal, R., Debs, L. H., Patel, A. P., Nguyen, D., Patel, Okay., O’Connor, G., et al. (2017). Neurotransmitters: the vital modulators regulating gut-brain axis. J. Cell. Physiol. 232, 2359–2372. doi: 10.1002/jcp.25518
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Mohammadi, A. A., Jazayeri, S., Khosravi-Darani, Okay., Solati, Z., Mohammadpour, N., Asemi, Z., et al. (2016). The consequences of probiotics on psychological well being and hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in petrochemical employees. Nutr. Neurosci. 19, 387–395. doi: 10.1179/1476830515Y.0000000023
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Montiel-Castro, A. J., Gonzlez-Cervantes, R. M., Bravo-Ruiseco, G., and Pacheco-Lapez, G. (2013). The microbiota-gut-brain axis: neurobehavioral correlates, well being and sociality. Entrance. Integr. Neurosci. 7:70. doi: 10.3389/fnint.2013.00070
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Morais, L. H., Schreiber, H. L., and Mazmanian, S. Okay. (2021). The intestine microbiota-brain axis in habits and mind problems. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 19, 241–255. doi: 10.1038/s41579-020-00460-0
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Morimoto, R., Satoh, F., Murakami, O., Totsune, Okay., Saruta, M., Suzuki, T., et al. (2008). Expression of peptide YY in human mind and pituitary tissues. Vitamin 24, 878–884. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2008.06.011
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Morris, G., Berk, M., Carvalho, A., Caso, J. R., Sanz, Y., Walder, Okay., et al. (2017). The function of the microbial metabolites together with tryptophan catabolites and short-chain fatty acids within the pathophysiology of immune-inflammatory and neuroimmune illness. Mol. Neurobiol. 54, 4432–4451. doi: 10.1007/s12035-016-0004-2
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Mulle, J. G., Sharp, W. G., and Cubells, J. F. (2013). The intestine microbiome: a brand new frontier in autism analysis. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 15, 1–9. doi: 10.1007/s11920-012-0337-0
Muller, P. A., Schneeberger, M., Matheis, F., Wang, P., Kerner, Z., Ilanges, A., et al. (2020). Microbiota modulate sympathetic neurons through a gut-brain circuit. Nature 583, 441–446. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-2474-7
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Naseribafrouei, A., Hestad, Okay., Avershina, E., Sekelja, M., Linlkken, A., and Wilson, R. (2014). Correlation between the human fecal microbiota and despair. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 26, 1155–1162. doi: 10.1111/nmo.12378
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Nohr, M. Okay., Egerod, Okay. L., Christiansen, S. H., Gille, A., Offermanns, S., and Schwartz, T. W. (2015). Expression of the short-chain fatty acid receptor GPR41/FFAR3 in autonomic and somatic sensory ganglia. Neuroscience 290, 126–137. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2015.01.040
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Nohr, M. Okay., Pedersen, M. H., Gille, A., Egerod, Okay. L., Engelstoft, M. S., and Husted, A. S. (2013). GPR41/FFAR3 and GPR43/FFAR2 as cosensors for short-chain fatty acids in enteroendocrine cells vs FFAR3 in enteric neurons and FFAR2 in enteric leukocytes. Endocrinology 154, 3552–3564. doi: 10.1210/en.2013-1142
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Nonaka, N., Shioda, S., Niehoff, M. L., and Banks, W. A. (2003). Characterization of blood–mind barrier permeability to PYY3-36 within the mouse. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Th. 306, 948–953. doi: 10.1124/jpet.103.051821
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Obata, Y., Castaño, Á., Boeing, S., Bon-Frauches, A. C., Fung, C., Fallesen, T., et al. (2020). Neuronal programming by microbiota regulates intestinal physiology. Nature 578, 284–289. doi: 10.1038/s41586-020-1975-8
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Ogbonnaya, E. S., Clarke, G., Shanahan, F., Dinan, T. G., Cryan, J. F. O., and Leary, O. F. (2015). Grownup hippocampal neurogenesis is regulated by the microbiome. Biol. Psychiatry 78, e7–e9. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.12.023
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Ojala, J., Alafuzoff, I., Herukka, S., van Groen, T., Tanila, H., and Pirttil, T. (2009). Expression of interleukin-18 is elevated within the brains of Alzheimer’s illness sufferers. Neurobiol. Getting older 30, 198–209. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2007.06.006
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Oleskin, A. V., and Shenderov, B. A. (2016). Neuromodulatory results and targets of the SCFAs and gasotransmitters produced by the human symbiotic microbiota. Microb. Ecol. Well being Dis. 27:30971. doi: 10.3402/mehd.v27.30971
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Perry, R. J., Peng, L., Barry, N. A., Cline, G. W., Zhang, D., Cardone, R. L., et al. (2016). Acetate mediates a microbiome–mind–β-cell axis to advertise metabolic syndrome. Nature 534, 213–217. doi: 10.1038/nature18309
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Petrov, V. A., Saltykova, I. V., Zhukova, I. A., Alifirova, V. M., Zhukova, N. G., Dorofeeva, Y. B., et al. (2017). Evaluation of intestine microbiota in sufferers with Parkinsons illness. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 162, 734–737. doi: 10.1007/s10517-017-3700-7
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Pirbaglou, M., Katz, J., de Souza, R. J., Stearns, J. C., Motamed, M., and Ritvo, P. (2016). Probiotic supplementation can positively have an effect on anxiousness and depressive signs: a scientific evaluation of randomized managed trials. Nutr Res 36, 889–898.
Plassais, J., Gbikpi-Benissan, G., Figarol, M., Scheperjans, F., Gorochov, G., Derkinderen, P., et al. (2021). Intestine microbiome alpha-diversity isn’t a marker of Parkinson’s illness and a number of sclerosis. Mind Commun. 3:fcab113. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcab113
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Porter, D. W., Irwin, N., Flatt, P. R., Hscher, C., and Gault, V. A. (2011). Extended GIP receptor activation improves cognitive operate, hippocampal synaptic plasticity and glucose homeostasis in high-fat fed mice. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 650, 688–693. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.10.059
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Poutahidis, T., Kearney, S. M., Levkovich, T., Qi, P., Varian, B. J., Lakritz, J. R., et al. (2013). Microbial symbionts speed up wound therapeutic through the neuropeptide hormone oxytocin. PLoS One 8:e78898. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0078898
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Pröbstel, A.-Okay., and Baranzini, S. E. (2018). The function of the intestine microbiome in a number of sclerosis threat and development: in direction of characterization of the “MS Microbiome”. Neurotherapeutics 15, 126–134. doi: 10.1007/s13311-017-0587-y
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Psichas, A., Sleeth, M. L., Murphy, Okay. G., Brooks, L., Bewick, G. A., and Hanyaloglu, A. C. (2015). The short-chain fatty acid propionate stimulates GLP-1 and PYY secretion through free fatty acid receptor 2 in rodents. Int. J. Obes. 39, 424–429. doi: 10.1038/ijo.2014.153
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Qian, Y., Yang, X., Xu, S., Wu, C., Tune, Y., Qin, N., et al. (2018). Alteration of the fecal microbiota in Chinese language sufferers with Parkinson ‘s illness. Mind Behav. Immun. 70, 194–202. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2018.02.016
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Radde, R., Bolmont, T., Kaeser, S. A., Coomaraswamy, J., Lindau, D., Stoltze, L., et al. (2006). Abeta42-driven cerebral amyloidosis in transgenic mice reveals early and strong pathology. EMBO Rep. 7, 940–946. doi: 10.1038/sj.embor.7400784
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Rhee, S. H., Pothoulakis, C., and Mayer, E. A. (2009). Rules and medical implications of the brainngut enteric microbiota axis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 6, 306–314. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2009.35
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Rincel, M., and Darnaudery, M. (2020). Maternal separation in rodents: a journey from intestine to mind and dietary views. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 79, 113–132. doi: 10.1017/S0029665119000958
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Rodrigues, H. G., Sato, F. T., Curi, R., and Vinolo, M. A. R. (2016). Fatty acids as modulators of neutrophil recruitment, operate and survival. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 785, 50–58. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.03.098
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Ronchi, F., Basso, C., Preite, S., Reboldi, A., Baumjohann, D., Perlini, L., et al. (2016). Experimental priming of encephalitogenic Th1/Th17 cells requires pertussis toxin-driven IL-1β manufacturing by myeloid cells. Nat. Commun. 7, 1–11. doi: 10.1038/ncomms11541
Rutsch, A., Kantsj, J. B., and Ronchi, F. (2020). The gut-brain axis: how microbiota and host inflammasome affect mind physiology and pathology. Entrance. Immunol. 11:604179. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.604179
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Sadler, R., Cramer, J. V., Heindl, S., Kostidis, S., Betz, D., Zuurbier, Okay. R., et al. (2020). Brief-chain fatty acids enhance poststroke restoration through immunological mechanisms. J. Neurosci. 40, 1162–1173. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1359-19.2019
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Sampson, T. R., Debelius, J. W., Thron, T., Janssen, S., Shastri, G. G., Ilhan, Z. E., et al. (2016). Intestine microbiota regulate motor deficits and neuroinflammation in a mannequin of Parkinson’s illness. Cells 167, 1469–1480.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.018
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Sampson, T. R., and Mazmanian, S. Okay. (2015). Management of mind growth, operate, and habits by the microbiome. Cell Host Microbe 17, 565–576. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.04.011
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Saresella, M., la Rosa, F., Piancone, F., Zoppis, M., Marventano, I., Calabrese, E., et al. (2016). The NLRP3 and NLRP1 inflammasomes are activated in Alzheimer’s illness. Mol. Neurodegener. 11, 1–14. doi: 10.1186/s13024-016-0088-1
Savignac, H. M., Dinan, T. G., and Cryan, J. F. (2011). Resistance to early-life stress in mice: results of genetic background and stress period. Entrance. Behav. Neurosci. 5:13. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2011.00013
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Schachtle, M. A., and Rosshart, S. P. (2021). The microbiota-gut-brain axis in well being and illness and its implications for translational analysis. Entrance. Cell. Neurosci 15:698172. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2021.698172
Scheltens, P., Blennow, Okay., Breteler, M. M., de Strooper, B., Frisoni, G. B., Salloway, S., et al. (2016). Alzheimer’s illness. Lancet (London, England) 388, 505–517. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)01124-1
Scheperjans, F., Aho, V., Pereira, P. A. B., Koskinen, Okay., Paulin, L., Pekkonen, E., et al. (2015). Intestine microbiota are associated to Parkinson’s illness and medical phenotype. Motion. Disord. Clin. Pract. 30, 350–358. doi: 10.1002/mds.26069
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Sekirov, I., Russell, S. L., Antunes, L. C. M., and Finlay, B. B. (2010). Intestine microbiota in well being and illness. Physiol. Rev. 90, 859–904. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00045.2009
Sgritta, M., Dooling, S. W., Buffington, S. A., Momin, E. N., Francis, M. B., Britton, R. A., et al. (2019). Mechanisms underlying microbial-mediated modifications in social habits in mouse fashions of autism spectrum dysfunction. Neuron 101:e246, –259.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2018.11.018
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Singh, V., Roth, S., Llovera, G., Sadler, R., Garzetti, D., Stecher, B. R., et al. (2016). Microbiota dysbiosis controls the neuroinflammatory response after stroke. J. Neurosci. 36, 7428–7440. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1114-16.2016
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Skonieczna Zydecka, Okay., Marlicz, W., Misera, A., Koulaouzidis, A., and Aoniewski, I. (2018). Microbiome the lacking hyperlink within the gut-brain axis: concentrate on its function in gastrointestinal and psychological well being. J. Clin. Med. 7:521. doi: 10.3390/jcm7120521
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Stojkovi, D., Kosti, M., Smiljkovi, M., Aleksi, M., Vasiljevi, P., Nikoli, M., et al. (2020). Linking antimicrobial potential of pure merchandise derived from aquatic organisms and microbes concerned in Alzheimers disease-a evaluation. Curr. Med. Chem. 27, 4372–4391. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180309103645
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Strandwitz, P., Kim, Okay. H., Terekhova, D., Liu, J. Okay., Sharma, A., Levering, J., et al. (2019). GABA-modulating micro organism of the human intestine microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 396–403. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0307-3
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Sudo, N., Chida, Y., Aiba, Y., Sonoda, J., Oyama, N., Yu, X. N., et al. (2004). Postnatal microbial colonization packages the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal system for stress response in mice. J. Physiol. 558, 263–275. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2004.063388
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Takagi, T., Naito, Y., Inoue, R., Kashiwagi, S., Uchiyama, Okay., Mizushima, Okay., et al. (2019). Variations in intestine microbiota related to age, intercourse, and stool consistency in wholesome Japanese topics. J. Gastroenterol. 54, 53–63. doi: 10.1007/s00535-018-1488-5
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Tarawneh, R., and Penhos, E. (2022). The intestine microbiome and Alzheimer’s illness: advanced and bidirectional interactions. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 141:104814. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2022.104814
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Tian, Y., Ullah, H., Gu, J., and Li, Okay. (2023). Immune-metabolic mechanisms of posttraumatic stress dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Entrance. Physiol. 14:1123692. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1123692
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Tiraboschi, P., Hansen, L. A., Thal, L. J., and Corey-Bloom, J. (2004). The significance of neuritic plaques and tangles to the event and evolution of AD. Neurology 62, 1984–1989. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000129697.01779.0A
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Tiwari, P., Dwivedi, R., Bansal, M., Tripathi, M., and Dada, R. (2023). Position of intestine microbiota in neurological problems and its therapeutic significance. J. Clin. Med. 12:1650. doi: 10.3390/jcm12041650
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Tognini, P. (2016). Intestine microbiota: a possible regulator of neurodevelopment. Entrance. Cell. Neurosci. 11:25.
Tolhurst, G., Heffron, H., Lam, Y. S., Parker, H. E., Habib, A. M., Diakogiannaki, E., et al. (2012). Brief-chain fatty acids stimulate glucagon-like peptide-1 secretion through the G-protein coupled receptor FFAR2. Diabetes 61, 364–371. doi: 10.2337/db11-1019
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Tomova, A., Husarova, V., Lakatosova, S., Bakos, J., Vlkova, B., Babinska, Okay., et al. (2015). Gastrointestinal microbiota in youngsters with autism in Slovakia. Physiol. Behav. 138, 179–187. doi: 10.1016/j.physbeh.2014.10.033
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Tremlett, H., Bauer, Okay. C., Appel-Cresswell, S., Finlay, B. B., and Waubant, E. (2017). The intestine microbiome in human neurological illness: a evaluation. Ann. Neurol. 81, 369–382. doi: 10.1002/ana.24901
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Twenge, J. M., Cooper, A. B., Joiner, T. E., Duffy, M. E., and Binau, S. G. (2019). Age, interval, and cohort tendencies in temper dysfunction indicators and suicide-related outcomes in a nationally consultant dataset, 2005-2017. J. Abnorm. Psychol. 128:185. doi: 10.1037/abn0000410
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Unger, M. M., Spiegel, J., Dillmann, Okay.-U., Grundmann, D., Philippeit, H., Bürmann, J., et al. (2016). Brief chain fatty acids and intestine microbiota differ between sufferers with Parkinson’s illness and age-matched controls. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 32, 66–72. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2016.08.019
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Valles-Colomer, M., Falony, G., Darzi, Y., Tigchelaar, E. F., Wang, J., Tito, R. Y., et al. (2019). The neuroactive potential of the human intestine microbiota in high quality of life and despair. Nat. Microbiol. 4, 623–632. doi: 10.1038/s41564-018-0337-x
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Vogt, N. M., Kerby, R. L., Dill-McFarland, Okay. A., Harding, S. J., Merluzzi, A. P., Johnson, S. C., et al. (2017). Intestine microbiome alterations in Alzheimer’ s illness. Sci. Stories. 7, 1–11.
Vogt, N. M., Romano, Okay. A., Darst, B. F., Engelman, C. D., Johnson, S. C., Carlsson, C. M., et al. (2018). The intestine microbiota-derived metabolite trimethylamine N-oxide is elevated in Alzheimer’s illness. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 10, 1–8. doi: 10.1186/s13195-018-0451-2
Waise, T. M., Dranse, H. J., and Lam, T. Okay. T. (2018). The metabolic function of vagal afferent innervation. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 15, 625–636. doi: 10.1038/s41575-018-0062-1
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Wang, L., Christophersen, C. T., Sorich, M. J., Gerber, J. P., Angley, M. T., and Conlon, M. A. (2013). Elevated abundance of Sutterella spp. and Ruminococcus torques in feces of kids with autism spectrum dysfunction. Mol. Autism. 4, 1–4. doi: 10.1186/2040-2392-4-42
Weinberger, A. H., Gbedemah, M., Martinez, A. M., Nash, D., Galea, S., and Goodwin, R. D. (2018). Traits in despair prevalence within the USA from 2005 to 2015: widening disparities in weak teams. Psychol. Med. 48, 1308–1315. doi: 10.1017/S0033291717002781
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Williams, B. L., Hornig, M., Buie, T., Bauman, M. L., Cho Paik, M., Wick, I., et al. (2011). Impaired carbohydrate digestion and transport and mucosal dysbiosis within the intestines of kids with autism and gastrointestinal disturbances. PLoS One 6:e24585. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0024585
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Received, Y.-J., Lu, V. B., Puhl, H. L., and Ikeda, S. R. (2013). b-Hydroxybutyrate modulates N-type calcium channels in rat sympathetic neurons by performing as an agonist for the G-protein-coupled receptor FFA3. J. Neurosci. 33, 19314–19325. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3102-13.2013
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Xiang, L., Lou, Y., Liu, L., Liu, Y., Zhang, W., Deng, J., et al. (2020). Intestine microbiotic options aiding the prognosis of acute ischemic stroke. Entrance. Cell. Infect. 10:587284. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.587284
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Xu, D. J., Wang, Okay. C., Yuan, L. B., Li, H. F., Xu, Y. Y., Wei, L. Y., et al. (2021). Compositional and purposeful alterations of intestine microbiota in sufferers with stroke. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 31, 3434–3448. doi: 10.1016/j.numecd.2021.08.045
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Xu, M., Xu, X., Li, J., and Li, F. (2019). Affiliation between intestine microbiota and autism spectrum dysfunction: a scientific evaluation and meta-analysis. Entrance. Psych. 10:473. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00473
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Yano, J. M., Yu, Okay., Donaldson, G. P., Shastri, G. G., Ann, P., Ma, L., et al. (2015). Indigenous micro organism from the intestine microbiota regulate host serotonin biosynthesis. Cells 161, 264–276. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.047
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Yin, J., Liao, S. X., He, Y., Wang, S., Xia, G. H., Liu, F. T., et al. (2015). Dysbiosis of intestine microbiota with decreased trimethylamine‐n‐oxide stage in sufferers with giant‐artery atherosclerotic stroke or transient ischemic assault. J. Am. Coronary heart Assoc. 4:e002699. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002699
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Yoo, B. B., and Mazmanian, S. Okay. (2017). The enteric community: interactions between the immune and nervous techniques of the intestine. Immunity 46, 910–926. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2017.05.011
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Zhang, L., Wang, Y., Xiayu, X., Shi, C., Chen, W., Tune, N., et al. (2017). Altered intestine microbiota in a mouse mannequin of Alzheimer’s illness. J. Alzheimers Dis. 60, 1241–1257. doi: 10.3233/JAD-170020
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Zhao, Z. X., Fu, J., Ma, S. R., Peng, R., Yu, J. B., Cong, L., et al. (2018). Intestine-brain axis metabolic pathway regulates antidepressant efficacy of albiflorin. Theranostics 8, 5945–5959. doi: 10.7150/thno.28068
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar
Zheng, P., Zeng, B., Zhou, C., Liu, M., Fang, Z., Xu, X., et al. (2016). Intestine microbiome reworking induces depressive-like behaviors by a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Mol. Psychiatry 21, 786–796. doi: 10.1038/mp.2016.44
PubMed Summary | CrossRef Full Textual content | Google Scholar