Life continues from one technology to the opposite on account of replication, transcription, and translation of genetic code saved in DNA and RNA.
Genetic code incorporates the sequence of nucleotide bases inside DNA and RNA. DNA consists of 4 nucleotide bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C), and thymine (T). The genetic code inside DNA is transcribed to RNA which acts as a template for protein synthesis. RNA consists of the bases adenine, guanine, cytosine, and uracil (U). They code for amino acids that hyperlink collectively to kind proteins. So genetic code acts as a set of directions that assemble amino acids within the right order to kind proteins.
The genetic code is learn in units of three nucleotides and this sequence of three DNA or RNA nucleotides is named codons. Every codon specifies a specific amino acid or acts as a sign to begin or cease protein synthesis.
The primary codon was found by Marshall Nirenberg and J. Heinrich Matthaei’s poly-U experiment which recognized {that a} chain of three uracil models (UUU) in RNA acted as a code phrase for the amino acid phenylalanine. Nirenberg’s subsequent work, alongside a staff of researchers, led to the identification of all 64 potential codons and their corresponding amino acids. Nirenberg was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Drugs in 1968, sharing the glory with Robert W. Holley and Har Gobind Khorana for his or her mixed efforts in deciphering the genetic code.
What’s a Codon Chart?
A codon chart or desk is used as a reference instrument that correlates particular codons with the corresponding amino acids they encode.
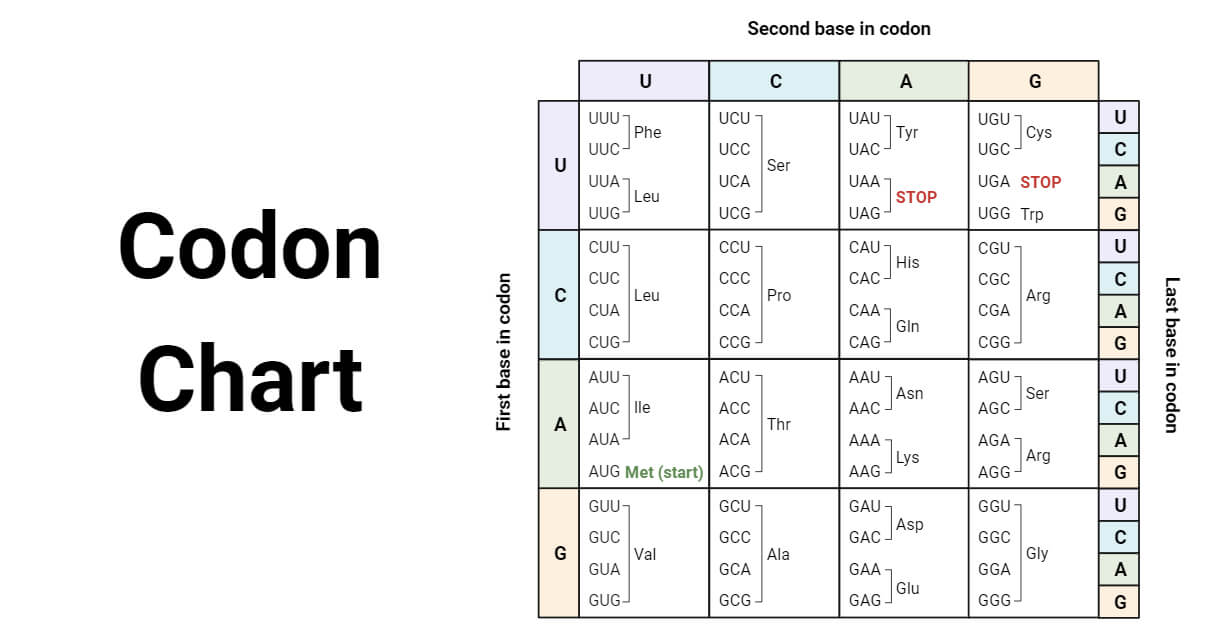
- The chart helps to decipher the genetic code and perceive which amino acids are synthesized primarily based on the sequence of nucleotides.
- In complete, there are 64 potential codons. Out of those, 61 codons correspond to the 20 totally different amino acids and the remaining three are cease codons that sign the top of protein synthesis.
- Within the chart, we are able to see {that a} single amino acid could be coded by a number of codons, so the genetic code is redundant or degenerate. For instance, the codons CCU, CCC, CCA, and CCG all code for a similar amino acid proline.
- The codon chart outlines the assorted codon combos and their corresponding amino acids.
- To make use of the codon chart, for instance, if the primary codon place incorporates uracil (U), the second incorporates adenine (A), and the third incorporates cytosine (C), the ensuing codon, UAC, represents the amino acid tyrosine.
Right here is the record of the 20 amino acids, together with their three-letter and one-letter abbreviation:
| Amino Acid | Abbreviation | One-Letter Abbreviation |
| Alanine | Ala | A |
| Arginine | Arg | R |
| Asparagine | Asn | N |
| Aspartic acid | Asp | D |
| Cysteine | Cys | C |
| Glutamic acid | Glu | E |
| Glutamine | Gln | Q |
| Glycine | Gly | G |
| Histidine | His | H |
| Isoleucine | Ile | I |
| Leucine | Leu | L |
| Lysine | Lys | Ok |
| Methionine | Met | M |
| Phenylalanine | Phe | F |
| Proline | Professional | P |
| Serine | Ser | S |
| Threonine | Thr | T |
| Tryptophan | Trp | W |
| Tyrosine | Tyr | Y |
| Valine | Val | V |
Begin Codons
- Begin codons are codons inside an mRNA molecule that point out the beginning of protein translation.
- AUG is the most typical begin codon and serves as the beginning sign for translation initiation.
- In eukaryotes, AUG codes for the amino acid methionine (Met), whereas in prokaryotes, AUG codes for formyl methionine (fMet).
- Initiation elements and tRNA are concerned in recognizing the beginning codon AUG and initiating the interpretation course of.
- Though AUG is the first begin codon, various codons also can function begin websites. These non-AUG begin codons are comparatively uncommon in eukaryotes.
- Prokaryotes like E. coli use numerous codons together with AUG, GUG, and UUG as begin codons.
Cease Codons
- Out of the whole 64 codons, there are three codons that don’t specify or correspond to any amino acids. These codons are generally known as cease codons.
- Cease codons, additionally referred to as termination or nonsense codons, function indicators to terminate the method of protein synthesis throughout translation.
- The three cease codons are UAA, UAG, and UGA.
- Cease codons have been first found in 1965 by Sydney Brenner’s experiment on T4 bacteriophage.
- UAG was the primary cease codon to be recognized. It is usually referred to as the amber codon. UGA is named the opal codon, and UAA is named the ochre codon.
Codon Translation
- Codon translation is a vital step in protein synthesis. Proteins are important molecules in dwelling organisms which might be synthesized throughout translation.
- The genetic info saved in DNA is just not instantly used to construct proteins; as an alternative, it’s first transcribed into RNA.
- DNA transcription is a vital step in protein synthesis the place genetic directions are copied from DNA to RNA. The enzyme RNA polymerase transcribes DNA right into a single-stranded RNA molecule generally known as messenger RNA (mRNA).
- Protein synthesis happens within the cytoplasm, the place the mRNA, together with ribosomes and switch RNA (tRNA), interprets the transcribed genetic code into chains of amino acids.
- Translation entails studying every RNA codon and including the corresponding amino acid to the chain of amino acids carried by tRNA molecules. This course of stops when a cease codon is encountered within the mRNA sequence.
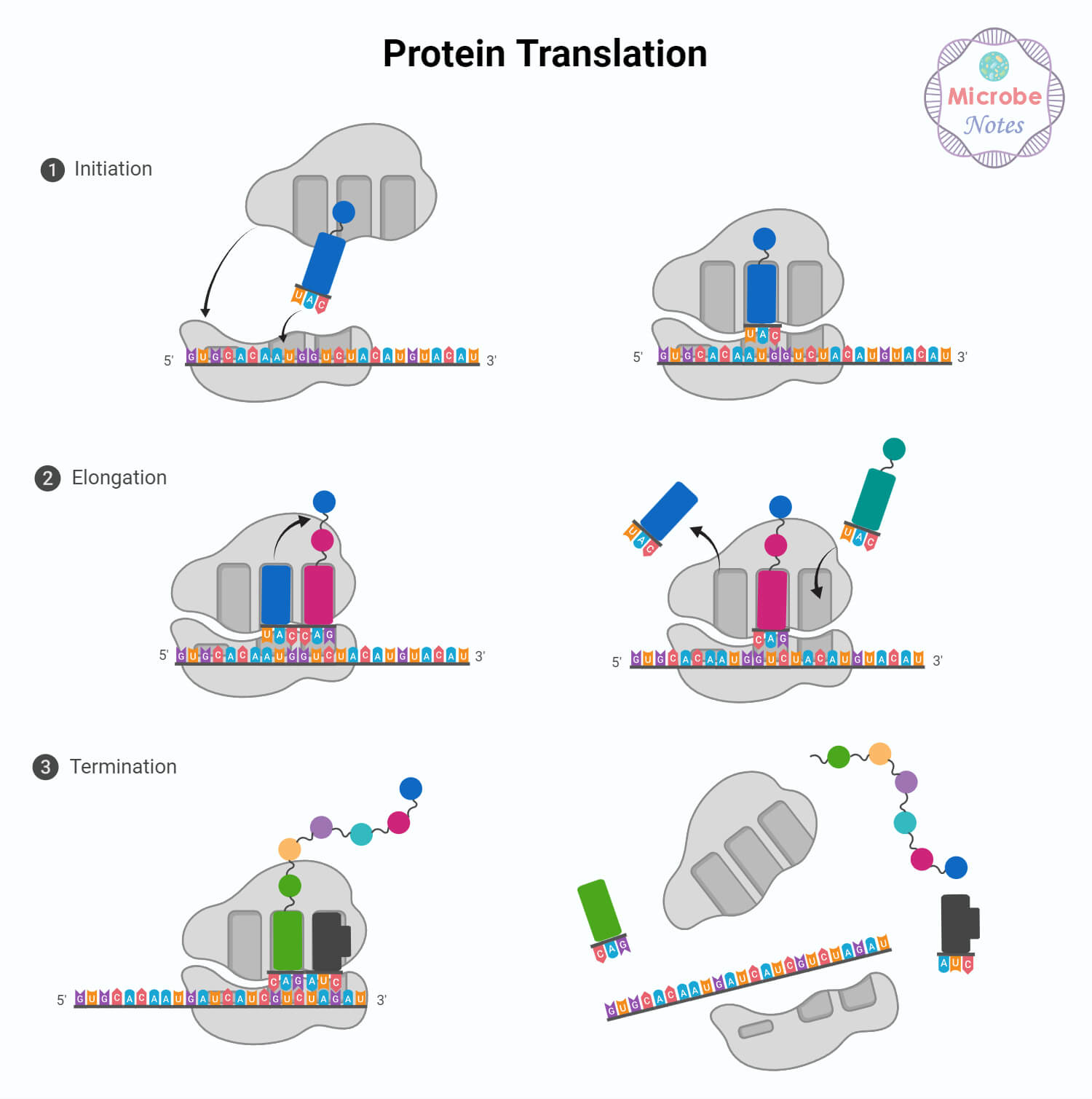
- The distinctive construction of tRNA helps within the exact matching between mRNA codon and the corresponding amino acid.
- The tRNA molecule, which resembles a cloverleaf form, includes 4 double-helical stems and three single-stranded loops. The central loop is known as the anticodon loop, because it carries a set of three nucleotides generally known as the anticodon.
- The tRNA anticodon sequence is complementary to the mRNA codon and this complementarity permits for a selected and correct interplay between the anticodon and the codon.
- As soon as transcription and translation are full, the newly shaped chain of amino acids undergoes modifications to rework right into a useful protein.
References
- American Chemical Society Nationwide Historic Chemical Landmarks. Deciphering the Genetic Code. http://www.acs.org/content material/acs/en/schooling/whatischemistry/landmarks/geneticcode.html
- Bailey, Regina. “Understanding the Genetic Code.” ThoughtCo, Aug. 29, 2020, thoughtco.com/genetic-code-373449.
- Clancy, S. & Brown, W. (2008) Translation: DNA to mRNA to Protein. Nature Training 1(1):101
- Griffiths, A. J. F., Miller, J. H., Suzuki, D. T., Lewontin, R. C., Gelbart, W. M. (2000). An introduction to genetic evaluation (seventh ed.). New York: W. H. Freeman.
- https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Codon
- https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/codon-155/
- https://www.nature.com/scitable/definition/genetic-code-13/
- Koonin, E. V., & Novozhilov, A. S. (2009). Origin and evolution of the genetic code: The common enigma. Iubmb Life, 61(2), 99. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.146
- Smith, A. (2008) Nucleic acids to amino acids: DNA specifies protein. Nature Training 1(1):126.
- The Info in DNA Determines Mobile Perform by way of Translation | Be taught Science at Scitable (nature.com)
- Translating the Code of Life and the Nobel Prize, 1962-1968 | Marshall W. Nirenberg – Profiles in Science (nih.gov)



