Genes are primary models of inheritance that comprise the genetic data obligatory to find out the particular traits in an organism. Genes comprise the directions for producing proteins that carry out numerous capabilities to maintain the cell alive and functioning. Protein performs particular roles within the cell, contributing to the construction, operate, and regulation of varied organic processes. To ensure that a cell to operate, it’s essential that particular proteins are created on the proper time.
This means of activation of genes to provide proteins known as gene expression. This activation results in the creation of messenger RNA (mRNA), which acts as a template for constructing the proteins. Merely, gene expression is the stream of genetic data from gene to protein. Gene expression is an important course of in cells that ensures particular proteins are created on the proper time and in the best portions.
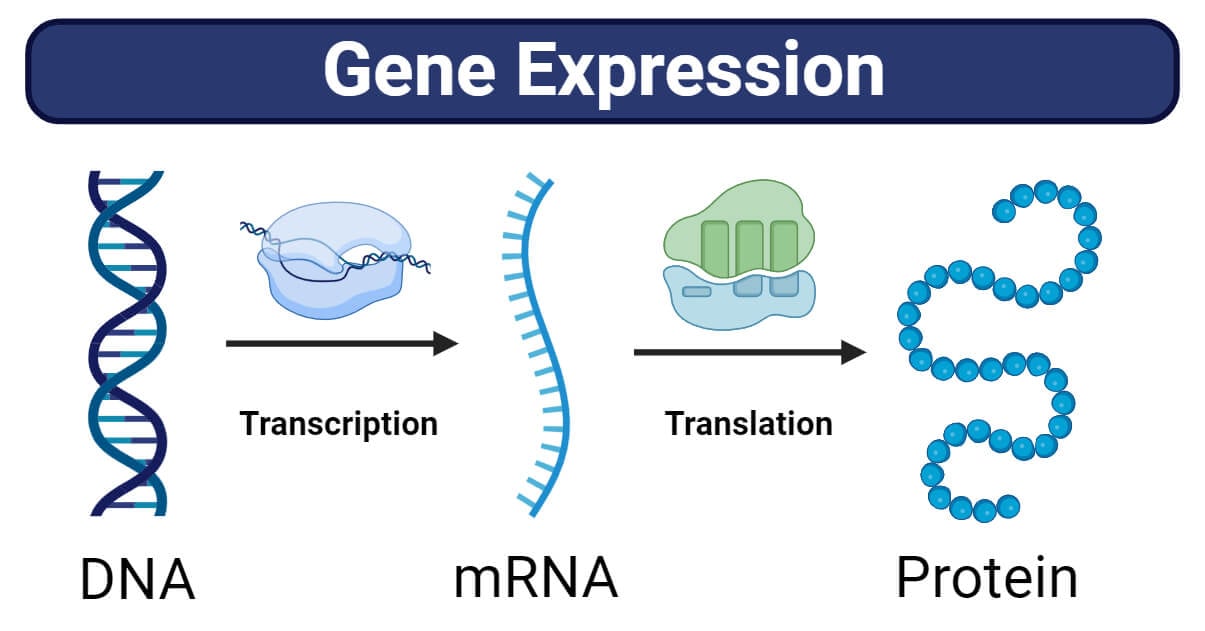
When a cell requires a selected protein, it prompts the corresponding gene. This activation initiates a collection of steps. First, an mRNA copy of the gene is produced via a course of known as transcription. The mRNA acts as a template for protein synthesis throughout translation. This course of includes studying the mRNA sequence in triplets and assembling the corresponding amino acids to kind a selected protein. The exact sequence of amino acids determines the construction and performance of the protein.
Phases in Gene Expression
Gene expression is a organic course of by which the genetic data contained inside genes is translated into purposeful outcomes. This course of consists of two fundamental phases: transcription and translation.
Transcription
Transcription is step one in gene expression, the place the genetic data encoded in DNA is transcribed into mRNA by an enzyme known as RNA polymerase.
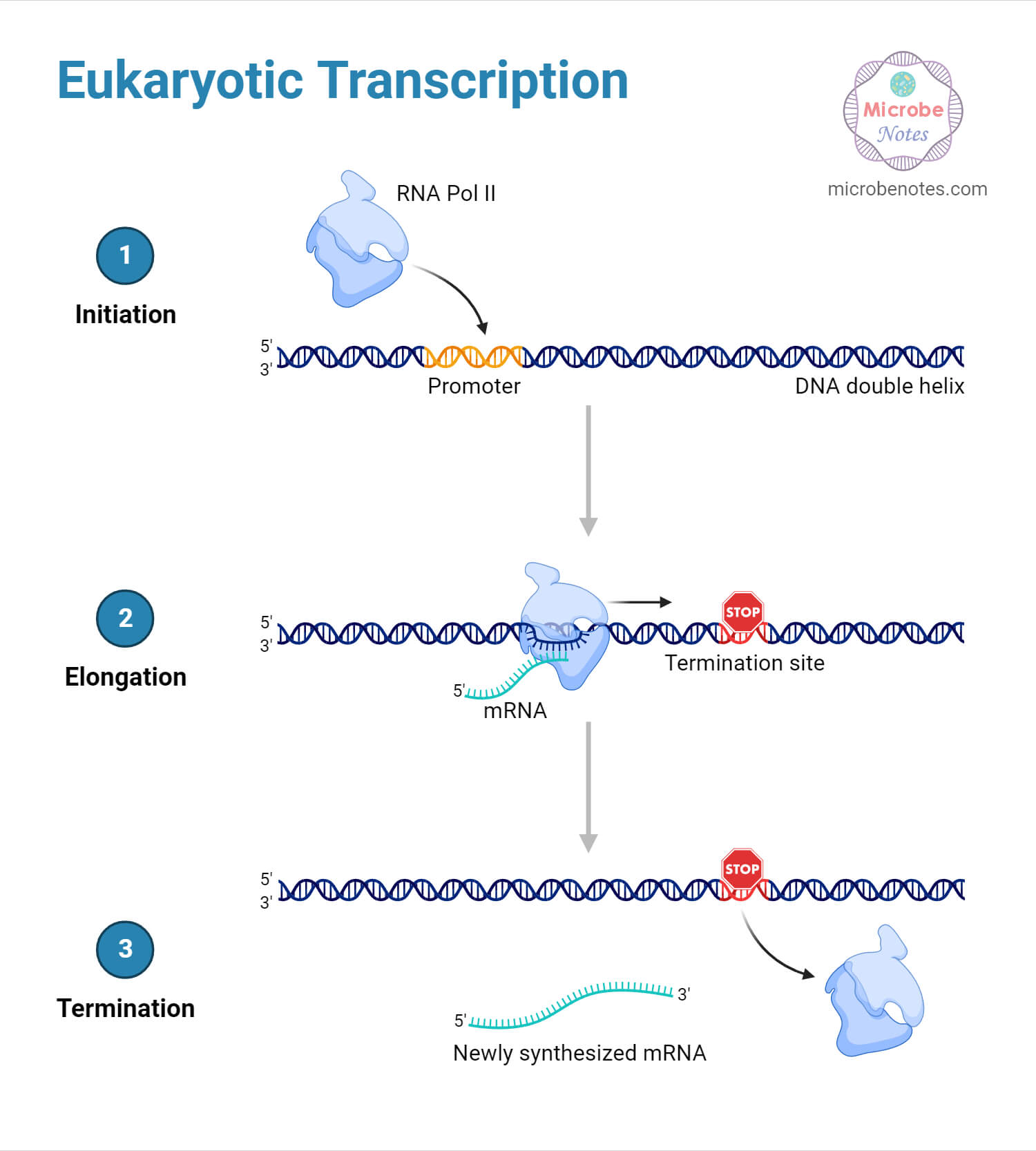
- The method of transcription begins with the binding of RNA polymerase to a selected area of the DNA molecule known as the promoter. The promoter alerts the place to begin for transcription.
- RNA polymerase unwinds the DNA double helix close to the promoter area. This permits one of many DNA strands to behave as a template for the synthesis of mRNA.
- As RNA polymerase strikes alongside the DNA template, it provides complementary RNA nucleotides to the rising mRNA chain. The RNA molecule is synthesized within the 5′ to three′ path, complementary to the DNA template strand.
- Transcription continues till a termination sign is reached within the DNA sequence. This sign causes RNA polymerase to separate from the DNA template and the mRNA molecule is launched.
- In prokaryotes, transcription and translation happen in the identical compartment.
- In eukaryotes, the preliminary RNA transcript (pre-mRNA) undergoes modifications earlier than changing into mature mRNA. These modifications embrace capping, splicing, and including a poly-A tail to the mRNA molecule.
- As soon as processed, mature mRNA molecules are transported from the cell nucleus into the cytoplasm, the place they function templates for protein synthesis throughout translation.
Translation
Translation is the method that makes use of the genetic data encoded in mRNA to synthesize a selected sequence of amino acids, forming a purposeful protein.
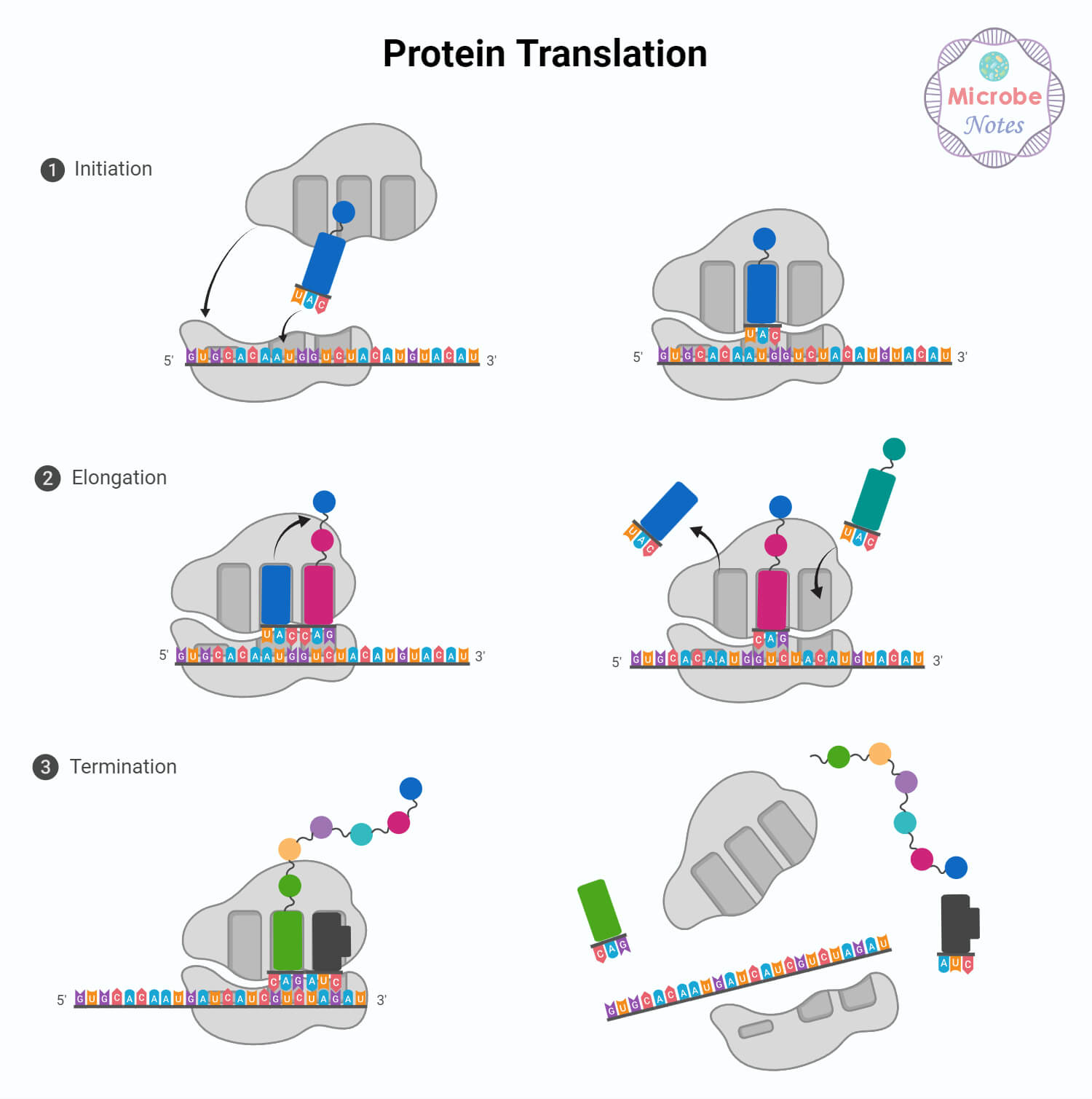
- Translation begins when the mRNA binds to the ribosome which acknowledges the beginning codon (AUG) on the mRNA, marking the initiation level for translation.
- Switch RNA (tRNA) molecules, every carrying a selected amino acid, match their anticodon sequences with the corresponding codons on the mRNA.
- Throughout elongation, the ribosome strikes alongside the mRNA, and every codon is matched with the suitable tRNA anticodon. Amino acids carried by tRNAs are joined collectively in a selected sequence, forming a polypeptide chain.
- Because the ribosome strikes alongside the mRNA, this chain grows, creating the first construction of the protein.
- Translation continues till a cease codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA) is encountered on the mRNA. Cease codons don’t code for any amino acids; as an alternative, they sign the top of the interpretation course of.
- After translation, the newly synthesized protein could bear numerous post-translational modifications. These modifications can embrace folding into a selected three-dimensional form, addition of purposeful teams, or cleavage of particular segments to activate the protein.
Regulation of gene expression
Regulation of gene expression is an important course of that controls when and the way a lot genes produce proteins. Gene expression is regulated to make sure that proteins are generated in particular cells at particular occasions.
Gene expression is regulated at a number of phases: transcription, RNA processing, translation, and post-translational modification.
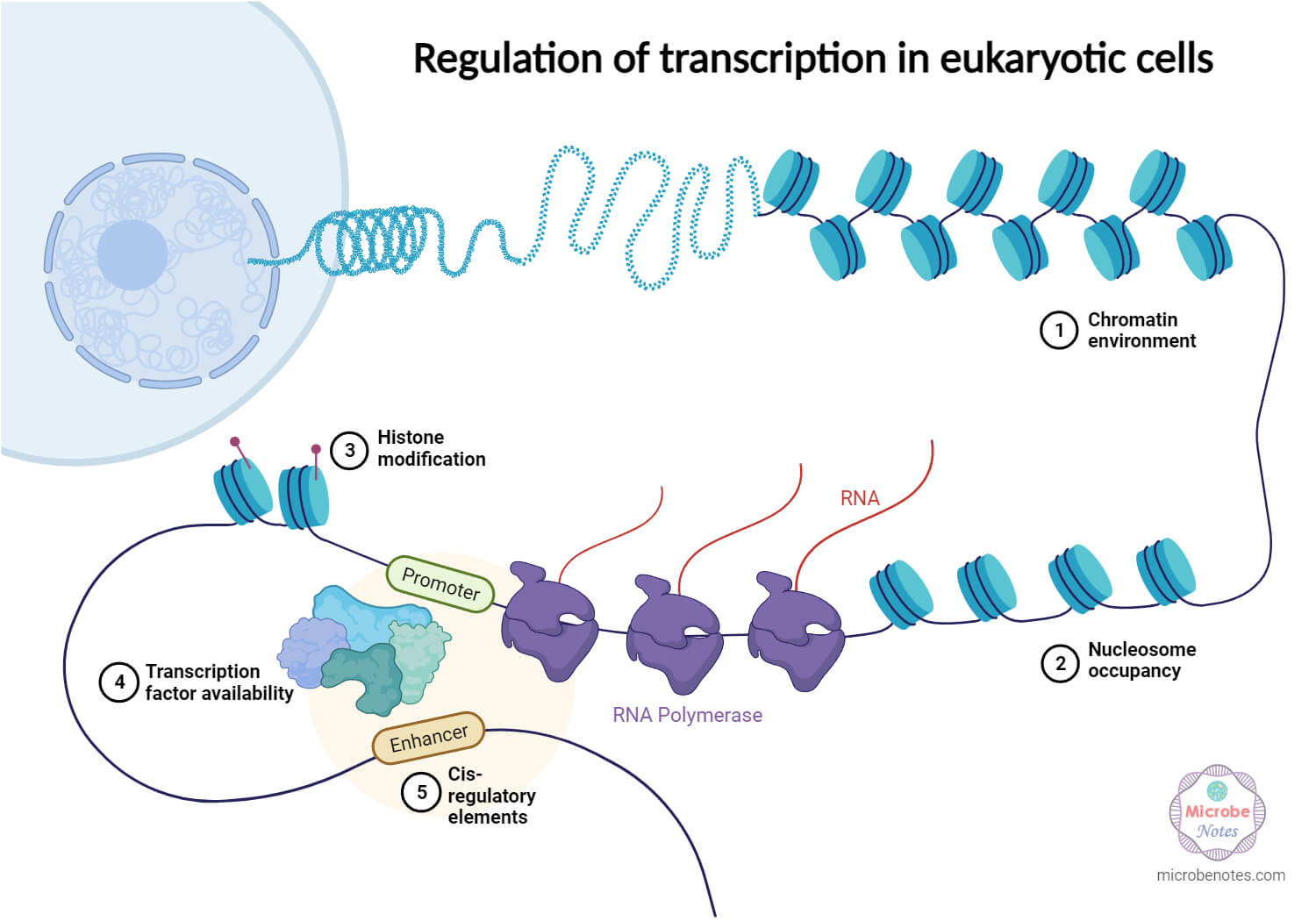
1. Transcriptional regulation
Transcription regulation includes genetic interactions with particular DNA websites and epigenetic results. Transcription components work together with DNA, enhancing or inhibiting RNA polymerase binding. Epigenetic modifications, like DNA methylation and histone alterations, change gene accessibility with out altering the DNA sequence.
2. Submit-transcriptional regulation
Gene expression could be regulated by post-transcriptional mRNA processing. In eukaryotes, transcribed mRNA undergoes splicing and different modifications that defend the ends of the RNA strand from degradation. Splicing removes non-coding segments known as introns and joins the protein-coding areas known as exons.
3. Translational regulation
Translation could be regulated by microRNAs that connect to a selected mRNA sequence, blocking translation initiation or inflicting mRNA degradation. Moreover, translational repressors can connect to RNA and intervene with translation initiation. Varied different components, together with RNA-binding proteins and particular sequence parts within the mRNA, also can affect the method of translation.
4. Submit-translational regulation
Translated polypeptides are processed to create purposeful proteins. Submit-translational regulation alters the construction and performance of proteins by including or eradicating chemical teams like phosphorylation and acetylation, which have an effect on protein exercise and gene expression.
Strategies for measuring gene expression
Measuring and quantifying gene expression is vital for understanding organic processes. A few of the frequent strategies and instruments for measuring gene expression are:
- Northern Blotting is a hybridization-based technique used to find out the dimensions and amount of particular RNA in a pattern. It separates RNA by gel electrophoresis and transfers it to a nitrocellulose membrane, the place it kinds covalent bonds. Labeled probes complementary to the RNA transcript are used for hybridization. The strategy is straightforward and cost-effective, however it’s time-consuming and has low throughput.
- Quantitative Polymerase Chain Response (qPCR) measures gene expression in real-time by changing mRNA to complementary DNA (cDNA) and amplifying it utilizing PCR. Fluorescent labels are added, and the fluorescence is measured after every cycle, which supplies quantitative knowledge. This technique is straightforward to make use of and has a comparatively brief assay time. Nevertheless, it requires prior information of the goal sequence and has restricted throughput.
- Microarray measures gene expression by hybridizing cDNA strands to quantify transcripts. Microarrays use oligonucleotides or cDNA hooked up to a chip floor. It permits high-throughput evaluation. Regardless of its capacity to measure a lot of transcripts, microarrays require separate preparation of management and check samples. Additionally, specialised tools is important for knowledge evaluation.
- RNA-Seq immediately sequences RNA and measures expression by counting sequences. RNA samples are processed into libraries, sequenced, and the information is analyzed to find out gene expression ranges. It supplies the next vary than microarrays and might detect numerous RNA varieties however it comes at the next value and requires extra computational assets.
References
- Clancy, S. & Brown, W. (2008) Translation: DNA to mRNA to Protein. Nature Training 1(1):101. https://www.nature.com/scitable/topicpage/translation-dna-to-mrna-to-protein-393/
- Gene Expression (genome.gov)
- Gene Expression (nih.gov)
- Gene Expression | Study Science at Scitable (nature.com)
- Gene Expression: Transcription, Splicing and Translation | Biology | JoVE
- Lewin B. (2000) Genes VII. Oxford College Press Inc., New York, USA.
- P, Surat. (2021, January 27). A Information to Understanding Gene Expression. AZoLifeSciences. https://www.azolifesciences.com/article/A-Information-to-Understanding-Gene-Expression.aspx.
- Parker, J. (2001). Gene Expression. Brenner’s Encyclopedia of Genetics, 187–189. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-374984-0.00587-8
- Singh, Ok. P., Miaskowski, C., Dhruva, A. A., Flowers, E., & Kober, Ok. M. (2018). Mechanisms and Measurement of Adjustments in Gene Expression. Organic Analysis for Nursing, 20(4), 369-382. https://doi.org/10.1177/1099800418772161
- What’s Gene Expression Evaluation? | Bio-Rad



