Individuals’ info
Bacterial DNA was remoted from swabs of pores and skin and PI of 27 contributors with traumatic SCI [all males; median age: 58 (range 29–78) years] who had been present process reconstructive surgical procedure, between June 2020 and September 2022 (Desk 1). In 63% of the instances, the spinal twine harm was localized within the thoracic area and 67% of the sufferers confirmed no sensory or motor perform within the sacral segments S4–S5 (ISNCSCI A). Moreover, 59% of the sufferers had been categorized as obese or overweight (BMI over 22.5 kg/m2 22), and 22% had been lively people who smoke. Majority of the sufferers (37%) had no pre-existing medical situations on the time of surgical procedure, whereas the most typical co-morbidities had been hypertension (18%), peripheral vascular illness (11%) and renal illness (7%). Notably, 15% of the sufferers had a number of co-morbidities.
On this examine, all included sufferers had a extreme type of pelvic PI: 52% grade III (no bone publicity) and 48% grade IV (with bone publicity). Osteomyelitis was current in 18% of the sufferers. The affected areas had been the ischium (67%), sacrum (11%) and trochanter (22%). The median dimension of the harm was 25 cm2 (starting from 6 to 77 cm2), and 52% of the accidents had been current for a couple of month. Nearly all of the reconstructive surgical procedures concerned fasciocutaneous flaps (96%) and 30% of sufferers skilled wound dehiscence after the intervention.
Blood markers, equivalent to albumin, prealbumin and creatinine, had been investigated to evaluate the sufferers’ dietary standing, notably decreased protein consumption. Outcomes confirmed that the people within the examine had ranges of albumin (36 g/L) and prealbumin (0.21 g/L) throughout the regular reference ranges (albumin 34–54 g/L; prealbumin 0.15–0.36 g/L). Nevertheless, the imply creatinine degree (55 µmol/L) was under normal ranges (61.9–114.9 µmol/L). Moreover, 34% of contributors had low haematocrit ranges in comparison with the conventional vary of 40.7–50.3% for males with out SCI. Moreover, we noticed barely increased ranges of C-reactive protein (CRP) ranges within the SCI contributors (in common 13 mg/L) in comparison with typically accepted regular vary (under 8–10 mg/L).
Microbial richness and variety of pores and skin and PI microbiota
The V1-V9 area of the 16S rRNA gene was amplified by PCR methodology and the MinION™ sequencing. Following adapter trimming, high quality filtering and dimension choice, a median of 57,628 reads per pattern (with a median learn size of 1462 bp and 96.7% of reads categorized) had been retained for bacterial identification.
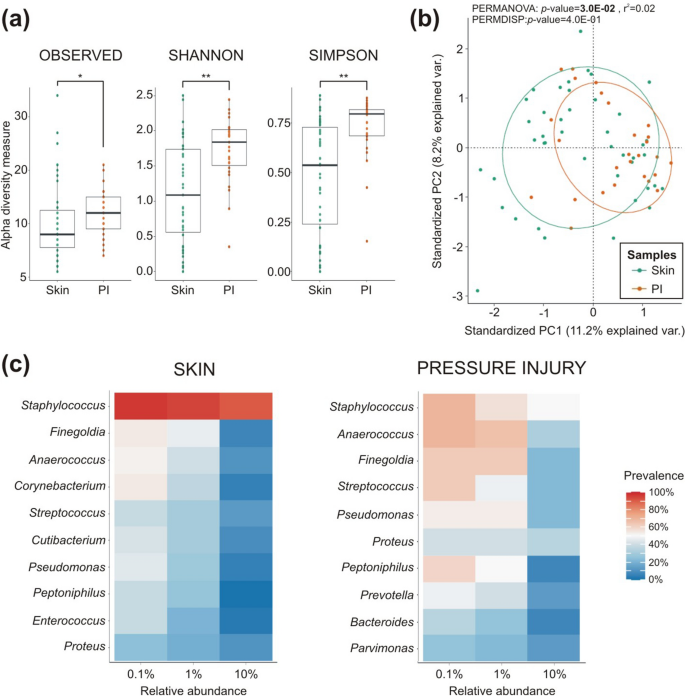
The sequencing recognized a median of 8 genera within the intact pores and skin (vary 6–33) and with 12 genera within the PI (vary 7–21; Fig. 1a). The PI confirmed a considerably increased degree of microbial alpha range, as indicated by noticed richness (p-value = 3.5E−02), Shannon (p-value = 3.8E−03) and Simpson (p-value = 4.3E−05) range indices in comparison with the pores and skin microbiome (shoulder and pelvis collectively). Which means the PI samples contained a higher variety of bacterial genera and a extra even illustration in comparison with the pores and skin microbiome. As well as, a major dissimilarity within the microbial composition (beta-diversity) was discovered between the pores and skin and PI (p-value = 3.0E−02; Fig. 1b).
Comparability of bacterial communities remoted from pores and skin (shoulder and pelvis samples) and PI in SCI sufferers. (a) Variations are proven by alpha range (variety of noticed genera, Shannon and Simpson indices) within the boxplots and (b) by beta range for the whole inhabitants. Ellipses signify 95% confidence area of every group, pores and skin in inexperienced and PI in orange (PC, principal part). (c) Ten most represented genera in pores and skin and PI microbiomes. Genera are represented by their relative abundance (0.1%, 1% and 10%) and their prevalence throughout all samples analysed (pores and skin, n = 43; PI, n = 27; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).
Pores and skin and PI harboured totally different proportions of phyla, with Firmicutes and Actinobacteria being prevalent within the pores and skin (in over 50% of the samples), whereas Proteobacteria was dominant within the PI. Among the many Firmicutes phylum, Staphylococcus, Finegoldia and Anaerococcus had been the most typical in each the pores and skin and PI, whereas Streptococcus (additionally Firmicutes phylum) was extra prevalent in PI, and Corynebacterium (Actinobacteria phylum) was primarily discovered within the pores and skin (Fig. 1c). The PI additionally confirmed elevated prevalence of Proteus and Pseudomonas (Proteobacteria phylum) and Peptoniphilus (Bacillota phylum). The differential abundance evaluation confirmed that Staphylococcus, Corynebacterium, Acinetobacter, Cutibacterium and Brevibacterium had been considerably extra considerable within the pores and skin (Extra file 1: Desk S1).
The pores and skin microbiota of SCI sufferers: variations between pelvis and shoulder
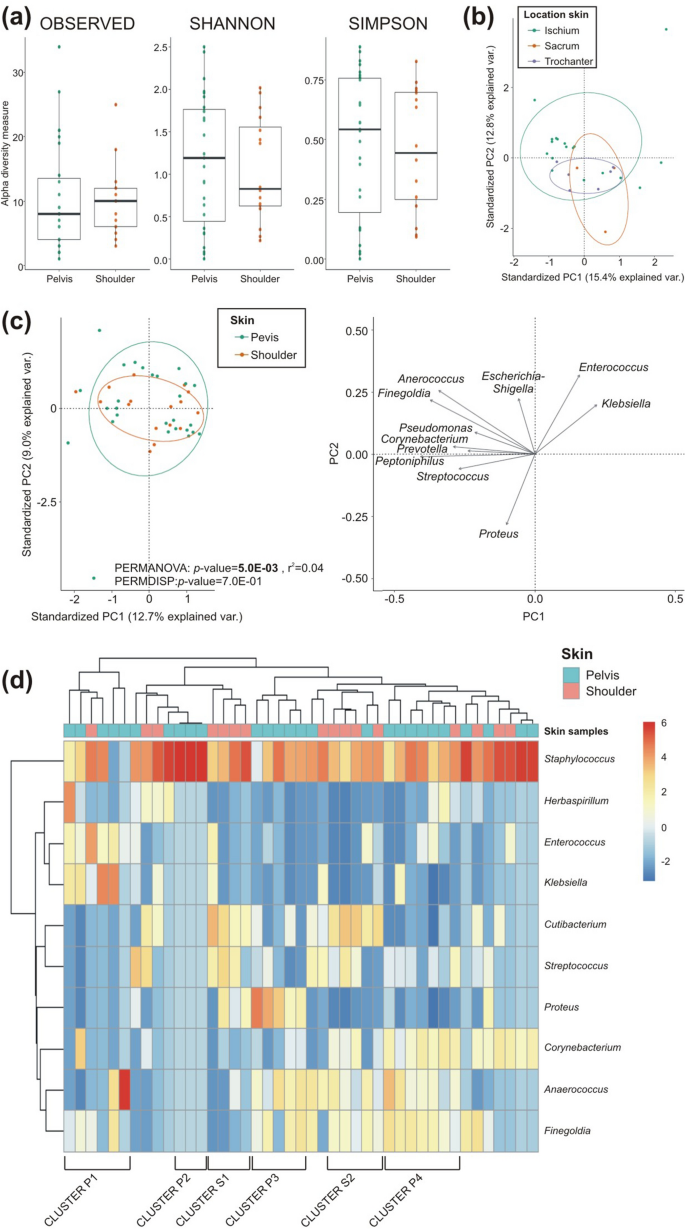
We in contrast the bacterial DNA remoted from the pores and skin close to the PI, on the pelvis (inside few centimetres distance; n = 27), with DNA remoted from the shoulder (removed from the harm; n = 16). The median variety of genera recognized within the pelvic pores and skin was 8 (vary 2–33), whereas within the shoulder it was 10 (vary 4–25; Fig. 2a). No important variations had been discovered within the microbial alpha range. When analyzing the pelvis, no variations had been noticed within the composition of the pores and skin microbiome based mostly on location on the pelvis (ischium, sacrum and trochanter; Fig. 2b). A rise in dispersion was famous shifting nearer to the anus—from the trochanter to the ischium—brought on by contamination from faecal micro organism. Nevertheless, the composition of the pelvic and shoulder microbiomes was considerably totally different (p-value = 5.0E−03, Fig. 2c). The presence of Enterococcus and Klebsiella was negatively correlated with the presence of Proteus.
Variations in pores and skin microbiomes of SCI sufferers between shoulder and pelvis samples. (a) Variety between shoulder and pelvic samples had been analysed by alpha range evaluation (variety of noticed genera, Shannon and Simpson indices) within the boxplots. (b) Samples from totally different location throughout the pelvis area, specifically ischium, sacrum and trochanter, had been in contrast for beta-diversity within the biplot (ischium pores and skin, n = 18; sacrum pores and skin, n = 3; trochanteric pores and skin, n = 6). (c) Beta range between pelvic and shoulder pores and skin samples was analysed and arrows signify the influential loadings for principal part (PC)1 and PC2 of the principal coordinate evaluation. (d) Hierarchical clustering of the centre-log ratio of the ten most relative considerable genera in pelvic and shoulder pores and skin samples is proven (pelvic pores and skin, n = 27; shoulder pores and skin, n = 16; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).
Hierarchical clustering of the centre-log ratio of the ten most relative considerable genera revealed distinct clusters within the pelvis and shoulder pores and skin samples (Fig. 2d). All samples had been characterised by the dominance of Staphylococcus, besides in two pelvic samples the place Anaerococcus was dominant (Cluster P1). On this similar cluster, a excessive prevalence of Enterococcus and Klebsiella was noticed. In pelvic pores and skin, threes further clusters had been recognized: one was characterised by the distinctive presence of Staphylococcus (Cluster P2), whereas the opposite two had been composed of Anaerococcus and Finegoldia, however differed within the presence of both Proteus (Cluster P3) or Corynebacterium (Cluster P4). Within the shoulder samples, two clusters had been recognized, each characterised by Cutibacterium and Streptococcus (Cluster S1), however differing within the presence of Anaerococcus and Finegoldia (Cluster S2). Within the comparative evaluation, solely Cutibacterium and Streptococcus confirmed considerably increased abundance within the shoulder pores and skin in comparison with the pelvic pores and skin (Extra file 1: Desk S1).
PI microbiota: affect of wound severity grade and placement on the pelvis
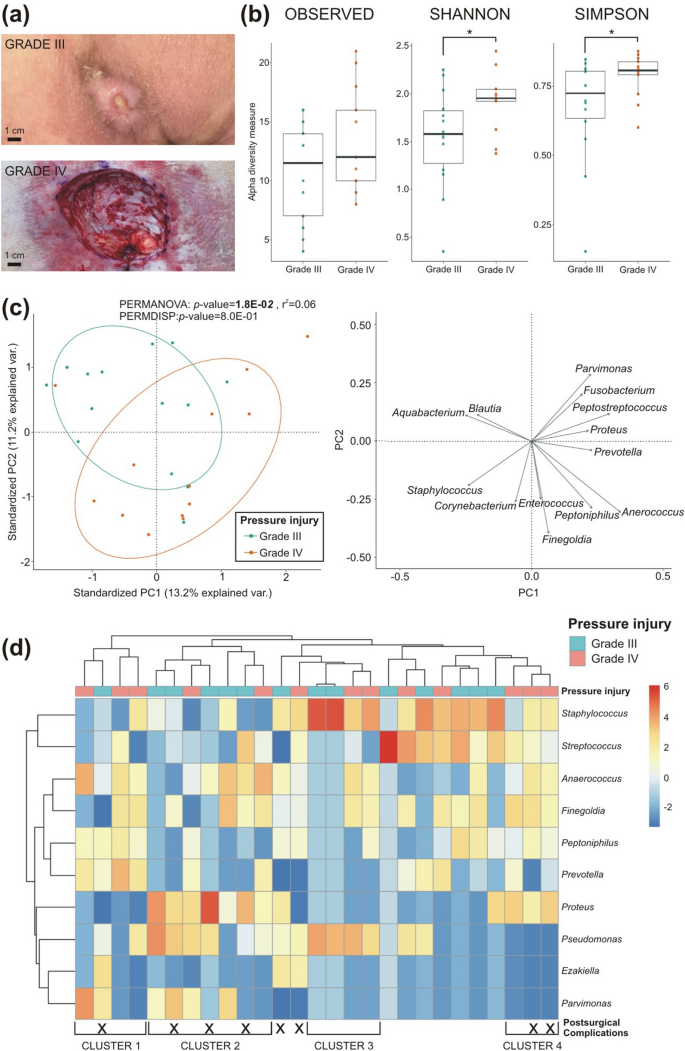
The microbial communities in PI had been discovered to vary based mostly on severity grades (grade III vs grade IV; Fig. 3a). The evaluation revealed a comparable median variety of noticed genera in grade III (12; vary 4–16) and in grade IV (13; vary 7–21; Fig. 3b). Nevertheless, microbial alpha range as assessed by the Shannon (p-value = 3.8E−02) and Simpson (p-value = 4.3E−02) indices confirmed a major enhance in grade IV in comparison with grade III communities. The beta range between the 2 PI grades microbiomes was statistically important (p-value = 1.8E−02, Fig. 3c). Greater presence of genera equivalent to Aquabacterium and Blautia and decrease presence of Prevotella, Anaerococcus, Peptoniphilus and Finegoldia had been noticed in grades III PI, as reverse to grade IV.
Variations in PI microbiomes of SCI sufferers between grade III and grade IV samples. (a) Consultant footage of grade III (above) and grade IV (under) strain accidents included on this examine. (b) Variety between grade III and grade IV PI samples had been analysed by alpha range evaluation (variety of noticed genera, Shannon and Simpson indices) within the boxplots. (c) Beta range between grade III (inexperienced ellipse) and grade IV (orange ellipse) PI samples was analyses and arrows signify the influential loadings for principal part (PC)1 and PC2 of the principal coordinate evaluation. (d) Hierarchical clustering of the centre-log ratio of the ten most relative considerable genera in grade III and grade IV PI samples is proven (grade III PI samples, n = 14; grade IV PI samples, n = 13; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01).
Hierarchical clustering of the ten most relative considerable genera revealed 4 distinct clusters, which differed in composition and the speed of postoperative problems (Fig. 3d). These 4 clusters had been characterised by: (i) Prevotella, Peptoniphilus and Anaerococcus (Cluster 1; 1/4 instances with problems), (ii) Pseudomonas and Proteus (Cluster 2; 4/7 instances with problems), (iii) Pseudomonas and Staphylococcus (Cluster 3; 0/4 instances with problems) and (iv) Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Anaerococcus, Finegoldia, Peptoniphilus and Proteus (Cluster 4; 2/3 instances with problems). Differential abundance evaluation confirmed that Campylobacter, Prevotella, Facklamia, Anaerococcus and Finegoldia had been extra considerably considerable in grade IV PI (Extra file 1: Desk S1).
The situation of the PI on the ischium, sacrum or trochanter didn’t considerably have an effect on the median variety of noticed genera (Extra file 1: Fig. S2a): ischium 12 (vary 4 to 16), sacrum 17 (vary 10 to twenty) and trochanter 11 (vary 6 to 21). The microbial composition of PI was discovered to be comparable no matter location, however the microbial composition dispersion was decrease within the trochanter in comparison with the ischium and sacrum (Extra file 1: Fig. S2b).
Comparability of normal microbial cultures and sequencing knowledge of PI microbiome
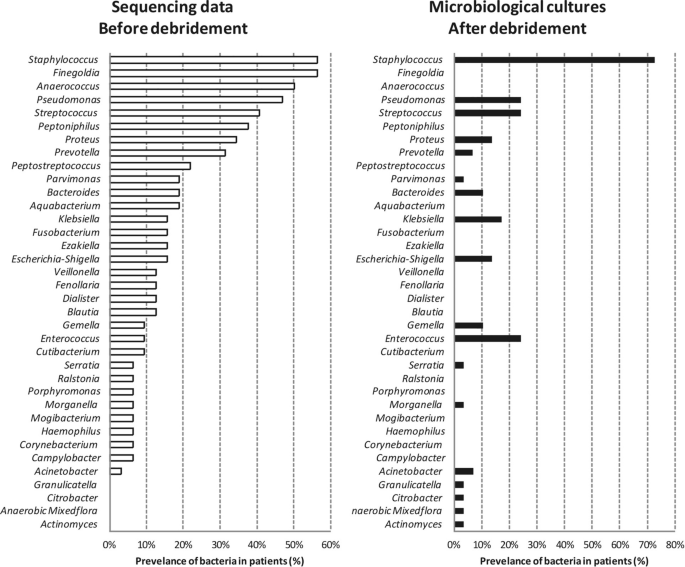
Outcomes from each bacterial tradition evaluation utilizing MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry and DNA sequencing from donors’ PI had been in contrast (Fig. 4). A bacterial genus was thought of current within the PI with a relative sequencing abundance above 3%. Essentially the most prevalent genus was Staphylococcus, represented in 72% of the cultures and 56% of the sequenced DNA. Klebsiella, Escherichia-Shigella and Gemella had been recognized in the identical proportions from each methodologies. Nevertheless, bacterial cultures recognized solely 27% of the whole genera remoted from the PI, lacking the continuously detected by 16S sequencing anaerobes, equivalent to Finegoldia (56%), Anaerococcus (50%), Peptoniphilus (38%) and Peptostreptococcus (22%). Moreover, bacterial tradition evaluation underrepresented bacterial genera equivalent to Pseudomonas, Streptococcus, Proteus, Prevotella, Parvimonas and Bacteroides. Conversely, bacterial cultures recognized Enterococcus and Acinetobacter extra continuously in comparison with DNA sequencing.
Affect of spinal harm degree on pores and skin and PI microbiota
We examined the impact of SCI degree on microbial range in pores and skin and PI. The main focus was on the affect of the lack of autonomic management of the pores and skin, notably the impact on sympathetic management over sweat glands and blood vessels (sympathetic pores and skin responses) in cervical and thoraco-lumbar lesions (Extra file 1: Fig. S3a). The potential integrity of the sympathetic plexus gives extra secure pores and skin setting by regulating blood circulate and sweating23. Certainly, in comparison with sufferers with thoraco-lumbar SCI, sufferers with cervical SCI confirmed a higher variation of microbial communities in pelvic (Extra file 1: Fig. S3b) and shoulder (Extra file 1: Fig. S3c) pores and skin, even when non-statistically important. Klebsiella related negatively to Streptococcus within the pores and skin pelvis and to Peptoniphilus and Corynebacterium within the shoulder. Within the PI, the microbiome was not influenced by the lesion degree both, however it was characterised by the absence of Corynebacterium, Enterococcus, and Finegoldia with cervical lesions (Extra file 1: Fig. S3d).
Affect of surrounding pores and skin on the PI microbiome
A comparability of pores and skin and PI microbiomes was carried out to research their interdependence. Beta range evaluation confirmed no distinction in microbiome based mostly on pelvis location, however a bigger dispersion close to the anus (Extra file 1: Fig. S4a). Additional comparability of alpha and beta range between pelvic pores and skin and PI within the ischium, sacrum and trochanter (Extra file 1: Fig. S4b–d) confirmed no important distinction in microbial composition, suggesting that the pores and skin surrounding the PI has a direct position in shaping the PI microbiome. Nevertheless, the microbial alpha range in ischial PI was discovered to be considerably increased for Shannon (p-value = 1.7E−02) and Simpson (p-value = 4.4E−03) range indices in comparison with the close by pores and skin microbiome communities.
Postsurgical problems after PI surgical procedure and evaluation of microbiome
Eight sufferers (30%) skilled a complication with wound therapeutic post-surgery (Extra file 1: Fig. S5a). The microbial neighborhood distribution various between these with and with out problems (p-value = 9.0E−03, Extra file 1: Fig. S5b) and Ezakiella was extra considerable in post-surgical complication sufferers’ PI (Extra file 1: Desk S1). Moreover, sufferers with therapeutic points had bigger wound dimension (38 cm2 vs. 20 cm2; p = 2.9E−02) and decrease creatinine ranges (38 µmol/L vs. 60 µmol/L; p = 7.0E−03) in comparison with these with out wound dehiscence (Extra file 1: Desk S2). However, the affect of renal pathologies on creatinine ranges can’t be dominated out. Moreover, we discovered that PI microbial communities of sufferers with elevated CRP ranges (above 10 mg/L) differed considerably from these with decrease plasma CRP (under 10 mg/L) (p-value = 4.2E−02; Extra file 1: Fig. S5c).