What’s Haploid?
- Within the realm of mobile biology, the time period “haploid” is derived from the Greek phrase “haplous,” signifying “single.” It describes a mobile or organismal situation characterised by the presence of a singular set of chromosomes, which is exactly half of the homologous chromosomes present in somatic cells. These homologous chromosomes, outlined by their an identical gene sequences, loci, chromosomal size, and centromere location, are paired such that one originates maternally and the opposite paternally.
- To elucidate additional, ploidy denotes the variety of genome copies current in a cell. The categorization of cells based mostly on their chromosomal units will be as follows:
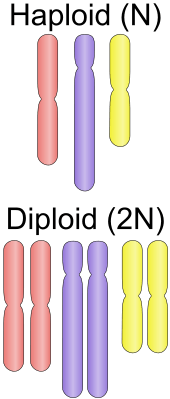
- Haploid (n): Cells containing a single set of chromosomes. That is emblematic of gametes in people, which possess 23 chromosomes.
- Diploid (2n): Cells with two full units of chromosomes, typical of most human cells, amounting to 46 chromosomes.
- Polyploid: Cells that home greater than two full chromosome units. This class encompasses triploids, tetraploids, and different higher-order ploidies.
- Two major lessons emerge when contemplating adjustments in chromosome numbers: Euploidy and Aneuploidy.
- The importance of haploidy is paramount within the reproductive aspect of biology. Haploid cells, primarily gametes, are engendered by means of the intricate strategy of meiosis, which ensures a halving of the chromosomal quantity from a mother or father diploid cell. This discount is pivotal for sexual replica, permitting for the fusion of two haploid gametes to kind a diploid zygote. Such a mechanism not solely reinstates the diploid state within the offspring but additionally introduces genetic range, a cornerstone for evolutionary adaptability.
- Sure organisms, like particular algae species, exhibit a haploid section of their life cycle. Intriguingly, male ants stay haploid all through their existence.
- In summation, haploidy is a elementary idea in biology, denoting a state the place a cell or organism possesses half the everyday chromosomal set present in somatic cells. This situation, pivotal for genetic range and adaptableness, is only one aspect of the broader spectrum of ploidy, which additionally consists of monoploidy, diploidy, and polyploidy, amongst others.
Within the realm of mobile biology, the time period “haploid” denotes a particular chromosomal state wherein a cell or organism possesses half the variety of homologous chromosomes sometimes present in somatic cells. Derived from the Greek phrase “haplous,” which interprets to “single,” the idea of haploidy is pivotal in understanding the genetic make-up and reproductive processes of varied organisms.
- Defining Haploidy: At its core, haploidy refers back to the situation the place a cell or organism incorporates a singular set of unpaired chromosomes. These chromosomes will be of maternal or paternal origin, with homologous chromosomes being those who share an identical gene sequences, chromosomal lengths, loci, and centromere places. In essence, a haploid cell has half the chromosomal content material of its diploid counterpart.
- Terminological Clarifications: The phrases “haploidic” and “haploidy” are carefully associated to “haploid.” Whereas “haploidic” will be interchangeably used with “haploid” when describing one thing as an adjective, “haploidy” is a noun that particularly denotes the state or situation of being haploid. It’s important to distinguish between these phrases to make sure readability in scientific discourse.
- Ploidy and Its Variants: Ploidy is a measure of the variety of full units of chromosomes inside a cell. Primarily based on this metric, cells will be categorized into:
- Haploid (n): Incorporates one set of chromosomes.
- Diploid (2n): Incorporates two units of chromosomes, typical in lots of organisms together with people.
- Polyploid: Incorporates greater than two units of chromosomes, with variations like triploid (three units) and tetraploid (4 units).
- Euploidy vs. Aneuploidy: Whereas ploidy refers back to the full units of chromosomes, the excellence between euploidy and aneuploidy is predicated on the kind of chromosomal change. Euploidy represents a change in the entire set of chromosomes, whereas aneuploidy signifies a change in particular person chromosome numbers.
- Haploidy in Copy: Haploid cells play an important function in sexual replica. In people, gametes (sperm and egg cells) are haploid, every containing 23 chromosomes. This halving of chromosomal content material, achieved by means of meiosis, ensures that upon fertilization, the resultant zygote could have the everyday diploid variety of chromosomes (2n=46). This discount and subsequent mixture throughout replica introduce genetic variability, a cornerstone of evolutionary adaptation.
- Haploidy in Numerous Organisms: Whereas people predominantly exhibit diploidy in somatic cells, sure organisms like some algae and male ants manifest haploidy all through particular or total life levels.
In summation, haploidy is a elementary idea in genetics, underscoring the intricate processes of replica and genetic variation. By understanding the nuances of chromosomal states, one good points perception into the complicated tapestry of life and its myriad manifestations.
Definition of Haploid
A haploid is a cell or organism that incorporates a single set of chromosomes, which is half the quantity current in diploid cells. Sometimes, gametes, resembling sperm and egg cells, are haploid.
Haploid quantity
- Within the realm of genetics, the time period “chromosome quantity” refers back to the particular depend of chromosomes inherent to a selected species. This quantity stays constant in asexually reproducing organisms, guaranteeing genetic stability throughout generations. Nevertheless, in sexually reproducing species, the chromosomal panorama is extra intricate.
- Somatic cells, which represent the vast majority of an organism’s physique, sometimes possess a diploid chromosome quantity, denoted as “2n”. This suggests that these cells include two units of every chromosome: one inherited from the mom and the opposite from the daddy. In distinction, gametes, the reproductive cells concerned in sexual replica, exhibit a haploid chromosome quantity, symbolized as “n”. Because of this gametes possess solely a single set of chromosomes.
- The transition from diploid to haploid happens throughout meiosis, a specialised type of cell division. Meiosis ensures the halving of the chromosome quantity, producing gametes with the haploid quantity. This discount is pivotal for sexual replica, because the fusion of two haploid gametes (e.g., sperm and egg) ends in a diploid zygote, thereby restoring the species’ attribute chromosome quantity.
- Apparently, sure organisms can produce offspring from unfertilized eggs, resulting in haploid progeny. A quintessential instance of this phenomenon is noticed in male bees. These haploid people come up from unfertilized eggs and possess solely half the everyday chromosome variety of their species.
- In summation, the haploid quantity is a elementary idea in genetics, signifying the chromosome depend in gametes. It performs an important function in sustaining genetic continuity and variety in sexually reproducing organisms.
Variations between Haploid and Diploid cells
Within the intricate realm of mobile biology, cells are categorized based mostly on their chromosomal content material. Two major classifications on this context are haploid and diploid cells. Herein, we delineate the basic distinctions between these two cell sorts:
| Standards | Haploid Cells | Diploid Cells |
|---|---|---|
| Chromosomal Units | Comprise a single set of chromosomes. | Possess two units of chromosomes, one from every mother or father. |
| Cell Sort | Predominantly germ cells. | Somatic cells, which represent the vast majority of an organism’s physique. |
| Cell Division Resultant | Come up from meiosis, a specialised type of cell division. | Produced by means of mitosis, a strategy of cell division yielding an identical cells. |
| Genetic Identification | Genetically various because of the cross-over occasions throughout meiosis. | Genetically an identical to the mother or father cell, owing to the character of mitotic division. |
| Cell Varieties in People | In people, these are the intercourse cells, together with sperm and eggs. | All human cells, barring the intercourse cells, are diploid. These are termed somatic cells. |
| Examples | Sperm and egg cells. | Cells forming tissues like muscle mass, bones, and nerves. |
In essence, whereas haploid cells are characterised by a singular set of chromosomes and are pivotal for sexual replica, diploid cells, with their twin chromosomal units, kind the structural and practical models of organisms. Understanding the dichotomy between these cell sorts is key to greedy the intricacies of genetics and replica.
Haploid vs. Different Ploidies
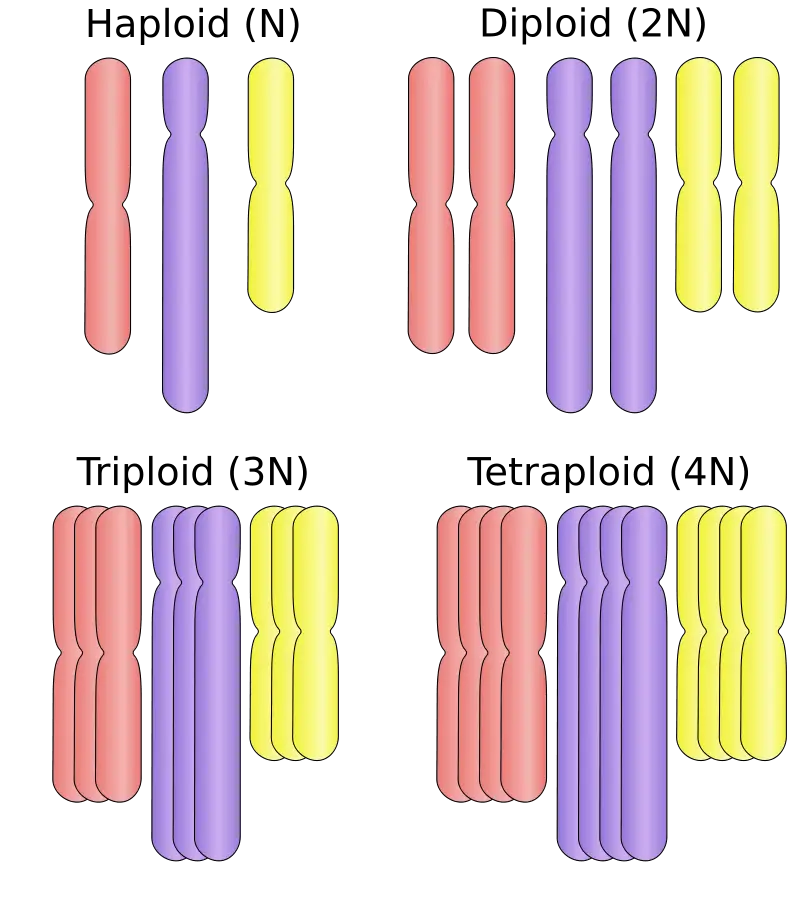
- Haploid (n): Haploidy denotes the situation the place a cell or organism possesses a single set of chromosomes. This state is emblematic of gametes, resembling sperm and egg cells. On this context, the time period “haploid” is commonly symbolized by the notation “n”, indicating that the cell incorporates just one set of chromosomes, which is half the quantity present in somatic cells of diploid organisms. For example, human gametes are haploid and include 23 chromosomes.
- Diploid (2n): Diploidy represents the situation the place a cell or organism has two full units of chromosomes, one from every mother or father. Somatic cells, which represent the vast majority of an organism’s physique excluding germ and intercourse cells, are sometimes diploid. In people, somatic cells are diploid, containing 46 chromosomes, and are denoted by the image “2n”.
- Monoploid: The phrases “haploid” and “monoploid” are often used interchangeably, particularly when defining a cell that incorporates a single copy of the chromosome set. Each phrases describe the state of getting just one set of chromosomes. Nevertheless, whereas “haploid” usually refers to having half the chromosomal set of a diploid cell, “monoploid” strictly pertains to the presence of a singular chromosome set.
- Polyploid: Polyploidy describes the situation the place a cell or organism possesses greater than two units of chromosomes. This state is extra widespread in vegetation than in animals. Polyploidy can come up resulting from numerous genetic mechanisms and might confer sure benefits, resembling elevated genetic range and adaptableness. Polyploids are additional categorized based mostly on the variety of chromosome units they include:
- Triploid (3n): Cells or organisms with three units of chromosomes.
- Tetraploid (4n): These with 4 units of chromosomes.
- Pentaploid (5n): Entities with 5 units of chromosomes. And the checklist continues with rising numbers of chromosome units.
In conclusion, ploidy ranges, from haploid to varied polyploid states, provide a spectrum of genetic configurations in cells and organisms. Every ploidy degree has its distinctive organic implications and evolutionary significance. Understanding these variations is essential for insights into genetics, evolution, and the adaptability of organisms.
How does the ensuing diploid cell in the end have 2 full units of chromosomes?
The journey from a single cell to a diploid state, housing two full units of chromosomes, is a meticulously orchestrated organic course of. The inspiration of this course of is meiosis, a specialised type of cell division.
- Initiation – DNA Replication in Interphase: Earlier than the graduation of meiosis, the mother or father cell undergoes a section termed the interphase. Throughout this section, the cell replicates its DNA, successfully doubling its chromosomal content material. This ensures that every chromosome now consists of two an identical sister chromatids, linked at a area referred to as the centromere.
- Meiosis I – Homologous Chromosome Separation: Because the cell embarks on the primary meiotic division, it undergoes numerous levels, culminating within the separation of homologous chromosomes. By the conclusion of meiosis I, two daughter cells are shaped, every inheriting a whole set of the replicated chromosomes. It’s essential to notice that, at this juncture, every chromosome nonetheless consists of two sister chromatids.
- Meiosis II – Sister Chromatid Separation: The daughter cells from meiosis I proceed to the second meiotic division. Right here, the first occasion is the separation of sister chromatids. Publish meiosis II, 4 cells are produced, every containing half the unique variety of chromosomes, rendering them haploid.
- Sexual Copy – Fusion of Gametes: The end result of meiosis ends in the formation of gametes, that are haploid intercourse cells. Throughout sexual replica, two gametes, sometimes an egg from the mom and a sperm from the daddy, fuse in a course of referred to as fertilization. This union restores the chromosomal quantity, with the zygote inheriting one set of chromosomes from every mother or father. Consequently, the zygote, and all subsequent somatic cells derived from it, are diploid, possessing two full units of chromosomes.
In essence, the orchestrated sequence of DNA replication, adopted by two rounds of meiotic divisions and the eventual fusion of gametes, ensures that the resultant diploid cell inherits two full units of chromosomes, one from every mother or father. This intricate course of underscores the continuity and variety of life.
Discount and Chromosome Doubling: A Genetic Perspective
Chromosomal dynamics, significantly discount and doubling, play pivotal roles in guaranteeing genetic stability and continuity throughout generations. These processes are integral to each mitosis and meiosis, the first mechanisms of cell division in organisms.
- Chromosome Doubling in Meiosis: Within the context of meiosis, chromosome doubling is a prerequisite to make sure that the resultant gametes preserve the species-specific chromosomal quantity. Absent this doubling, the 4 daughter cells produced post-meiosis would every possess merely 1 / 4 of the mother or father cell’s chromosomes. Such a situation could be detrimental, because the fusion of those gametes would yield offspring with solely half the requisite chromosomal content material, rendering them haploid. Such haploid people wouldn’t solely be genetically distinct from their diploid progenitors however would even be rendered sterile, unable to perpetuate their lineage.
- Chromosome Doubling in Mitosis: Mitosis, liable for common mobile development and restore, necessitates chromosome doubling to make sure that the 2 resultant daughter cells inherit a whole chromosomal set from the mother or father cell. A failure on this doubling course of would result in daughter cells with solely half the chromosomal content material. Such a chromosomal deficit can precipitate genetic anomalies and mutations, compromising the organism’s well being and viability.
- Chromosome Discount in Meiosis: Chromosome discount is quintessential to meiosis, guaranteeing that gametes are haploid and possess half the chromosomal content material of diploid somatic cells. If this discount had been to be bypassed, gametes would retain a diploid state. Consequently, their fusion throughout fertilization would produce offspring with a tetraploid (4n) chromosomal set, successfully birthing a definite species. Such tetraploid people could be genetically misaligned with the diploid members of their inhabitants.
- Implications of Chromosomal Anomalies in Mitosis: In mitotic divisions, any aberration in chromosome discount would lead to daughter cells with a tetraploid chromosomal set. Such cells could be genetically incongruent with the diploid cells of the organism, doubtlessly resulting in developmental anomalies and illnesses.
In summation, the processes of discount and chromosome doubling are genetic safeguards, guaranteeing the preservation of species-specific chromosomal numbers and the prevention of genetic problems. Their meticulous orchestration underscores the precision and complexity of mobile replica, emphasizing the fragile steadiness that underpins life.
Upkeep of the chromosomal quantity
The preservation of a species-specific chromosomal quantity is paramount for the continuity and stability of genetic data throughout generations. Two major mobile mechanisms, meiosis and mitosis, are intricately designed to make sure this chromosomal fidelity.
- Function of Meiosis and Mitosis: Each meiosis and mitosis are orchestrated to ensure that the offspring’s chromosomal quantity aligns with that of its progenitors. Whereas meiosis is liable for producing gametes with half the chromosomal content material, guaranteeing genetic range and facilitating sexual replica, mitosis focuses on common mobile development and restore, producing genetically an identical daughter cells.
- Nondisjunction and Its Implications: A essential facet of cell division is karyokinesis, the place chromosomes segregate into their respective daughter cells. Nevertheless, anomalies can come up, resembling nondisjunction, the place chromosomes fail to separate appropriately. This aberration ends in daughter cells with an imbalanced chromosomal depend.
- Monosomy: Publish-nondisjunction, sure daughter cells could exhibit monosomy, the place they possess fewer chromosomes than required. In such a situation, a chromosome that ought to have been current in a pair exists as a singleton.
- Trisomy: Conversely, some cells may manifest trisomy, housing an additional chromosome. As a substitute of the everyday pair, these cells include a triplet of a selected chromosome.
- Polyploidy and Allopolyploidy: Past the everyday diploid state, cells also can exhibit polyploidy, the place they include greater than two units of chromosomes. A specialised type of polyploidy is allopolyploidy. On this situation, daughter cells inherit full diploid chromosome units from mother or father cells of various species. An illustrative instance of allopolyploidy is the mule, a sterile hybrid offspring of a horse and a donkey.
In conclusion, the meticulous orchestration of meiosis and mitosis is pivotal for sustaining the chromosomal quantity, guaranteeing genetic stability and continuity. Any deviation from this precision, resembling nondisjunction or polyploidy, can have profound genetic and evolutionary implications. The intricate steadiness of those processes underscores the complexity and precision inherent within the realm of mobile biology.
Significance/Capabilities of Haploid
The haploid state, characterised by a single set of chromosomes, performs a number of pivotal roles in biology, significantly within the context of sexual replica and genetic range. Listed here are the first features of haploid cells:
- Sexual Copy:
- Haploid cells, particularly gametes (sperm in males and eggs in females), are important for sexual replica. When two gametes fuse throughout fertilization, they kind a diploid zygote, guaranteeing the offspring has the proper variety of chromosomes.
- Genetic Range:
- Meiosis, the method that produces haploid gametes, entails genetic recombination and unbiased assortment. These occasions shuffle alleles and be sure that every gamete is genetically distinctive. This genetic range is essential for the adaptability and evolution of species.
- Discount of Chromosome Quantity:
- The haploid state ensures that the chromosome quantity is halved, stopping a steady doubling of chromosomes with every technology. That is important to take care of a constant chromosome quantity throughout generations.
- Facilitation of Genetic Change:
- In some organisms, haploid cells can mate or fuse with cells from totally different people, facilitating genetic alternate and rising genetic range.
- Life Cycle Variation:
- Some organisms, like sure algae and fungi, have life cycles that alternate between haploid and diploid phases. The haploid section permits for genetic variation and recombination.
- Simplification of Genetic Evaluation:
- In sure fungi, just like the mannequin organism Neurospora crassa, the haploid state simplifies genetic evaluation. Since there’s just one allele for every gene in a haploid cell, any genetic mutation’s results are instantly observable with out the complication of dominant or recessive interactions.
- Formation of New Species:
- In some circumstances, when haploid cells fail to endure fusion or if diploid cells endure meiosis prematurely, it will probably result in the formation of organisms with a number of units of chromosomes (polyploidy). This may end up in the emergence of recent species, particularly in vegetation.
In essence, haploid cells aren’t only a organic curiosity however are elementary to the processes of replica, genetic range, and evolution. Their roles underscore the intricate steadiness and complexity inherent within the realm of genetics and mobile biology.
Examples of Haploid
1. Haploid Cells in Human Copy
Human cells predominantly exist in a diploid state, every containing two units of chromosomes. Nevertheless, a definite exception arises throughout the reproductive course of. Gametes, the reproductive cells, are haploid in nature. The genesis of a human begins when two haploid gametes, an egg from the mom and a sperm from the daddy, fuse to kind a diploid zygote. This zygote undergoes quite a few mitotic divisions, sustaining its diploid state, finally giving rise to a multicellular organism. But, the reproductive tissues in people have a novel function. Inside these tissues, particular cells endure meiosis, a course of distinct from mitosis. Meiosis ensures the separation of homologous chromosomes, ensuing within the formation of haploid daughter cells. Consequently, the eggs in females and the sperm in males are the only real haploid entities within the human physique, poised to merge and provoke a brand new life cycle.
2. Haplodiploidy in Bugs
Bugs, significantly sure bees and ants, exhibit an enchanting ploidy-based intercourse willpower system. In these species, the vast majority of the colony, together with the queen and employee bees, are diploid. These diploid people undertake numerous obligations, starting from foraging and nurturing the younger to managing the deceased.
Nevertheless, a novel member of this insect society is the haploid drone. This drone’s major perform is to move sperm to different colonies. The queens of those colonies make the most of the sperm from these drones to fertilize their haploid eggs. The fusion of those gametes ends in the formation of a diploid cell. Underneath customary situations, these diploid offspring mature into employee bees. Intriguingly, when sure larvae are nourished with “royal jelly,” they metamorphose into queens. This specialised vitamin triggers pathways that increase the dimensions of the bee and confer upon it the flexibility to put eggs. Because the lifecycle progresses, a longtime hive witnesses the start of a brand new queen. The reigning queen, accompanied by a cohort of staff, departs to inaugurate a brand new hive, leaving the successor to proceed the legacy. This successor queen, nevertheless, should first mate with a haploid drone to begin laying eggs.
In abstract, haploidy performs a pivotal function in numerous organic programs, from human replica to insect colonies, underscoring its significance within the perpetuation of life.
Quiz
What’s the chromosome variety of haploid cells in people?
a) 23
b) 46
c) 92
d) 12
a) 23
Which of the next cells in people is haploid?
a) Muscle cells
b) Bone cells
c) Sperm cells
d) Pores and skin cells
c) Sperm cells
Wherein course of are haploid cells produced from a diploid cell?
a) Mitosis
b) Meiosis
c) Binary fission
d) Budding
b) Meiosis
Which of the next organisms has a life cycle that alternates between haploid and diploid phases?
a) Mammals
b) Birds
c) Algae
d) Reptiles
c) Algae
Which of the next is NOT a perform of haploid cells?
a) Sexual replica
b) Genetic range
c) Mobile restore
d) Discount of chromosome quantity
c) Mobile restore
Wherein of the next organisms are males sometimes haploid?
a) Mammals
b) Fish
c) Bees
d) Amphibians
c) Bees
If a plant has a haploid variety of 10, what’s its diploid quantity?
a) 5
b) 10
c) 20
d) 40
c) 20
Which section of the life cycle is haploid in mosses?
a) Sporophyte
b) Gametophyte
c) Zygote
d) Seed
b) Gametophyte
Which of the next occasions results in the formation of haploid cells?
a) DNA replication
b) Cytokinesis
c) Separation of sister chromatids
d) Separation of homologous chromosomes
d) Separation of homologous chromosomes
Wherein of the next processes do two haploid cells mix to kind a diploid cell?
a) Mitosis
b) Meiosis
c) Fertilization
d) Budding
c) Fertilization
FAQ
What’s a haploid cell?
A haploid cell is a cell that incorporates a single set of chromosomes. It has half the variety of chromosomes as a diploid cell.
How are haploid cells shaped?
Haploid cells are shaped by means of a course of referred to as meiosis, the place a diploid cell undergoes two rounds of cell division to provide 4 haploid cells.
Why are haploid cells essential?
Haploid cells, particularly gametes (sperm and egg cells), are important for sexual replica. When two gametes fuse, they kind a diploid zygote, guaranteeing genetic range and continuity of species.
Are human cells haploid or diploid?
Most human cells are diploid, containing two units of chromosomes. Nevertheless, the gametes (sperm and egg cells) are haploid.
What’s the distinction between haploid and diploid cells?
Haploid cells include one set of chromosomes, whereas diploid cells include two units of chromosomes.
The place can haploid cells be present in people?
Haploid cells in people are discovered within the reproductive organs, particularly as sperm cells in males and egg cells in females.
What occurs if haploid cells don’t fuse throughout replica?
If haploid cells don’t fuse, fertilization doesn’t happen, and a zygote is just not shaped. Because of this no offspring shall be produced.
Can organisms exist in a haploid state all through their life cycle?
Sure, sure organisms, resembling some fungi and algae, can exist in a haploid state for a good portion and even all through their total life cycle.
What’s the significance of meiosis in relation to haploid cells?
Meiosis is the method that reduces the chromosome quantity by half, producing haploid cells from a diploid mother or father cell. It ensures genetic variation and the upkeep of a constant chromosome quantity throughout generations.
How does the chromosome quantity in haploid cells examine to the unique mother or father cell?
Haploid cells have half the variety of chromosomes as the unique diploid mother or father cell.



